3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and
... Cyclobutane has less angle strain than cyclopropane but more torsional strain because of its larger number of ring hydrogens, and their proximity to each other Cyclobutane is slightly bent out of plane - one carbon atom is about 25° above The bend increases angle strain but decreases torsional str ...
... Cyclobutane has less angle strain than cyclopropane but more torsional strain because of its larger number of ring hydrogens, and their proximity to each other Cyclobutane is slightly bent out of plane - one carbon atom is about 25° above The bend increases angle strain but decreases torsional str ...
Ch 22 Organic
... A group of atoms that determines an organic molecules’ chemical properties. It can take the place of a hydrogen in a hydrocarbon. ...
... A group of atoms that determines an organic molecules’ chemical properties. It can take the place of a hydrogen in a hydrocarbon. ...
synthpp - Knockhardy
... the reagents required to convert one functional group into another the presence of other functional groups - in case also they react the conditions required - temperature, pressure, catalyst the rate of the reaction the yield - especially important for equilibrium reactions atom economy safety - tox ...
... the reagents required to convert one functional group into another the presence of other functional groups - in case also they react the conditions required - temperature, pressure, catalyst the rate of the reaction the yield - especially important for equilibrium reactions atom economy safety - tox ...
Supported Homogeneous Catalysts
... the polymer support is the most important feature of the work with titanocene (23). A necessary feature of a homogeneous catalyst is the existence of a free coordination site on the metal atom to which alkene molecules can attach themselves. Often attempts to produce a free site results in polymeris ...
... the polymer support is the most important feature of the work with titanocene (23). A necessary feature of a homogeneous catalyst is the existence of a free coordination site on the metal atom to which alkene molecules can attach themselves. Often attempts to produce a free site results in polymeris ...
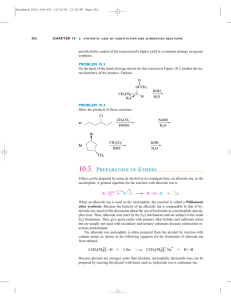
10.3 PREPARATION OF ETHERS
... ether synthesis. Because the basicity of an alkoxide ion is comparable to that of hydroxide ion, much of the discussion about the use of hydroxide as a nucleophile also applies here. Thus, alkoxide ions react by the SN2 mechanism and are subject to the usual SN2 limitations. They give good yields wi ...
... ether synthesis. Because the basicity of an alkoxide ion is comparable to that of hydroxide ion, much of the discussion about the use of hydroxide as a nucleophile also applies here. Thus, alkoxide ions react by the SN2 mechanism and are subject to the usual SN2 limitations. They give good yields wi ...
Quiz 2 - MSU Chemistry
... 2. 2-butanol shows the base peak (highest intensity) in its mass spectrum at m/z = 45. Draw the molecular ion of 2-butanol (M ) and the fragmentation mechanism that leads to this peak. Use these molecular masses in your calculations: C = 12; O = 16; H = 1. ...
... 2. 2-butanol shows the base peak (highest intensity) in its mass spectrum at m/z = 45. Draw the molecular ion of 2-butanol (M ) and the fragmentation mechanism that leads to this peak. Use these molecular masses in your calculations: C = 12; O = 16; H = 1. ...
iupac nomenclature of organic chemistry
... Cycloalkanes and aromatic compounds can be treated as the main parent chain of the compound, in which case the position of substituents are numbered around the ring structure. For example, the three isomers of xylene CH3C6H4CH3, commonly the ortho-, meta-, and para- forms, are 1,2-dimethylbenzene, 1 ...
... Cycloalkanes and aromatic compounds can be treated as the main parent chain of the compound, in which case the position of substituents are numbered around the ring structure. For example, the three isomers of xylene CH3C6H4CH3, commonly the ortho-, meta-, and para- forms, are 1,2-dimethylbenzene, 1 ...
Chapter 24. Amines
... chiral (in principle but not in practice) : the lone pair of electrons is the fourth substituent Most amines that have 3 different substituents on N cannot be resolved because the molecules interconvert by pyramidal inversion ...
... chiral (in principle but not in practice) : the lone pair of electrons is the fourth substituent Most amines that have 3 different substituents on N cannot be resolved because the molecules interconvert by pyramidal inversion ...
Microsoft Word
... aldehydes with nitroalkane in moderate to excellent yields using nanocrystalline magnesium oxide as a reusable catalyst was developed for the first time. The nitro group of the niroaldol reaction products can undergo the Nef reaction, reduction to amino group, or nucleophilic displacement. The resul ...
... aldehydes with nitroalkane in moderate to excellent yields using nanocrystalline magnesium oxide as a reusable catalyst was developed for the first time. The nitro group of the niroaldol reaction products can undergo the Nef reaction, reduction to amino group, or nucleophilic displacement. The resul ...
7. Organic halides
... strain, also called Baeyer strain. Because the sp3 orbitals in cyclopropane cannot overlap so effectively as they do in alkanes, the C–C bonds are weaker and the molecule has greater potential energy and higher reactivity. Furthermore, the hydrogens in the planar ring are all eclipsed, that is torsi ...
... strain, also called Baeyer strain. Because the sp3 orbitals in cyclopropane cannot overlap so effectively as they do in alkanes, the C–C bonds are weaker and the molecule has greater potential energy and higher reactivity. Furthermore, the hydrogens in the planar ring are all eclipsed, that is torsi ...
Reactions to know from Chapters 17, 18, 19
... Reactions to know from Chapters 17, 18, and 19 1. Oxidation of aldehydes O ...
... Reactions to know from Chapters 17, 18, and 19 1. Oxidation of aldehydes O ...
Phosphine-Catalyzed Additions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles to
... Key characteristics required for successful nucleophilic catalysis lie in the balance of leaving group ability, nucleophilicity, and ease of ylid formation. Increasing leaving group ability can often be correlated with decreasing basicity. Whereas phosphines are less basic than amines (pKa values: H ...
... Key characteristics required for successful nucleophilic catalysis lie in the balance of leaving group ability, nucleophilicity, and ease of ylid formation. Increasing leaving group ability can often be correlated with decreasing basicity. Whereas phosphines are less basic than amines (pKa values: H ...
SYNOPSIS
... Chapter III: Lithium perchlorate catalyzed reactions of indoles: An expeditious synthesis of Bis (indolyl) methanes. The acid-catalyzed reaction of electron-rich heterocyclic compounds with pdimethylamino benzaldehyde is known as Ehrlich test for -electron excessive heterocycles such as pyroles and ...
... Chapter III: Lithium perchlorate catalyzed reactions of indoles: An expeditious synthesis of Bis (indolyl) methanes. The acid-catalyzed reaction of electron-rich heterocyclic compounds with pdimethylamino benzaldehyde is known as Ehrlich test for -electron excessive heterocycles such as pyroles and ...
Formose reaction controlled by boronic acid - Beilstein
... salts. As can be seen in Figure 2b, the HPLC chart for the formose reaction in the absence of boronic acid compounds contains a number of signals in a wide range of elution time, indicative for the formation of a complicated mixture. On the other hand, the HPLC chart for SPB indicates a broad signal ...
... salts. As can be seen in Figure 2b, the HPLC chart for the formose reaction in the absence of boronic acid compounds contains a number of signals in a wide range of elution time, indicative for the formation of a complicated mixture. On the other hand, the HPLC chart for SPB indicates a broad signal ...
... observed at 1 -1.5ppm in 3a-c attributed to the methyl groups of dimedone and that one of isopropanol. 13CNMR of 3a-c showed a characteristic peak at δc 198ppm for carbonyl group and 155-157ppm for aromatic substituent. The chemical shift of C=C in pyridyl ring was appeared clearly as two peaks at 1 ...
Exp 4_Properties of Alcohols
... ion from hydrochloric acid (HCl), forming an alkyl chloride, as shown in the following equation. Zinc chloride (ZnCl2) is a catalyst for this reaction, which is called the Lucas test. The resultant alkyl chloride is insoluble in water and separates from the Lucas reagent (ZnCl2 in concentrated HCl), ...
... ion from hydrochloric acid (HCl), forming an alkyl chloride, as shown in the following equation. Zinc chloride (ZnCl2) is a catalyst for this reaction, which is called the Lucas test. The resultant alkyl chloride is insoluble in water and separates from the Lucas reagent (ZnCl2 in concentrated HCl), ...
Unit 4 Chemistry of Carbon
... 9. Rarely, the number need not be provided because the size of the carbon chain length limits the available positions of the functional groups. (ie. butanone not 2-butanone) 10. Some compounds have a cyclic structure, for most of those we add in the term cyclo in front of the main chain name and the ...
... 9. Rarely, the number need not be provided because the size of the carbon chain length limits the available positions of the functional groups. (ie. butanone not 2-butanone) 10. Some compounds have a cyclic structure, for most of those we add in the term cyclo in front of the main chain name and the ...
Organometallic Chemistry
... reaction for C-C bond formation, it is often accompanied by competing side reactions such as enolization, reduction, or aldol condensation of the carbonyl substrate. • Organomagnesium compounds can act not only as nucleophiles, but also as bases • It can convert ketones with enolizable hydrogens to ...
... reaction for C-C bond formation, it is often accompanied by competing side reactions such as enolization, reduction, or aldol condensation of the carbonyl substrate. • Organomagnesium compounds can act not only as nucleophiles, but also as bases • It can convert ketones with enolizable hydrogens to ...
Chapter 4 powerpoint
... 2. Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of molecules • With a total of 6 electrons, a carbon atom has 2 in the first shell and 4 in the second shell. • Carbon has little tendency to form ionic bonds by loosing or gaining 4 electrons. • Instead, carbon usually completes its valence sh ...
... 2. Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of molecules • With a total of 6 electrons, a carbon atom has 2 in the first shell and 4 in the second shell. • Carbon has little tendency to form ionic bonds by loosing or gaining 4 electrons. • Instead, carbon usually completes its valence sh ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.