Methanol Synthesis
... In that chart, the arrow width represents the total carbon moles that reacts (averaged among sets) for every reaction and direction. Please note that the reverse of CO2-to-Methanol is very thin compared to other reactions. Thus, we may eliminate that direction by unincluding it in the Chemistry→Kine ...
... In that chart, the arrow width represents the total carbon moles that reacts (averaged among sets) for every reaction and direction. Please note that the reverse of CO2-to-Methanol is very thin compared to other reactions. Thus, we may eliminate that direction by unincluding it in the Chemistry→Kine ...
Alcohols, Thiols, and Ethers Ch#5
... The longest chain contains six carbon atoms, but it does not contain the carbon bonded to the hydroxyl group. The longest chain containing the carbon bonded to the —OH group is the one outlined by the green box, containing five carbon atoms. This chain is numbered from right to left in order to give ...
... The longest chain contains six carbon atoms, but it does not contain the carbon bonded to the hydroxyl group. The longest chain containing the carbon bonded to the —OH group is the one outlined by the green box, containing five carbon atoms. This chain is numbered from right to left in order to give ...
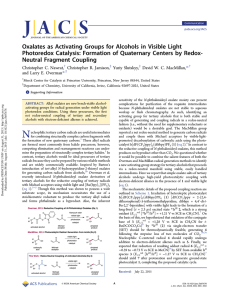
103. Oxalates as Activating Groups for Alcohols in Visible Light Photoredox Catalysis: Formation of Quaternary Centers by Redox-Neutral Fragment Coupling
... are stable and do not readily disproportionate. (11) The cesium oxalates were most conveniently prepared via hydrolysis of the corresponding tert-alkyl methyl oxalates with aqueous CsOH. This route avoids the potentially unstable alkyl hydrogen oxalate moiety; the tert-alkyl methyl oxalate intermedi ...
... are stable and do not readily disproportionate. (11) The cesium oxalates were most conveniently prepared via hydrolysis of the corresponding tert-alkyl methyl oxalates with aqueous CsOH. This route avoids the potentially unstable alkyl hydrogen oxalate moiety; the tert-alkyl methyl oxalate intermedi ...
Worked_Examples
... attractions or hydrogen bonds, pentane has the lowest boiling point of the three compounds. With a polar carbonyl group, butanone molecules form dipole–dipole attractions, but no hydrogen bonds. Butanone has a higher boiling point than pentane. Because molecules of 2-butanol can form hydrogen bonds ...
... attractions or hydrogen bonds, pentane has the lowest boiling point of the three compounds. With a polar carbonyl group, butanone molecules form dipole–dipole attractions, but no hydrogen bonds. Butanone has a higher boiling point than pentane. Because molecules of 2-butanol can form hydrogen bonds ...
Basic definitions for organic chemistry
... Organic chemistry is a vast subject so is split it into small sections for study. This is done by studying compounds which behave in a similar way because they have a particular atom, or group of atoms, (FUNCTIONAL GROUP) in their structure. ...
... Organic chemistry is a vast subject so is split it into small sections for study. This is done by studying compounds which behave in a similar way because they have a particular atom, or group of atoms, (FUNCTIONAL GROUP) in their structure. ...
Functional Group Isomerism
... • For example, most amino acids (and so proteins) are chiral, along with many other molecules. • In nature, only one optical isomer occurs (e.g. all natural amino acids are rotate polarised right to the left). • Many drugs are optically active, with one enantiomer only having the beneficial effect. ...
... • For example, most amino acids (and so proteins) are chiral, along with many other molecules. • In nature, only one optical isomer occurs (e.g. all natural amino acids are rotate polarised right to the left). • Many drugs are optically active, with one enantiomer only having the beneficial effect. ...
Identification of Functional Groups
... Permanganate ions will oxidize different functional groups at different rates. In the case of especially slow reactions, gentle heating in a hot water bath may be required. Hydrocarbons and carboxylic acids are the only two of all the types of compounds being studied that will not react with dilute ...
... Permanganate ions will oxidize different functional groups at different rates. In the case of especially slow reactions, gentle heating in a hot water bath may be required. Hydrocarbons and carboxylic acids are the only two of all the types of compounds being studied that will not react with dilute ...
Alkyl halide
... • The kinds of reactions they undergo – nucleophilic substitutions and eliminations – are frequently involved • Alkyl halide chemistry acts as a relatively simple model for many mechanistically similar but structurally more complex reactions found in biomolecules ...
... • The kinds of reactions they undergo – nucleophilic substitutions and eliminations – are frequently involved • Alkyl halide chemistry acts as a relatively simple model for many mechanistically similar but structurally more complex reactions found in biomolecules ...
Chemical Reactions
... Identify the type of reaction for each of the following synthesis or decomposition reactions, and write the balanced equation: Nitrogen and oxygen react to form nitrogen ...
... Identify the type of reaction for each of the following synthesis or decomposition reactions, and write the balanced equation: Nitrogen and oxygen react to form nitrogen ...
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
... recognize and name carboxylic acids both by common and IUPAC names. describe the physical properties of carboxylic acids, especially with respect to their intermolecular interactions. describe the acidity or carboxylic acids with particular emphasis as compared to mineral acids. describe resonance a ...
... recognize and name carboxylic acids both by common and IUPAC names. describe the physical properties of carboxylic acids, especially with respect to their intermolecular interactions. describe the acidity or carboxylic acids with particular emphasis as compared to mineral acids. describe resonance a ...
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
... recognize and name carboxylic acids both by common and IUPAC names. describe the physical properties of carboxylic acids, especially with respect to their intermolecular interactions. describe the acidity or carboxylic acids with particular emphasis as compared to mineral acids. describe resonance a ...
... recognize and name carboxylic acids both by common and IUPAC names. describe the physical properties of carboxylic acids, especially with respect to their intermolecular interactions. describe the acidity or carboxylic acids with particular emphasis as compared to mineral acids. describe resonance a ...
Section 3 d ethanol
... 3.12 describe the dehydration of ethanol to ethene, using aluminium oxide ...
... 3.12 describe the dehydration of ethanol to ethene, using aluminium oxide ...
Unit 4 - INTEC Chemistry Blog
... Redox (reduction oxidation reaction) describes / all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation number/state changed Oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic Oxidation describes the loss of electrons by ...
... Redox (reduction oxidation reaction) describes / all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation number/state changed Oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic Oxidation describes the loss of electrons by ...
2.6 M - Thierry Karsenti
... .3. An alkane is a hydrocarbon that has only single bonds. Alkanes that do not contain rings have he formula CnH2n+2. An alkane in the shape of a ring is called a cycloalkane. Cycloalkanes have the formula CnH2n. ..4. An alkene is a compound that has at least one double bond. A straight-chain alkene ...
... .3. An alkane is a hydrocarbon that has only single bonds. Alkanes that do not contain rings have he formula CnH2n+2. An alkane in the shape of a ring is called a cycloalkane. Cycloalkanes have the formula CnH2n. ..4. An alkene is a compound that has at least one double bond. A straight-chain alkene ...
Agostic Interactions
... Significance σ bond complexation Catalysis σ bond metathesis Some synthesis Conclusion ...
... Significance σ bond complexation Catalysis σ bond metathesis Some synthesis Conclusion ...
Lecture 2
... failure or death. Because ethanol impairs judgment in humans, it can be a catalyst for reckless or irresponsible behavior. The LD50 of ethanol for rats is 10.3 g/kg. Other alcohols are substantially more poisonous than ethanol, partly because they take much longer to be metabolized and partly becaus ...
... failure or death. Because ethanol impairs judgment in humans, it can be a catalyst for reckless or irresponsible behavior. The LD50 of ethanol for rats is 10.3 g/kg. Other alcohols are substantially more poisonous than ethanol, partly because they take much longer to be metabolized and partly becaus ...
Alcohols and Phenols
... • An electron-withdrawing substituent makes a phenol more acidic by delocalizing the negative charge • Phenols with an electron-donating substituent are less acidic because these substituents concentrate the charge ...
... • An electron-withdrawing substituent makes a phenol more acidic by delocalizing the negative charge • Phenols with an electron-donating substituent are less acidic because these substituents concentrate the charge ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.