calculations-questions-part
... (Total for question = 13 marks) Q2. Brand X is unlike many conventional toilet cleaners in that it does not contain bleach, but instead contains hydrochloric acid. The label states that the toilet cleaner contains 9 g of HCl per 100 cm3 of the toilet cleaner. An industrial technician was given the t ...
... (Total for question = 13 marks) Q2. Brand X is unlike many conventional toilet cleaners in that it does not contain bleach, but instead contains hydrochloric acid. The label states that the toilet cleaner contains 9 g of HCl per 100 cm3 of the toilet cleaner. An industrial technician was given the t ...
Article Summaries
... West, N. M.; Templeton, J. L. Can. J. Chem. 2009, 87, 288-296. One of the major downsides to the original Shilov reaction is the fact that it uses platinum consumptively. The goal of this set of experiments was to determine if a non-consumptive pathway was possible. The scorpionate ligands Tp’ (hydr ...
... West, N. M.; Templeton, J. L. Can. J. Chem. 2009, 87, 288-296. One of the major downsides to the original Shilov reaction is the fact that it uses platinum consumptively. The goal of this set of experiments was to determine if a non-consumptive pathway was possible. The scorpionate ligands Tp’ (hydr ...
Lecture notes for chapter 6
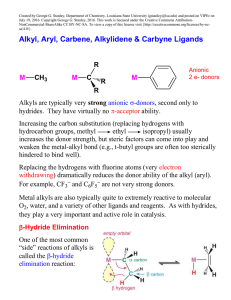
... higher metals with a d6 or d8 electron count (sometimes d4). 4) Schrock alkylidenes as dianionic 4 e- donor ligands. Typically group 4 or 5 metals with d0 electron counts. Also later transition metals in high oxidation states (d0, d2, or d4). Of course, in order to do method 3 or 4, you have to real ...
... higher metals with a d6 or d8 electron count (sometimes d4). 4) Schrock alkylidenes as dianionic 4 e- donor ligands. Typically group 4 or 5 metals with d0 electron counts. Also later transition metals in high oxidation states (d0, d2, or d4). Of course, in order to do method 3 or 4, you have to real ...
Hydrogenation of fatty acid methyl ester to fatty alcohol
... temperature on the reaction mainly reflected by the variation of catalytic activity. The choice of the reaction temperature depended on the activation temperature of the catalyst and the by-product. The positive effect of increment of temperature on reaction rate became slighter in the case that the ...
... temperature on the reaction mainly reflected by the variation of catalytic activity. The choice of the reaction temperature depended on the activation temperature of the catalyst and the by-product. The positive effect of increment of temperature on reaction rate became slighter in the case that the ...
Organic Chemistry II Laboratory
... Other electrophilic addition mechanisms may lead to different stereochemical outcomes. In the addition of molecular bromine to trans-anethole, conjugation with the ring stabilizes a carbocation intermediate. This carbocation intermediate is planar and can be attacked by the nucleophilic bromide ion ...
... Other electrophilic addition mechanisms may lead to different stereochemical outcomes. In the addition of molecular bromine to trans-anethole, conjugation with the ring stabilizes a carbocation intermediate. This carbocation intermediate is planar and can be attacked by the nucleophilic bromide ion ...
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY
... and NH3 are roughly tetrahedral (104o and 107o respectively) and CH4 is exactly tetrahedral (109.5o) !!! Problem: Orbitals available for bonding are 2s () and 2p (right angles to each other) In order to account for the observed geometry, hybridization was proposed as a convenient model. Hybrid ...
... and NH3 are roughly tetrahedral (104o and 107o respectively) and CH4 is exactly tetrahedral (109.5o) !!! Problem: Orbitals available for bonding are 2s () and 2p (right angles to each other) In order to account for the observed geometry, hybridization was proposed as a convenient model. Hybrid ...
An Overview of Carbonyl Compound Chemistry
... as the final products. For example, when organometallic compounds, Grignard or organolithium reagents, are used as the carbanion species, they can react with the ketone or aldehyde intermediates very rapidly to form a second tetrahedral intermediate, in which no good leaving groups are present. Over ...
... as the final products. For example, when organometallic compounds, Grignard or organolithium reagents, are used as the carbanion species, they can react with the ketone or aldehyde intermediates very rapidly to form a second tetrahedral intermediate, in which no good leaving groups are present. Over ...
Effect of nucleophile on reaction
... Better leaving group - faster both reactions are Bond strength - stronger the bond worse the leaving group Stability of X - neutral or stable anions (more electronegative) make good leaving groups ...
... Better leaving group - faster both reactions are Bond strength - stronger the bond worse the leaving group Stability of X - neutral or stable anions (more electronegative) make good leaving groups ...
Ethers and Epoxides
... Addition of HO-X to an alkene gives a halohydrin Treatment of a halohydrin with base gives an epoxide Intramolecular Williamson ether synthesis ...
... Addition of HO-X to an alkene gives a halohydrin Treatment of a halohydrin with base gives an epoxide Intramolecular Williamson ether synthesis ...
Alcohols - Chem1-tsu
... Some alcohols, phenols and ethers occur in nature and are used in the manufacture of perfumes and flavors due to their pleasant odors. From alcohols various other classes of organic compounds can be synthesized. Phenols are used in the manufacture of dyes are resins like bakelite. [It must be noted ...
... Some alcohols, phenols and ethers occur in nature and are used in the manufacture of perfumes and flavors due to their pleasant odors. From alcohols various other classes of organic compounds can be synthesized. Phenols are used in the manufacture of dyes are resins like bakelite. [It must be noted ...
File - Riske Science
... • The two molecules below both have the same empirical and molecular formulas but they have very different characteristics. They are structural isomers and are considered different compounds. ...
... • The two molecules below both have the same empirical and molecular formulas but they have very different characteristics. They are structural isomers and are considered different compounds. ...
Metal Carbenes
... Further functionalization is possible by reaction with a suitable electrophile ...
... Further functionalization is possible by reaction with a suitable electrophile ...
INTRODUCING ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
... Important reactions of the carbonyl group The slightly positive carbon atom in the carbonyl group can be attacked by nucleophiles. A nucleophile is a negatively charged ion (for example, a cyanide ion, CN-), or a slightly negatively charged part of a molecule (for example, the lone pair on a nitroge ...
... Important reactions of the carbonyl group The slightly positive carbon atom in the carbonyl group can be attacked by nucleophiles. A nucleophile is a negatively charged ion (for example, a cyanide ion, CN-), or a slightly negatively charged part of a molecule (for example, the lone pair on a nitroge ...
Electron Delocalization, Resonance and Aromaticity
... HBr adds HBr independently to each double bond Markovnikov’s Rule is followed Chapter 7 ...
... HBr adds HBr independently to each double bond Markovnikov’s Rule is followed Chapter 7 ...
A Brief History of Organic Chemistry
... Three classes of aliphatic hydrocarbons can be defined based upon carbon to carbon bond type. They are the alkanes, alkenes and alkynes. Note that each term differs from the other two by a single letter. The endings, -ane, -ene, and -yne, indicate the presence of single, double and triple bonds res ...
... Three classes of aliphatic hydrocarbons can be defined based upon carbon to carbon bond type. They are the alkanes, alkenes and alkynes. Note that each term differs from the other two by a single letter. The endings, -ane, -ene, and -yne, indicate the presence of single, double and triple bonds res ...
unit 6 alcohols
... Acid chlorides: Cl- is a good LG, and so, with one mole of the Grignard, a ketone forms. The ketone can be attacked by a second mole of the Grignard reagent. Esters: Now the LG is RO-, not usually considered “good,” but the reaction takes ...
... Acid chlorides: Cl- is a good LG, and so, with one mole of the Grignard, a ketone forms. The ketone can be attacked by a second mole of the Grignard reagent. Esters: Now the LG is RO-, not usually considered “good,” but the reaction takes ...
PP Aldehyde and ketone
... 2,4-DINITROPHENYLHYDRAZINE C6H3(NO2)2NHNH2 The following structural isomers have similar boiling points because of similar van der Waals forces and dipole-dipole interactions. They would be impossible to identify with any precision using boiling point determination. ...
... 2,4-DINITROPHENYLHYDRAZINE C6H3(NO2)2NHNH2 The following structural isomers have similar boiling points because of similar van der Waals forces and dipole-dipole interactions. They would be impossible to identify with any precision using boiling point determination. ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.