π bonded ligands
... Protonation at the terminal methylene in the η1-allyl Mn complex creates a carbonium ion having a metal at the β position. Since the carbonium ion is a zeroelectron ligand like a proton, it can coordinate to the 18e metal to give the alkene complex. ...
... Protonation at the terminal methylene in the η1-allyl Mn complex creates a carbonium ion having a metal at the β position. Since the carbonium ion is a zeroelectron ligand like a proton, it can coordinate to the 18e metal to give the alkene complex. ...
Descriptive Chemistry for the Final Exam
... Holding one carbon in a fixed position, the other carbon with its three bonding positions can freely rotate in a circle. This can occur because the σ molecular orbital containing the bonding electrons is not distorted. In general, little energy is needed. As a consequence, all three positions for a ...
... Holding one carbon in a fixed position, the other carbon with its three bonding positions can freely rotate in a circle. This can occur because the σ molecular orbital containing the bonding electrons is not distorted. In general, little energy is needed. As a consequence, all three positions for a ...
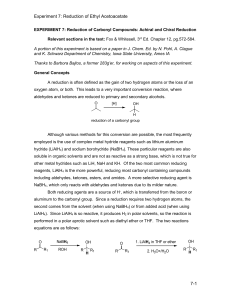
Experiment 7-Reduction
... the two isomers are different and become diastereomeric. Thus, the amounts of each will not by equal. Chemists have been developing several chiral reducing agents, in combination with ligands, solvents and agents, to find the most efficient. One of the most common is L-tartaric acid, which selective ...
... the two isomers are different and become diastereomeric. Thus, the amounts of each will not by equal. Chemists have been developing several chiral reducing agents, in combination with ligands, solvents and agents, to find the most efficient. One of the most common is L-tartaric acid, which selective ...
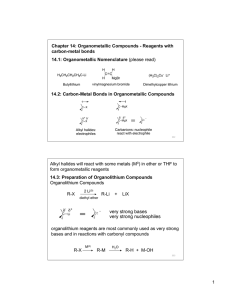
Organometallic Compounds - Reagents
... Acetylide anions react with ketones and aldehydes to form a C-C bond; the product is an acetylenic (propargyl) alcohols R1 C C ...
... Acetylide anions react with ketones and aldehydes to form a C-C bond; the product is an acetylenic (propargyl) alcohols R1 C C ...
Functional Groups
... 2. Identify the groups (other than H) that are joined to the longest chain. Add the names of these groups as a prefix along with di-, tri-, etc. to indicate the number of each group. CH3-CH-CH2-CH-CH3 ...
... 2. Identify the groups (other than H) that are joined to the longest chain. Add the names of these groups as a prefix along with di-, tri-, etc. to indicate the number of each group. CH3-CH-CH2-CH-CH3 ...
Chemical Reactions
... In a synthesis reaction two or more substances combine to form a more complex substance. A decomposition reaction is the opposite of synthesis and breaks down a compound into two or more substances. In a single replacement reaction, one substance in a compound is replaced by another, more active, su ...
... In a synthesis reaction two or more substances combine to form a more complex substance. A decomposition reaction is the opposite of synthesis and breaks down a compound into two or more substances. In a single replacement reaction, one substance in a compound is replaced by another, more active, su ...
Bio Inorganic Chemistry
... Hemoglobin: A dioxygen‐carrying hemeprotein of red blood cells HiPIP: High‐Potential Iron‐sulfur Protein (ferredoxin). Cluster which undergoes oxidation‐reduction between the [4Fe‐4S]2+and [4Fe‐4S]3+states Holoenzyme: An enzyme containing its characteristic prosthetic group(s) and/or metal(s)• Ion ...
... Hemoglobin: A dioxygen‐carrying hemeprotein of red blood cells HiPIP: High‐Potential Iron‐sulfur Protein (ferredoxin). Cluster which undergoes oxidation‐reduction between the [4Fe‐4S]2+and [4Fe‐4S]3+states Holoenzyme: An enzyme containing its characteristic prosthetic group(s) and/or metal(s)• Ion ...
Carbon Chemistry
... • Branched Chains – Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas are isomers. ...
... • Branched Chains – Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas are isomers. ...
Transesterification of Animal Fat to Biodiesel Over Calcined
... its abundance, cost effectiveness and better physic chemical properties [7]. In addition, the type of catalyst that can be used for transesterification can be either acidic or basic or rather in the category of homogeneous or heterogeneous. Homogenous catalysts such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and po ...
... its abundance, cost effectiveness and better physic chemical properties [7]. In addition, the type of catalyst that can be used for transesterification can be either acidic or basic or rather in the category of homogeneous or heterogeneous. Homogenous catalysts such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and po ...
2014
... pressure of the PCl5 (g) is 1.00 atm. The temperature is held constant until the PCl5 (g) reaches equilibrium with its decomposition products. At equilibrium, the total pressure in the 1.00 L container is 1.40 atm. 7) Which of the following is the most likely cause for the increase in pressure obser ...
... pressure of the PCl5 (g) is 1.00 atm. The temperature is held constant until the PCl5 (g) reaches equilibrium with its decomposition products. At equilibrium, the total pressure in the 1.00 L container is 1.40 atm. 7) Which of the following is the most likely cause for the increase in pressure obser ...
higher chemistry revision. - Deans Community High School
... (a) Olive oil can be hardened using a nickel catalyst to produce a fat. (i) What type of catalyst is nickel in this reaction? (ii) In what way does the structure of a fat molecule differ from that of an oil molecule? (b) Olive oil can be hydrolysed using sodium hydroxide solution to produce sodium s ...
... (a) Olive oil can be hardened using a nickel catalyst to produce a fat. (i) What type of catalyst is nickel in this reaction? (ii) In what way does the structure of a fat molecule differ from that of an oil molecule? (b) Olive oil can be hydrolysed using sodium hydroxide solution to produce sodium s ...
Rapid Ether and Alcohol CO Bond Hydrogenolysis Catalyzed by
... of polymerization.1 For example, cyclic ethers such as tetrahydrofuran/-pyran derivatives are important targets since they can be obtained from renewable cellulosic biomass resources,1f and efficient, selective routes to convert cyclic ethers to hydrocarbons present a major challenge in biomass resear ...
... of polymerization.1 For example, cyclic ethers such as tetrahydrofuran/-pyran derivatives are important targets since they can be obtained from renewable cellulosic biomass resources,1f and efficient, selective routes to convert cyclic ethers to hydrocarbons present a major challenge in biomass resear ...
Organic Molecules
... Functional Groups Functional Groups - Groups of atoms attached to carbon skeletons that behave/react in known ways. ...
... Functional Groups Functional Groups - Groups of atoms attached to carbon skeletons that behave/react in known ways. ...
32 GRIGNARD REACTION Alkyl halides can react with magnesium
... reagent reacts with water to give hydrocarbons (benzene in this case). Mount a 50 mL round bottom flask with a condenser. Do not run water through your condenser. Place 0.7 g Mg turnings in the flask. Add 10 mL of dry ether, followed by 0.5 mL of bromobenzene. Your TA will then come around and add a ...
... reagent reacts with water to give hydrocarbons (benzene in this case). Mount a 50 mL round bottom flask with a condenser. Do not run water through your condenser. Place 0.7 g Mg turnings in the flask. Add 10 mL of dry ether, followed by 0.5 mL of bromobenzene. Your TA will then come around and add a ...
C. - Knights of The Periodic Table
... A. activation energy increases B. energy of the products increases C. frequency of collisions between reactants increases D. energy of the activated complex increases ...
... A. activation energy increases B. energy of the products increases C. frequency of collisions between reactants increases D. energy of the activated complex increases ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.