10.4 Alcohols - SCIS Teachers
... •Alcohols have the general formula: CnH2n+1OH •The physical properties of alcohols are similar to those of both water and hydrocarbons •The shorter chain alcohols such as methanol and ethanol are similar to water, in general they •have higher boiling points than hydrocarbons but lower than water •di ...
... •Alcohols have the general formula: CnH2n+1OH •The physical properties of alcohols are similar to those of both water and hydrocarbons •The shorter chain alcohols such as methanol and ethanol are similar to water, in general they •have higher boiling points than hydrocarbons but lower than water •di ...
rev2
... 2. Know that aldehydes and ketones are functional isomers (constitutional isomers that involve having different functional groups) 3. Understand why aldehydes and ketones have lower bps than alcohols, but about the same solubility in water as alcohols. 4. Know the chemical properties of aldehydes an ...
... 2. Know that aldehydes and ketones are functional isomers (constitutional isomers that involve having different functional groups) 3. Understand why aldehydes and ketones have lower bps than alcohols, but about the same solubility in water as alcohols. 4. Know the chemical properties of aldehydes an ...
Epoxidation and oxidation reactions using 1,4
... hydroperoxide reagent was used it is assumed to follow pseudo first-order kinetics. The reaction is assumed to involve the nucleophilic attack of the olefin on the hydroperoxide followed by proton transfer probably by a concerted intramolecular process. The intermediate formed then decays to give th ...
... hydroperoxide reagent was used it is assumed to follow pseudo first-order kinetics. The reaction is assumed to involve the nucleophilic attack of the olefin on the hydroperoxide followed by proton transfer probably by a concerted intramolecular process. The intermediate formed then decays to give th ...
m3 isomerismintro
... slightly different physical properties more branching = lower boiling point ...
... slightly different physical properties more branching = lower boiling point ...
On the Transition States of Electrophilic Radical Additions to Alkenes
... rate measurements for reactions of tert-butyl radicals with various alkenes exhibit comparable results.' These unequal substituent effects point to unsymmetrical transition states 1 in which only the attacked olefinic carbon atom deviates considerably from its ground-state geometry. Therefore substi ...
... rate measurements for reactions of tert-butyl radicals with various alkenes exhibit comparable results.' These unequal substituent effects point to unsymmetrical transition states 1 in which only the attacked olefinic carbon atom deviates considerably from its ground-state geometry. Therefore substi ...
amine
... • Name the longest chain attached to the nitrogen. • Replace the final –e with –amine. • Number the chain so the carbon bonded to the nitrogen has the lowest possible number. • Number the other substituents on the carbon chain. • An italic “N” is used as a prefix for a substituent on nitrogen. Examp ...
... • Name the longest chain attached to the nitrogen. • Replace the final –e with –amine. • Number the chain so the carbon bonded to the nitrogen has the lowest possible number. • Number the other substituents on the carbon chain. • An italic “N” is used as a prefix for a substituent on nitrogen. Examp ...
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
... aldehydes Electron-donating resonance effect of aromatic ring makes C=O ...
... aldehydes Electron-donating resonance effect of aromatic ring makes C=O ...
ppt - ChemConnections
... http://www.nytimes.com/2016/05/02/health/biggest-loser-weightloss.html?rref=collection%2Fsectioncollection%2Fscience&action=click&contentCollection=science®ion= ...
... http://www.nytimes.com/2016/05/02/health/biggest-loser-weightloss.html?rref=collection%2Fsectioncollection%2Fscience&action=click&contentCollection=science®ion= ...
PPT
... has the lowest possible number. • Number the other substituents on the carbon chain. • An italic “N” is used as a prefix for a substituent on nitrogen. Examples: ...
... has the lowest possible number. • Number the other substituents on the carbon chain. • An italic “N” is used as a prefix for a substituent on nitrogen. Examples: ...
Alcohols and Phenols
... Alcohols are derived from many types of compounds The alcohol hydroxyl can be converted to many other ...
... Alcohols are derived from many types of compounds The alcohol hydroxyl can be converted to many other ...
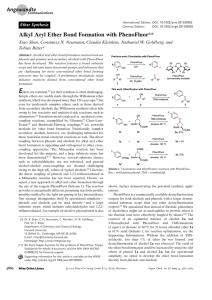
Alkyl Aryl Ether Bond Formation with PhenoFluor
... [f] Toluene was used as the solvent instead of dioxane. Bn = benzyl, Bz = benzoyl. ...
... [f] Toluene was used as the solvent instead of dioxane. Bn = benzyl, Bz = benzoyl. ...
MECH 558 Combustion Class Notes - Page: notes06
... Before learning how hydrocarbons react with oxygen in flames, we must first go over some nomenclature for the different classes of hydrocarbons. 2.1. Alkanes (paraffins): These molecules consist of carbon atoms which are all connected by ...
... Before learning how hydrocarbons react with oxygen in flames, we must first go over some nomenclature for the different classes of hydrocarbons. 2.1. Alkanes (paraffins): These molecules consist of carbon atoms which are all connected by ...
Microsoft Word
... Abstract o-Aminophenol (2-hydroxy aniline) is an important intermediate for the manufacture of dyes, drugs and pesticides. It is manufactured by catalytic liquid phase hydrogenation of o-nitrophenol. The most commonly used catalysts for the hydrogenation process are Raney nickel and supported pallad ...
... Abstract o-Aminophenol (2-hydroxy aniline) is an important intermediate for the manufacture of dyes, drugs and pesticides. It is manufactured by catalytic liquid phase hydrogenation of o-nitrophenol. The most commonly used catalysts for the hydrogenation process are Raney nickel and supported pallad ...
cycloadditions with singlet oxygen
... In 1867 Fritzsche reported the first instance of a singlet oxygen reaction when he observed that a precipitate forms in a solution of 2,3-benzanthracene exposed to air and ambient light.1 At the time, the nature of the reagent and product were unknown and the reaction did not elicit further interest ...
... In 1867 Fritzsche reported the first instance of a singlet oxygen reaction when he observed that a precipitate forms in a solution of 2,3-benzanthracene exposed to air and ambient light.1 At the time, the nature of the reagent and product were unknown and the reaction did not elicit further interest ...
WADE7Lecture10a
... The longest chain contains six carbon atoms, but it does not contain the carbon bonded to the hydroxyl group. The longest chain containing the carbon bonded to the —OH group is the one outlined by the green box, containing five carbon atoms. This chain is numbered from right to left in order to give ...
... The longest chain contains six carbon atoms, but it does not contain the carbon bonded to the hydroxyl group. The longest chain containing the carbon bonded to the —OH group is the one outlined by the green box, containing five carbon atoms. This chain is numbered from right to left in order to give ...
100 Problems and Exercises in Organometallic Chemistry Anil J. Elias
... (Fischer E. O. et al., J. Organomet. Chem., 1972, 35, 647 & 1974, 81, C23) 37. Write the structure of the most appropriate reagent and conditions for carrying out the following reactions resulting in the highest possible yields. Indicate ...
... (Fischer E. O. et al., J. Organomet. Chem., 1972, 35, 647 & 1974, 81, C23) 37. Write the structure of the most appropriate reagent and conditions for carrying out the following reactions resulting in the highest possible yields. Indicate ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.