PP - Columbia University
... • So when calulating Go, instead of writing in “55” when water participates in a reaction (e.g., a hydrolysis) we write “1.” • This is not cheating; we are in charge of what is a “standard” condition, and we all agree to this: 55 M H20 is unit (“1”) concentration for the purpose of defining Go. ...
... • So when calulating Go, instead of writing in “55” when water participates in a reaction (e.g., a hydrolysis) we write “1.” • This is not cheating; we are in charge of what is a “standard” condition, and we all agree to this: 55 M H20 is unit (“1”) concentration for the purpose of defining Go. ...
Major 1 Term 101 - KFUPM Faculty List
... C) H2S That is either hydrogen sulfide when in gas phase, or hydrosulfuric acid when in aqueous solution. D) H2SO3 Correct: the acid related to sulfite ion, SO32-, is sulfurous acid E) H2SO4 Incorrect: the acid related to sulfate ion, SO42-, is sulfuric acid 16. To which one of the following reactio ...
... C) H2S That is either hydrogen sulfide when in gas phase, or hydrosulfuric acid when in aqueous solution. D) H2SO3 Correct: the acid related to sulfite ion, SO32-, is sulfurous acid E) H2SO4 Incorrect: the acid related to sulfate ion, SO42-, is sulfuric acid 16. To which one of the following reactio ...
111 Exam I Outline
... Key: You must have a balanced equation!! How many grams of chromic chloride reacts with 6.0 mole Cr? ...
... Key: You must have a balanced equation!! How many grams of chromic chloride reacts with 6.0 mole Cr? ...
111 Exam I Outline
... Key: You must have a balanced equation!! How many grams of chromic chloride reacts with 6.0 mole Cr? ...
... Key: You must have a balanced equation!! How many grams of chromic chloride reacts with 6.0 mole Cr? ...
New AQA C3 revison guide
... 1) It is difficult to make a good lather. 2) Scum is formed with soap. 3) Lime scale forms in kettles, pipes etc. Hard water contains Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions in solution. These ions react with soap to form scum. This is because soap is sodium stearate, which reacts with calcium ions to form insoluble calc ...
... 1) It is difficult to make a good lather. 2) Scum is formed with soap. 3) Lime scale forms in kettles, pipes etc. Hard water contains Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions in solution. These ions react with soap to form scum. This is because soap is sodium stearate, which reacts with calcium ions to form insoluble calc ...
3(aq)
... • When dissolved in water (aqueous), a metal can replace another metal within a compound. 1. Doesn’t ALWAYS happen: it depends upon the reactivity of the metal dissolved compared to the metal within the compound. 2. Example: Copper wire, when placed into an aqueous solution of silver nitrate, will r ...
... • When dissolved in water (aqueous), a metal can replace another metal within a compound. 1. Doesn’t ALWAYS happen: it depends upon the reactivity of the metal dissolved compared to the metal within the compound. 2. Example: Copper wire, when placed into an aqueous solution of silver nitrate, will r ...
Chapter 7-8-9
... 22. Why do atoms share electrons in covalent bonds? a. to become ions and attract each other b. to attain a noble-gas electron configuration c. to become more polar d. to increase their atomic numbers 23. Which molecule has a single covalent bond? a. CO b. Cl c. CO d. N 24. What causes water molecul ...
... 22. Why do atoms share electrons in covalent bonds? a. to become ions and attract each other b. to attain a noble-gas electron configuration c. to become more polar d. to increase their atomic numbers 23. Which molecule has a single covalent bond? a. CO b. Cl c. CO d. N 24. What causes water molecul ...
unit 7 h chem notes - chemical equations
... II. Sometimes it is necessary to abbreviate the “phase” of the substance to the lower right of the substance. Some abbreviations are: s = solid, l= liquid, g ( )= gas, aq= aqueous, ppt ( )= precipitate. III Write equations using correct formulas of diatomic molecules, then Balance the equation for e ...
... II. Sometimes it is necessary to abbreviate the “phase” of the substance to the lower right of the substance. Some abbreviations are: s = solid, l= liquid, g ( )= gas, aq= aqueous, ppt ( )= precipitate. III Write equations using correct formulas of diatomic molecules, then Balance the equation for e ...
Unit 19 Chemistry Honors
... Special Topics*: Organic Unit 18, Chapter 20 Mrs. Frost 2012 www.hinsdale86.org/staff/kfrost Objectives: 1. Name and write formulas for organic compounds such as alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and molecules containing basic organic functional groups. 2. Draw organic structures. 3. Draw and identify the d ...
... Special Topics*: Organic Unit 18, Chapter 20 Mrs. Frost 2012 www.hinsdale86.org/staff/kfrost Objectives: 1. Name and write formulas for organic compounds such as alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and molecules containing basic organic functional groups. 2. Draw organic structures. 3. Draw and identify the d ...
Chapter 7: Dienes
... …that the pi-bonding electrons rearrange themselves into new bonds, joining the diene and the dienophile together in a pericyclic, concerted reaction! The Diels-Alder cycloaddition results in 2 new σ bonds, with one π bond moving to a new position occurs when a diene meets an alkene or alkyne, p ...
... …that the pi-bonding electrons rearrange themselves into new bonds, joining the diene and the dienophile together in a pericyclic, concerted reaction! The Diels-Alder cycloaddition results in 2 new σ bonds, with one π bond moving to a new position occurs when a diene meets an alkene or alkyne, p ...
Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones
... - Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones for both steric and electronic reasons. - First, the H creates less steric hindrance so that the carbonyl C is more accessible. - Second, an organic group provides e- donating induction which stabilizes the + carbonyl C and makes it less reactive. - Formal ...
... - Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones for both steric and electronic reasons. - First, the H creates less steric hindrance so that the carbonyl C is more accessible. - Second, an organic group provides e- donating induction which stabilizes the + carbonyl C and makes it less reactive. - Formal ...
LC Chem Notes Organic Chemistry [PDF Document]
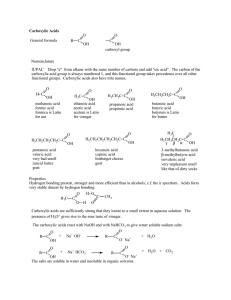
... A homologous series similar to alkanes but with a hydrogen replaced by an OH (hydroxyl) group. The ending is -anol (eg: propanol). The general formula is CNH2N+1OH. There are primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols. Primary alcohols are when the carbon attached to the hydroxyl group touches one oth ...
... A homologous series similar to alkanes but with a hydrogen replaced by an OH (hydroxyl) group. The ending is -anol (eg: propanol). The general formula is CNH2N+1OH. There are primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols. Primary alcohols are when the carbon attached to the hydroxyl group touches one oth ...
Chapter 2 polymers
... Condensation polymerization: a reaction in which two different monomers react at the functional group to form a polymer. Generally a reaction where two monomers are joined to form a unit called a dimer. A dimer generally consists of an ester or amide linkage. If a chemical is bi-functional (ha ...
... Condensation polymerization: a reaction in which two different monomers react at the functional group to form a polymer. Generally a reaction where two monomers are joined to form a unit called a dimer. A dimer generally consists of an ester or amide linkage. If a chemical is bi-functional (ha ...
Document
... terephthalate) from ethylene glycol and dimethyl terephthalete. The reaction between a carboxyl and an ester link is much slower, but other interchange reactions, such as amine-amide, amine-ester, and acetal-alcohol, are well known. iii) Carbonyl Addition – Substitution Reaction The reaction of alde ...
... terephthalate) from ethylene glycol and dimethyl terephthalete. The reaction between a carboxyl and an ester link is much slower, but other interchange reactions, such as amine-amide, amine-ester, and acetal-alcohol, are well known. iii) Carbonyl Addition – Substitution Reaction The reaction of alde ...
Review Sheet Chemistry II Final 2013
... Review Sheet Chemistry II Final 2013 Chapter 5 Atomic structure sample problems 1-3 Atom, electron, proton, neutron Diagram an atom Atomic number, atomic mass Ion, Cation, Anion, how is an ion formed Isotope, how to calculate average atomic mass Periodic Table metal, nonmetals, metalloids, noble gas ...
... Review Sheet Chemistry II Final 2013 Chapter 5 Atomic structure sample problems 1-3 Atom, electron, proton, neutron Diagram an atom Atomic number, atomic mass Ion, Cation, Anion, how is an ion formed Isotope, how to calculate average atomic mass Periodic Table metal, nonmetals, metalloids, noble gas ...
Unit 4, Lesson #3 - Patterson Science
... The value of Keq is determined experimentally. Chemists allow reactions to occur at stated temperatures, until the system no longer changes. At this point, they measure the amounts of both the reactants and products. Just as chemists monitor changes in pH, colour, gas pressure or conductivity of sol ...
... The value of Keq is determined experimentally. Chemists allow reactions to occur at stated temperatures, until the system no longer changes. At this point, they measure the amounts of both the reactants and products. Just as chemists monitor changes in pH, colour, gas pressure or conductivity of sol ...
Chemistry Lesson 40 Organic Chemistry
... g. Some compounds have more than one functional group – such as amino acids, which contain an amine (C-N) group and an organic acid (COOH) group. h. Naming organic compounds with functional groups involves using the alkane name, and adding the prefix/suffix for the functional group. ...
... g. Some compounds have more than one functional group – such as amino acids, which contain an amine (C-N) group and an organic acid (COOH) group. h. Naming organic compounds with functional groups involves using the alkane name, and adding the prefix/suffix for the functional group. ...
H3PO4 in a Direct Synthesis of Oligo–Poly(ethylene phosphate)
... polyesterification can be presented as shown in Scheme 1 (although some side reactions are also possible and not shown). During the next stages of the condensation–polyaddition steps, this sequence of reactions is repeated: presumably the (poly)pyrophosphate function is generated at the monoester cha ...
... polyesterification can be presented as shown in Scheme 1 (although some side reactions are also possible and not shown). During the next stages of the condensation–polyaddition steps, this sequence of reactions is repeated: presumably the (poly)pyrophosphate function is generated at the monoester cha ...
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper – 2015
... affinity towards oxygen and so cannot be reduced by carbon. (Note: Error in the question. Zinc oxide can be reduced to zinc metal by using carbon, but aluminium oxide cannot be reduced by a reducing agent.) (ii) Carbon tetrachloride is made of individual covalently bonded molecules, CCl 4. In additi ...
... affinity towards oxygen and so cannot be reduced by carbon. (Note: Error in the question. Zinc oxide can be reduced to zinc metal by using carbon, but aluminium oxide cannot be reduced by a reducing agent.) (ii) Carbon tetrachloride is made of individual covalently bonded molecules, CCl 4. In additi ...
Thermodynamics (Part 2)
... (all particles: monatomic and polyatomic) 2. rotation: polyatomic molecules only (although linear molecules can only have 2 types of rotation; others have 3) 3. vibrations: atoms periodically move toward and away from eachother (polyatomic: increases as molecules become more complicated/more atoms) ...
... (all particles: monatomic and polyatomic) 2. rotation: polyatomic molecules only (although linear molecules can only have 2 types of rotation; others have 3) 3. vibrations: atoms periodically move toward and away from eachother (polyatomic: increases as molecules become more complicated/more atoms) ...
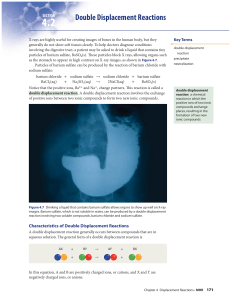
Double Displacement Reactions
... types of double displacement reactions. On the following pages, you will learn about these double displacement reactions: • a reaction that forms a solid • a reaction that forms a gas • a reaction that forms water You will also learn about guidelines you can use to predict whether the products that ...
... types of double displacement reactions. On the following pages, you will learn about these double displacement reactions: • a reaction that forms a solid • a reaction that forms a gas • a reaction that forms water You will also learn about guidelines you can use to predict whether the products that ...
Practice Writing AP Questions
... For the following reactions write a net ionic equation. Box your final answer. 1. Carbon disulfide vapor is burned in excess oxygen. a. What would be the products if the oxygen gas was not in excess? 2. Potassium permanganate solution is added to an acidic solution of hydrogen peroxide. a. This reac ...
... For the following reactions write a net ionic equation. Box your final answer. 1. Carbon disulfide vapor is burned in excess oxygen. a. What would be the products if the oxygen gas was not in excess? 2. Potassium permanganate solution is added to an acidic solution of hydrogen peroxide. a. This reac ...
POLYMERS
... A polyester may be formed by the reaction of a dicarboxylic acid and a diol. The reactants are heated together at temperatures up to 180oC, often in the presence of a titanium-containing catalyst. Water is released during the reaction. If the methyl ester of the dicarboxylic acid is used, there is l ...
... A polyester may be formed by the reaction of a dicarboxylic acid and a diol. The reactants are heated together at temperatures up to 180oC, often in the presence of a titanium-containing catalyst. Water is released during the reaction. If the methyl ester of the dicarboxylic acid is used, there is l ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.










![LC Chem Notes Organic Chemistry [PDF Document]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016025300_1-c73b23b1fa546a54a727ea311be04e3f-300x300.png)