Polymerization - WordPress.com
... a. Polymer – a large molecule consisting of repeating units. b. Repeating unit – recurring unit in a polymer c. Monomer – smallest molecule from which the polymer is made i. Naming Polymers: put poly- in front of the name of the monomer 3. There are many polymerization mechanisms. You need to know: ...
... a. Polymer – a large molecule consisting of repeating units. b. Repeating unit – recurring unit in a polymer c. Monomer – smallest molecule from which the polymer is made i. Naming Polymers: put poly- in front of the name of the monomer 3. There are many polymerization mechanisms. You need to know: ...
Worked_Examples
... attractions or hydrogen bonds, pentane has the lowest boiling point of the three compounds. With a polar carbonyl group, butanone molecules form dipole–dipole attractions, but no hydrogen bonds. Butanone has a higher boiling point than pentane. Because molecules of 2-butanol can form hydrogen bonds ...
... attractions or hydrogen bonds, pentane has the lowest boiling point of the three compounds. With a polar carbonyl group, butanone molecules form dipole–dipole attractions, but no hydrogen bonds. Butanone has a higher boiling point than pentane. Because molecules of 2-butanol can form hydrogen bonds ...
03 AP Bio Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... • Two percent of the carbon had formed amino acids that are used to make proteins in living cells, with glycine as the most abundant. Nucleic acids were not formed within the reaction. But the common 20 amino acids were formed, in ...
... • Two percent of the carbon had formed amino acids that are used to make proteins in living cells, with glycine as the most abundant. Nucleic acids were not formed within the reaction. But the common 20 amino acids were formed, in ...
... the hydrolysis of 1 was followed by TLC6 at pH 9.0, a steady state concentration of about 25% formylmethylcobalamin was observed; at pH 7.0 only 10% of the aldehyde was seen. As the pH is increased decomposition of formylmethylcobalamin becomes slower, and thus an increase in its concentration, with ...
Thermodynamics
... Not speed of reaction (kinetics) A reaction can be thermodynamically favored but still be ...
... Not speed of reaction (kinetics) A reaction can be thermodynamically favored but still be ...
to get Period 1 8
... Plastics, fuels, cleaning solutions come from petroleum or crude oil Many organic compounds have similar properties melting points, boiling points, odor, electrical conductivity, and solubility Many have low melting points and boiling points, liquids or gases at room temperature Organic compounds h ...
... Plastics, fuels, cleaning solutions come from petroleum or crude oil Many organic compounds have similar properties melting points, boiling points, odor, electrical conductivity, and solubility Many have low melting points and boiling points, liquids or gases at room temperature Organic compounds h ...
Alcohols
... The reactivity of LiAlH4 is much greater than that of NaBH4 and is less selective in its reactions. LiAlH4 reacts vigorously with water and ethanol and must be used in an aprotic solvent such as diethyl ether. ...
... The reactivity of LiAlH4 is much greater than that of NaBH4 and is less selective in its reactions. LiAlH4 reacts vigorously with water and ethanol and must be used in an aprotic solvent such as diethyl ether. ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment 2016
... Predict whether the following combinations will result in a reaction. Write a balanced reaction for those reactions. Indicate you understand the specific reactions by writing the net ionic equation for the reaction. Hopefully you would have memorized the solubility rules before attempting to answer ...
... Predict whether the following combinations will result in a reaction. Write a balanced reaction for those reactions. Indicate you understand the specific reactions by writing the net ionic equation for the reaction. Hopefully you would have memorized the solubility rules before attempting to answer ...
Transition Metals Complexes
... further exposure to light, any unreacted AgBr must be removed. This is done during the fixing process by adding sodium thiosulphate solution. The water-soluble linear complex ion [Ag(S2O3)2]3- is formed. AgBr + 2S2O32- ...
... further exposure to light, any unreacted AgBr must be removed. This is done during the fixing process by adding sodium thiosulphate solution. The water-soluble linear complex ion [Ag(S2O3)2]3- is formed. AgBr + 2S2O32- ...
Chapter 7- Alcohols
... Covalent OH bond ~ 480 kJ mol-1 Hydrogen bond ~ 20-40 kJ mol-1 Much weaker but has important effects (i) Boiling points of alcohols are higher than would be predicted based on molecular weight - Extra energy required to break the intermolecular hydrogen bonds (ii) Lower molecular weight alcohols ar ...
... Covalent OH bond ~ 480 kJ mol-1 Hydrogen bond ~ 20-40 kJ mol-1 Much weaker but has important effects (i) Boiling points of alcohols are higher than would be predicted based on molecular weight - Extra energy required to break the intermolecular hydrogen bonds (ii) Lower molecular weight alcohols ar ...
AP Biology - Nashville Christian School
... I am very excited for the opportunity to advance your knowledge and understanding living organisms and how they interact. But before we can start learning the “good stuff”, you need to remember ...
... I am very excited for the opportunity to advance your knowledge and understanding living organisms and how they interact. But before we can start learning the “good stuff”, you need to remember ...
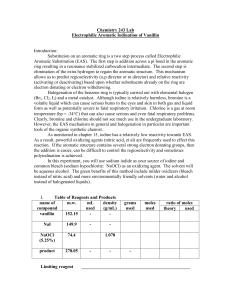
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution of Vanillin
... (activating or deactivating) based upon whether substituents already on the ring are electron donating or electron withdrawing. Halogenation of the benzene ring is typically carried out with elemental halogen (Br2, Cl2, I2) and a metal catalyst. Although iodine is relatively harmless, bromine is a v ...
... (activating or deactivating) based upon whether substituents already on the ring are electron donating or electron withdrawing. Halogenation of the benzene ring is typically carried out with elemental halogen (Br2, Cl2, I2) and a metal catalyst. Although iodine is relatively harmless, bromine is a v ...
6. Low valent of Vanadium catalyst in organic synthesis
... *the coordination of the phosphorus raises the reduction capability and selectivity. *the bulky reductant is liable to approach the bromide from the ...
... *the coordination of the phosphorus raises the reduction capability and selectivity. *the bulky reductant is liable to approach the bromide from the ...
100 Problems and Exercises in Organometallic Chemistry Anil J. Elias
... gives peaks in the range of 1859-1960 cm-1. Compound A on refluxing in toluene releases CO gas and on cooling and further bubbling acetylene gas for 12 hours converts to a new compound B with the empirical formula C8H6O2Mo. The infrared spectrum of this compound shows CO stretching bands in the ran ...
... gives peaks in the range of 1859-1960 cm-1. Compound A on refluxing in toluene releases CO gas and on cooling and further bubbling acetylene gas for 12 hours converts to a new compound B with the empirical formula C8H6O2Mo. The infrared spectrum of this compound shows CO stretching bands in the ran ...
Lecture: 2 OCCURRENCE AND STRUCTURE OF
... aminosugars such as glucosamine, galactosamine and mannosamine. ...
... aminosugars such as glucosamine, galactosamine and mannosamine. ...
Pages from PS 11 Textbook for Lab
... We know that the temperature increased so the reaction is exothermic and qrxn is thus negative. q = (50g)(4.18J/g-°C)(2.1K) = 439J Thus qrxn = −439J as heat was released by the reaction. The molecular weight of ATP is 573g/mole So: ΔHrxn = (−439J/10g)(573g/mole) = −25kJ/mole ...
... We know that the temperature increased so the reaction is exothermic and qrxn is thus negative. q = (50g)(4.18J/g-°C)(2.1K) = 439J Thus qrxn = −439J as heat was released by the reaction. The molecular weight of ATP is 573g/mole So: ΔHrxn = (−439J/10g)(573g/mole) = −25kJ/mole ...
NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2013
... (Distillation) is used because the aldehyde has a lower boiling point (than butan-1-ol and the carboxylic acid formed) / to prevent it from being oxidised further. (Both) reactions are oxidation–reduction because butan-1-ol has lost electrons/lost hydrogen/gained oxygen/oxidation number (of C) has i ...
... (Distillation) is used because the aldehyde has a lower boiling point (than butan-1-ol and the carboxylic acid formed) / to prevent it from being oxidised further. (Both) reactions are oxidation–reduction because butan-1-ol has lost electrons/lost hydrogen/gained oxygen/oxidation number (of C) has i ...
Ch 22 Organic
... A group of atoms that determines an organic molecules’ chemical properties. It can take the place of a hydrogen in a hydrocarbon. ...
... A group of atoms that determines an organic molecules’ chemical properties. It can take the place of a hydrogen in a hydrocarbon. ...
167KB - NZQA
... (Distillation) is used because the aldehyde has a lower boiling point (than butan-1-ol and the carboxylic acid formed) / to prevent it from being oxidised further. (Both) reactions are oxidation–reduction because butan-1-ol has lost electrons/lost hydrogen/gained oxygen/oxidation number (of C) has i ...
... (Distillation) is used because the aldehyde has a lower boiling point (than butan-1-ol and the carboxylic acid formed) / to prevent it from being oxidised further. (Both) reactions are oxidation–reduction because butan-1-ol has lost electrons/lost hydrogen/gained oxygen/oxidation number (of C) has i ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.