Reactions of Alcohols
... • Catalyzed by ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase. • Oxidizing agent is NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. • Ethanol oxidizes to acetaldehyde, then acetic acid, a normal metabolite. • Methanol oxidizes to formaldehyde, then formic acid, more toxic than methanol. • Ethylene glycol oxidizes to oxalic ac ...
... • Catalyzed by ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase. • Oxidizing agent is NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. • Ethanol oxidizes to acetaldehyde, then acetic acid, a normal metabolite. • Methanol oxidizes to formaldehyde, then formic acid, more toxic than methanol. • Ethylene glycol oxidizes to oxalic ac ...
Organic Chemistry
... Tollens reagent (Ag+(NH3)2 or Benedict’s solution (Cu2+ tartrate complex). Not synthetically useful due to side reactions. Bromine water oxidizes aldoses (not ketoses) to monocarboxylic acids (Aldonic Acids). Nitric Acid oxidizes aldoses to dicarboxylic acids (Aldaric acids). Enzyme catalyzed oxidat ...
... Tollens reagent (Ag+(NH3)2 or Benedict’s solution (Cu2+ tartrate complex). Not synthetically useful due to side reactions. Bromine water oxidizes aldoses (not ketoses) to monocarboxylic acids (Aldonic Acids). Nitric Acid oxidizes aldoses to dicarboxylic acids (Aldaric acids). Enzyme catalyzed oxidat ...
Article - Sociedade Brasileira de Química
... two ketones such as 9-fluorenone or 4-phenyl-2-butanone versus acetophenone; here, it was found that 9-fluorenone and 4-phenyl-2-butanone were reduced in high chemoselectivity (Table 4). Regioselective 1,2-reduction of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones is an easy way to obtain allylic alcohols w ...
... two ketones such as 9-fluorenone or 4-phenyl-2-butanone versus acetophenone; here, it was found that 9-fluorenone and 4-phenyl-2-butanone were reduced in high chemoselectivity (Table 4). Regioselective 1,2-reduction of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones is an easy way to obtain allylic alcohols w ...
Organic Chemistry
... and baseball catcher’s masks. • It is also used in the manufacture of safety and unbreakable windows. ...
... and baseball catcher’s masks. • It is also used in the manufacture of safety and unbreakable windows. ...
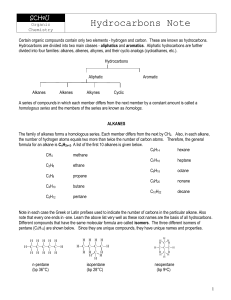
Hydrocarbons Note
... formula C6H6 and consists of a ring of six carbon atoms. Based on the chemical formula, one proposed structure for benzene was the following: CH HC ...
... formula C6H6 and consists of a ring of six carbon atoms. Based on the chemical formula, one proposed structure for benzene was the following: CH HC ...
Theoretical studies of mononuclear non-heme iron active sites Arianna Bassan
... assumes that in a molecule electrons move in a static nuclear framework; this approximation, known as the Born-Oppenheimer approximation, is justified by the significant difference of mass of electrons and nuclei and it practically allows the separation of the motion of the electrons from the motion ...
... assumes that in a molecule electrons move in a static nuclear framework; this approximation, known as the Born-Oppenheimer approximation, is justified by the significant difference of mass of electrons and nuclei and it practically allows the separation of the motion of the electrons from the motion ...
102 Lecture Ch19
... • Primary and secondary amides can H-bond with themselves, and so have high melting and boiling points • Tertiary amides can’t H-bond with themselves, so have lower melting and boiling points than primary or secondary • Amides have higher melting and boiling points than carboxylic acids because they ...
... • Primary and secondary amides can H-bond with themselves, and so have high melting and boiling points • Tertiary amides can’t H-bond with themselves, so have lower melting and boiling points than primary or secondary • Amides have higher melting and boiling points than carboxylic acids because they ...
STRUcruR.AL ASPEcrs AND COORDINATION CHEMISTRY OF
... all three structures (179. 178.4 and 175.8° for Fe(TPP)CO(Py), Ru(TPP)CO(Py) and Ru(TPP)CO(EtOH). respectively). In view of this and other data of model compounds [19], the "bent" or "tilted" geometry reported for the CO ligand in several carbonyl hemoproteins [20-24] has usually been attributed to ...
... all three structures (179. 178.4 and 175.8° for Fe(TPP)CO(Py), Ru(TPP)CO(Py) and Ru(TPP)CO(EtOH). respectively). In view of this and other data of model compounds [19], the "bent" or "tilted" geometry reported for the CO ligand in several carbonyl hemoproteins [20-24] has usually been attributed to ...
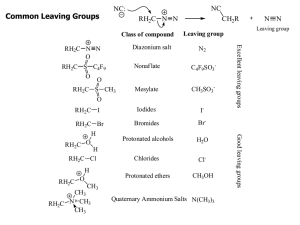
Common Leaving Groups
... Whenever substitution reactions are possible, we must also consider whether or not elimination reactions might occur under the same reaction conditions. In elimination reactions, a “neutral” molecule is „eliminated‟ from the substrate to form a π bond. The π bond is formed between the two carbon ato ...
... Whenever substitution reactions are possible, we must also consider whether or not elimination reactions might occur under the same reaction conditions. In elimination reactions, a “neutral” molecule is „eliminated‟ from the substrate to form a π bond. The π bond is formed between the two carbon ato ...
Photocatalytic Degradation of Cobalamin by Metalized TiO2
... used semiconductor (TiO2 and ZnO) is ~ 3.2 e.V. Therefore photocatalytic activities are shown only under UV irradiations. However, the presence of colored compounds on the surface of the semiconductor can absorb a radiation in the visible range and then is excited by a process called photosensitizat ...
... used semiconductor (TiO2 and ZnO) is ~ 3.2 e.V. Therefore photocatalytic activities are shown only under UV irradiations. However, the presence of colored compounds on the surface of the semiconductor can absorb a radiation in the visible range and then is excited by a process called photosensitizat ...
Basico- Teoria_Campo-Cristalino-Shriver-Atkins
... field. Figure 20.5 shows the case of a d6 ion. In both the free ion and the high-spin complex two electrons are paired, whereas in the low-spin case all six electrons occur as three pairs. Thus we do not need to consider the pairing energy in the high-spin case, as there is no additional pairing. Th ...
... field. Figure 20.5 shows the case of a d6 ion. In both the free ion and the high-spin complex two electrons are paired, whereas in the low-spin case all six electrons occur as three pairs. Thus we do not need to consider the pairing energy in the high-spin case, as there is no additional pairing. Th ...
M.Sc. Chemistry - Manonmaniam Sundaranar University
... Fock and SCF method - Born-Oppenheimer approximation - LCAO method-MO theory of hydrogen molecular ion and Heitler - London treatment of hydrogen molecule. Huckel π electron theory – electronic structure of conjugated systems - ethylene, 1, 3 - butadiene and benzene. UNIT-III: ELECTROCHEMISTRY-I Ion ...
... Fock and SCF method - Born-Oppenheimer approximation - LCAO method-MO theory of hydrogen molecular ion and Heitler - London treatment of hydrogen molecule. Huckel π electron theory – electronic structure of conjugated systems - ethylene, 1, 3 - butadiene and benzene. UNIT-III: ELECTROCHEMISTRY-I Ion ...
19F NMR in organometallic chemistry Applications of fluorinated aryls
... 19 F–19 F coupling is transmitted not only through bonding electrons, but also by a direct through space mechanism; (iv) solvent effects influence 19 F resonances far more strongly than 1 H resonances and solvent induced shifts of 5 ppm and higher are not unusual. It is clear from these features tha ...
... 19 F–19 F coupling is transmitted not only through bonding electrons, but also by a direct through space mechanism; (iv) solvent effects influence 19 F resonances far more strongly than 1 H resonances and solvent induced shifts of 5 ppm and higher are not unusual. It is clear from these features tha ...
Chapter 1--Title
... can form hydrogen bonds to hydrogen bond donors such as water Tertiary amines have lower boiling points than primary or secondary amines of comparable molecular weights Low molecular weight amines tend to be water soluble whether they are primary, secondary or tertiary ...
... can form hydrogen bonds to hydrogen bond donors such as water Tertiary amines have lower boiling points than primary or secondary amines of comparable molecular weights Low molecular weight amines tend to be water soluble whether they are primary, secondary or tertiary ...
Chapter 1--Title - Chemistry Workshop
... can form hydrogen bonds to hydrogen bond donors such as water Tertiary amines have lower boiling points than primary or secondary amines of comparable molecular weights Low molecular weight amines tend to be water soluble whether they are primary, secondary or tertiary ...
... can form hydrogen bonds to hydrogen bond donors such as water Tertiary amines have lower boiling points than primary or secondary amines of comparable molecular weights Low molecular weight amines tend to be water soluble whether they are primary, secondary or tertiary ...
08.Carboxylic acids. Functional derivates of carboxylic acids
... derivatives of alcohols. We have seen earlier that hydroxyl groups take precedence over double bonds, and double bonds take precedence over halogens and alkyl groups, in naming compounds. Carboxylic acids outrank all the common groups we have encountered to this point. Double bonds in the main chain ...
... derivatives of alcohols. We have seen earlier that hydroxyl groups take precedence over double bonds, and double bonds take precedence over halogens and alkyl groups, in naming compounds. Carboxylic acids outrank all the common groups we have encountered to this point. Double bonds in the main chain ...
Question Bank - Edudel.nic.in
... What is the value of Van’t Hoff factor (i) if solute molecules undergo dimerisation. [Ans. : i = 0.5] ...
... What is the value of Van’t Hoff factor (i) if solute molecules undergo dimerisation. [Ans. : i = 0.5] ...
Introduction to Nanochemistry
... Introduction, Harmonic and anharmonic vibrations, absorption of radiation by molecular vibrations, selection rules, force constant, vibration in polyatomic molecules, effects giving rise to absorption bands, Group vibrations, limitation of group vibration concept. Raman Spectroscopy : Introduction, ...
... Introduction, Harmonic and anharmonic vibrations, absorption of radiation by molecular vibrations, selection rules, force constant, vibration in polyatomic molecules, effects giving rise to absorption bands, Group vibrations, limitation of group vibration concept. Raman Spectroscopy : Introduction, ...
Quantitative Chemical Analysis 7e
... • Monodentate ligand: binds to a metal ion through only one atom. • Multidentate ligand: attaches to a metal ion through more than one ligand atom, also known as chelating ligand. • Chelate effect: the ability of multidentate ligands to form more stable metal complexes than those formed by similar m ...
... • Monodentate ligand: binds to a metal ion through only one atom. • Multidentate ligand: attaches to a metal ion through more than one ligand atom, also known as chelating ligand. • Chelate effect: the ability of multidentate ligands to form more stable metal complexes than those formed by similar m ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.