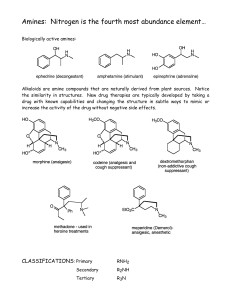
Amines: Nitrogen is the fourth most abundance element…
... amine group becomes a substituent (prefix) and is named as an “amino” group. ...
... amine group becomes a substituent (prefix) and is named as an “amino” group. ...
106KB - NZQA
... Process 1: Fractional distillation Process 2: Cracking Process 3: Polymerisation ...
... Process 1: Fractional distillation Process 2: Cracking Process 3: Polymerisation ...
Ch 6 Lecture 2
... LG Ability = how easy the LG can be replaced by a Nu What makes a good leaving group? 1) Stabilize negative charge: I- > Br- > Cl- > F2) Polarizability (size/charge) of I- allows it to readily handle (-) 3) F is a very poor leaving group: (high bond strength, low polarizability) 4) Other good leavin ...
... LG Ability = how easy the LG can be replaced by a Nu What makes a good leaving group? 1) Stabilize negative charge: I- > Br- > Cl- > F2) Polarizability (size/charge) of I- allows it to readily handle (-) 3) F is a very poor leaving group: (high bond strength, low polarizability) 4) Other good leavin ...
File
... The net result of this process is substitution of the –OR group of the alcohol for the -OH group of the acid. Hence the reaction is referred to as nucleophilic acylsubstitution. But the reaction is not a direct substitution. Instead, it occurs in two steps: (1) nucleophilic addition, followed by (2 ...
... The net result of this process is substitution of the –OR group of the alcohol for the -OH group of the acid. Hence the reaction is referred to as nucleophilic acylsubstitution. But the reaction is not a direct substitution. Instead, it occurs in two steps: (1) nucleophilic addition, followed by (2 ...
Name Reactions in Heterocyclic Chemistry-II
... Detailed procedures were published for synthesizing 2,4,6-trimethylpyrylium perchlorate,42 tetrafluoroborate,43 triflate,44 and sulfoacetate.45 Being salts, these compounds are insoluble in ether and are therefore easily purified from side-products such as mesityl oxide, so that yields are at least ...
... Detailed procedures were published for synthesizing 2,4,6-trimethylpyrylium perchlorate,42 tetrafluoroborate,43 triflate,44 and sulfoacetate.45 Being salts, these compounds are insoluble in ether and are therefore easily purified from side-products such as mesityl oxide, so that yields are at least ...
Summer Scholar Report
... THF solution was transferred to a beaker containing anhydrous magnesium sulfate and then filtered, the THF was then rotary evaporated off leaving an oil, which was 100% 9 ...
... THF solution was transferred to a beaker containing anhydrous magnesium sulfate and then filtered, the THF was then rotary evaporated off leaving an oil, which was 100% 9 ...
Mock-UP - GEOCITIES.ws
... Carbonyl group to have two strong poles from electronic in π bond, and that to be formed move aside by direction the oxygen atom, that have more electronegative, therefore the carbonyl carbon atom to be formed deficient electron, this property to become Carbonyl carbon is to work on strong the acidi ...
... Carbonyl group to have two strong poles from electronic in π bond, and that to be formed move aside by direction the oxygen atom, that have more electronegative, therefore the carbonyl carbon atom to be formed deficient electron, this property to become Carbonyl carbon is to work on strong the acidi ...
cork institute of technology
... of CO2 and 0.0892 g of H2O formed. Calculate the empirical and molecular formulae of this compound. (8 marks) ...
... of CO2 and 0.0892 g of H2O formed. Calculate the empirical and molecular formulae of this compound. (8 marks) ...
LESSON-3
... highly electronegative oxygen atoms. D. highly electropositive oxygen atoms. E. highly electropositive nitrogen atoms. 39. This functional group is weakly basic because it can accept an H+ ion: A. hydroxyl B. carbonyl C. amino D. phosphate E. sulfhydryl 40. Hydrocarbons are hydrophobic because: A. t ...
... highly electronegative oxygen atoms. D. highly electropositive oxygen atoms. E. highly electropositive nitrogen atoms. 39. This functional group is weakly basic because it can accept an H+ ion: A. hydroxyl B. carbonyl C. amino D. phosphate E. sulfhydryl 40. Hydrocarbons are hydrophobic because: A. t ...
CHM 222: Organic Chemistry III
... molecular formula is given. Then the absorptions in the 1H-NMR are listed as chemical shift (multiplicity, integral). Some compounds also have an important IR peak given. C4H9Cl; 3.35 (doublet, 2), 2.0 (multiplet, 1), 1.0 (doublet, 6). ...
... molecular formula is given. Then the absorptions in the 1H-NMR are listed as chemical shift (multiplicity, integral). Some compounds also have an important IR peak given. C4H9Cl; 3.35 (doublet, 2), 2.0 (multiplet, 1), 1.0 (doublet, 6). ...
Elimination Reactions
... E2 Reactions – Stereochemistry and Regiochemistry For SN2 reactions, you saw that the nucleophile had to attack from the backside of the electrophilic site. This restriction is still valid for E2 reactions. In E2, since we are concerned with bases and not nucleophiles, this restriction reads „the p ...
... E2 Reactions – Stereochemistry and Regiochemistry For SN2 reactions, you saw that the nucleophile had to attack from the backside of the electrophilic site. This restriction is still valid for E2 reactions. In E2, since we are concerned with bases and not nucleophiles, this restriction reads „the p ...
Elimination Reactions
... E2 Reactions – Stereochemistry and Regiochemistry For SN2 reactions, you saw that the nucleophile had to attack from the backside of the electrophilic site. This restriction is still valid for E2 reactions. In E2, since we are concerned with bases and not nucleophiles, this restriction reads ‘the p ...
... E2 Reactions – Stereochemistry and Regiochemistry For SN2 reactions, you saw that the nucleophile had to attack from the backside of the electrophilic site. This restriction is still valid for E2 reactions. In E2, since we are concerned with bases and not nucleophiles, this restriction reads ‘the p ...
Slides from Chapters 1,2
... for (HCONH)!. The true structure is a composite of both resonance forms and is called a resonance hybrid. • The hybrid shows characteristics of both structures. • Resonance allows certain electron pairs to be delocalized over several atoms, and this delocalization adds stability. • A molecule wit ...
... for (HCONH)!. The true structure is a composite of both resonance forms and is called a resonance hybrid. • The hybrid shows characteristics of both structures. • Resonance allows certain electron pairs to be delocalized over several atoms, and this delocalization adds stability. • A molecule wit ...
1P18 IR spectroscopic investigation on intermolecular proton
... acidities of cationic CH bonds have also been clarified for alkanes, alcohols, ethers, and amines, although their neutral CH bonds are normally aprotic.[1] These findings raise the question which is more acidic in cationic states, OH (and NH) or CH. To compare acidities of cationic CH and OH bonds, ...
... acidities of cationic CH bonds have also been clarified for alkanes, alcohols, ethers, and amines, although their neutral CH bonds are normally aprotic.[1] These findings raise the question which is more acidic in cationic states, OH (and NH) or CH. To compare acidities of cationic CH and OH bonds, ...
Peer-reviewed Article PDF
... Dendrimers are produced in an iterative sequence of reaction steps, in which each additional interaction leads to a higher generation material. The first example of an iterative synthetic procedure toward well-defined branched structures has been reported by Vogtle, [1] who named this procedure a “c ...
... Dendrimers are produced in an iterative sequence of reaction steps, in which each additional interaction leads to a higher generation material. The first example of an iterative synthetic procedure toward well-defined branched structures has been reported by Vogtle, [1] who named this procedure a “c ...
Learning materials
... 3. SN1 reaction 4. SN2 reaction 5. E1, E2 reactions 6. Applications of alkyl halides 7. Acidity and basicity of alcohols 8. Dehydration of alcohols 9. Synthesis of ethers 10. Solvents in organic chemistry ...
... 3. SN1 reaction 4. SN2 reaction 5. E1, E2 reactions 6. Applications of alkyl halides 7. Acidity and basicity of alcohols 8. Dehydration of alcohols 9. Synthesis of ethers 10. Solvents in organic chemistry ...
Hydrocarbon Derivatives:
... • contain only carbon & hydrogen • carbon can also form strong covalent bonds with other elements such as: O, N, F, Cl, Br, I, S, & P ...
... • contain only carbon & hydrogen • carbon can also form strong covalent bonds with other elements such as: O, N, F, Cl, Br, I, S, & P ...
Ir-catalysed formation of C− F bonds. From allylic alcohols to α
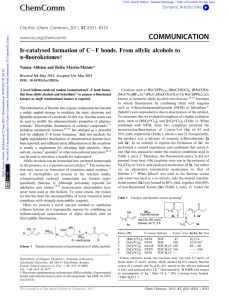
... (IIb).15b,19 In step (iii), the C–F bond is formed upon reaction with the electrophilic SelectF. Step (iii) can occur directly from II, or via formation of the free enol.y In conclusion, we have shown that a-fluorinated ketones can be prepared as single constitutional isomers by combining a tandem ir ...
... (IIb).15b,19 In step (iii), the C–F bond is formed upon reaction with the electrophilic SelectF. Step (iii) can occur directly from II, or via formation of the free enol.y In conclusion, we have shown that a-fluorinated ketones can be prepared as single constitutional isomers by combining a tandem ir ...
4888 Journal of the American Chemical Society 1OO:lS 1 July 19
... I) consistently led to a 1:l mixture of 7a and 7b. An 87:13 ratio of 7a to 7b was obtained by partial dehydroiodination of the 1:l mixture with 0.7 equiv of 1,5-diazabicyclo[5.4.O]undecS e n e (DBU). The configurational assignment for 7 was made on the basis of the following considerations: (1) a po ...
... I) consistently led to a 1:l mixture of 7a and 7b. An 87:13 ratio of 7a to 7b was obtained by partial dehydroiodination of the 1:l mixture with 0.7 equiv of 1,5-diazabicyclo[5.4.O]undecS e n e (DBU). The configurational assignment for 7 was made on the basis of the following considerations: (1) a po ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.