Microsoft Word - Open Access Repository of Indian Theses
... of organic chemists since it is a valuble precursor for the synthesis of nonpeptide neurokinin NK1 receptor antagonists 43 and 44 as showed in figure III. These nonpeptidic ligands 43 and 44 are known to exhibit a variety of biological activities including neurogenic inflammation, pain transmission ...
... of organic chemists since it is a valuble precursor for the synthesis of nonpeptide neurokinin NK1 receptor antagonists 43 and 44 as showed in figure III. These nonpeptidic ligands 43 and 44 are known to exhibit a variety of biological activities including neurogenic inflammation, pain transmission ...
a,b
... • Best reactions are derived from addition of a b-keto ester or other 1,3-dicarbonyl compound to an unhindered a,bunsaturated ketone • Ethyl acetoacetate reacts with but-3-en-2-one in the presence of sodium ethoxide to yield the Michael addition product ...
... • Best reactions are derived from addition of a b-keto ester or other 1,3-dicarbonyl compound to an unhindered a,bunsaturated ketone • Ethyl acetoacetate reacts with but-3-en-2-one in the presence of sodium ethoxide to yield the Michael addition product ...
Review Sheet - Evergreen Archives
... Be able to name alcohols and ethers. If provided a name, be able to draw the structure of an alcohol and an ether. Know Zaitsev’s Rule and when it is applied. Be able to draw structural formulas for an alcohol reaction that involves Zaitsev’s Rule. Know the important alcohols and their uses. Be able ...
... Be able to name alcohols and ethers. If provided a name, be able to draw the structure of an alcohol and an ether. Know Zaitsev’s Rule and when it is applied. Be able to draw structural formulas for an alcohol reaction that involves Zaitsev’s Rule. Know the important alcohols and their uses. Be able ...
Acidic and Basic Character of Carboxylic Acids
... Oxidation of primary alcohols and of aldehydes furnishes carboxylic acids. Primary alcohols oxidize first to aldehydes, which then may further oxidize to carboxylic acids. ...
... Oxidation of primary alcohols and of aldehydes furnishes carboxylic acids. Primary alcohols oxidize first to aldehydes, which then may further oxidize to carboxylic acids. ...
ASYMMETRIC CATALYSIS
... are based on readily available starting materials and reagents. Although mixing metal complexes and ligands in situ is a common way to evaluate catalyst performance and is used widely in organic synthesis, in many cases it is important to make metal-ligand complexes cleanly prior to reaction. Using ...
... are based on readily available starting materials and reagents. Although mixing metal complexes and ligands in situ is a common way to evaluate catalyst performance and is used widely in organic synthesis, in many cases it is important to make metal-ligand complexes cleanly prior to reaction. Using ...
No Slide Title
... 2,4-DINITROPHENYLHYDRAZINE C6H3(NO2)2NHNH2 The following structural isomers have similar boiling points because of similar van der Waals forces and dipole-dipole interactions. They would be impossible to identify with any precision using boiling point determination. ...
... 2,4-DINITROPHENYLHYDRAZINE C6H3(NO2)2NHNH2 The following structural isomers have similar boiling points because of similar van der Waals forces and dipole-dipole interactions. They would be impossible to identify with any precision using boiling point determination. ...
H - Knockhardy
... 2,4-DINITROPHENYLHYDRAZINE C6H3(NO2)2NHNH2 The following structural isomers have similar boiling points because of similar van der Waals forces and dipole-dipole interactions. They would be impossible to identify with any precision using boiling point determination. ...
... 2,4-DINITROPHENYLHYDRAZINE C6H3(NO2)2NHNH2 The following structural isomers have similar boiling points because of similar van der Waals forces and dipole-dipole interactions. They would be impossible to identify with any precision using boiling point determination. ...
Physical Properties OF Aldehydes And Ketones
... know the common and IUPAC nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones Know the physical properties of aldehydes and ketones Know how to synthesize an aldehyde or a ketone from a compound without that functionality. Know the different nucleophilic attack reactions at the carbonyl carbon and the spec ...
... know the common and IUPAC nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones Know the physical properties of aldehydes and ketones Know how to synthesize an aldehyde or a ketone from a compound without that functionality. Know the different nucleophilic attack reactions at the carbonyl carbon and the spec ...
10.1 Intro to Organic Chemistry 10.1 Organic Chemistry
... has 4 valence electrons and most often bonds to H, O, N and S. Because the C-C single bond (348 kJ mol1) and the C-H bond (412 kJ mol-1) are strong, carbon compounds are stable. Carbon can form chains and rings. ...
... has 4 valence electrons and most often bonds to H, O, N and S. Because the C-C single bond (348 kJ mol1) and the C-H bond (412 kJ mol-1) are strong, carbon compounds are stable. Carbon can form chains and rings. ...
Reprint - Horizon Research Publishing
... and other disorders related to the sympathetic nervous system. Aryloxy β-amino alcohol functionality is the key pharmacophore in β-blockers. Propranolol is the prototype agent for this class of compounds, which affects β1 and β2 receptors. The classical approach and the most straight forward synthet ...
... and other disorders related to the sympathetic nervous system. Aryloxy β-amino alcohol functionality is the key pharmacophore in β-blockers. Propranolol is the prototype agent for this class of compounds, which affects β1 and β2 receptors. The classical approach and the most straight forward synthet ...
Oxidation of Cyclohexanol
... Oxidation-reduction reactions play an important role in organic chemistry. Oxidation of alcohols to form aldehydes, ketones or carboxylic acids is a fundamental and widely used reaction. Primary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes or carboxylic acids while secondary alcohols oxidize to ketones. Te ...
... Oxidation-reduction reactions play an important role in organic chemistry. Oxidation of alcohols to form aldehydes, ketones or carboxylic acids is a fundamental and widely used reaction. Primary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes or carboxylic acids while secondary alcohols oxidize to ketones. Te ...
View/Open
... © 2008 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Thomson Learning WebTutorTM is a trademark of Thomson Learning, Inc. Library of Congress Control Number: 2006938700 ...
... © 2008 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Thomson Learning WebTutorTM is a trademark of Thomson Learning, Inc. Library of Congress Control Number: 2006938700 ...
Hydrogenation of Amino Acid Mixtures to Amino Alcohols
... serine and valine and their mixtures was studied to quantify reaction rates, understand interactions between the substrates and catalyst, and shed light onto the reaction mechanism. The understanding gained from this model system will aid in design of hydrogenation processes of more complex biorenew ...
... serine and valine and their mixtures was studied to quantify reaction rates, understand interactions between the substrates and catalyst, and shed light onto the reaction mechanism. The understanding gained from this model system will aid in design of hydrogenation processes of more complex biorenew ...
Carolina Aguirre, Rosa Arrieta, Soledad Anjarí, Andrés Illanes
... thermodynamically or kinetically controlled synthesis using enzymes. Kinetically controlled synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics, although requiring activated acyl donors, is usually a better strategy when product yield is a main issue (17) as is the case for antibiotic production (18), since it is not ...
... thermodynamically or kinetically controlled synthesis using enzymes. Kinetically controlled synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics, although requiring activated acyl donors, is usually a better strategy when product yield is a main issue (17) as is the case for antibiotic production (18), since it is not ...
A Model for Catalytically Active Zinc(I1) Ion in Liver
... 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane,L2),Zn"[ 14]aneN4, 3 ([ 14]aneN4 = 1,4,8,1I-tetraazacyclotetradecane,LJ,and free Zn" salts, 4. Variations in Zn" acidity and coordination environment in these complexes result in varying degrees of catalytic activity in the reduction of p-nitrobenzaldehyde (9) and an N ...
... 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane,L2),Zn"[ 14]aneN4, 3 ([ 14]aneN4 = 1,4,8,1I-tetraazacyclotetradecane,LJ,and free Zn" salts, 4. Variations in Zn" acidity and coordination environment in these complexes result in varying degrees of catalytic activity in the reduction of p-nitrobenzaldehyde (9) and an N ...
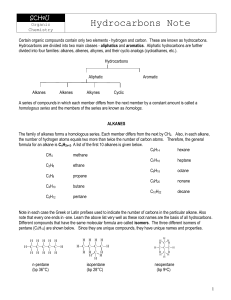
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.