Ch. 10 Notes with Answers
... • The carbonyl =O gets replaced by –OH • For formaldehyde, aldehydes, and ketones: the two attachments on the original carbonyl carbon remain attached as spectators • For esters or acid chlorides: the one non-heteroatom attachment on the original carbonyl carbon remain attached as spectators. o The ...
... • The carbonyl =O gets replaced by –OH • For formaldehyde, aldehydes, and ketones: the two attachments on the original carbonyl carbon remain attached as spectators • For esters or acid chlorides: the one non-heteroatom attachment on the original carbonyl carbon remain attached as spectators. o The ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... 1) Same molecular formula as Alcohol: CnH2n+2O 2) No Hydrogen Bonding is possible in R—O—R 3) Boiling Points are much lower than alcohols, more like haloalkanes 4) Water solubility much less than alcohols a) MeOMe and EtOEt have some water solubility b) Larger ethers are insoluble, very much like al ...
... 1) Same molecular formula as Alcohol: CnH2n+2O 2) No Hydrogen Bonding is possible in R—O—R 3) Boiling Points are much lower than alcohols, more like haloalkanes 4) Water solubility much less than alcohols a) MeOMe and EtOEt have some water solubility b) Larger ethers are insoluble, very much like al ...
1 Chapter 21: Organic and Biochemical Molecules
... Note: When the alcohol is functioning as an acid, the hydrogen bonded to the oxygen dissociates. When the alcohol is functioning as a base, a hydrogen bonds to the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen ...
... Note: When the alcohol is functioning as an acid, the hydrogen bonded to the oxygen dissociates. When the alcohol is functioning as a base, a hydrogen bonds to the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen ...
Limitations in Determining Enantiomeric Excess of Alcohols by 31P
... Following the global trend of working with enantiomerically enriched mixtures or pure enantiomers has brought a new problem to our research group, namely, enantiomeric discrimination. Chiral GC and HPLC columns and chiral eluents are not always efficient thus other methods of analysis to assess enan ...
... Following the global trend of working with enantiomerically enriched mixtures or pure enantiomers has brought a new problem to our research group, namely, enantiomeric discrimination. Chiral GC and HPLC columns and chiral eluents are not always efficient thus other methods of analysis to assess enan ...
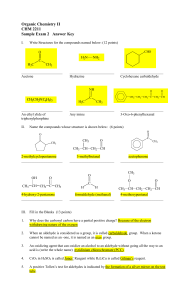
Organic Chemistry II CHM 2211 Sample Exam 2 Answer Key
... When an aldehyde is considered as a group, it is called carbaldehyde group. When a ketone cannot be named as an -one, it is named as an oxo- group. ...
... When an aldehyde is considered as a group, it is called carbaldehyde group. When a ketone cannot be named as an -one, it is named as an oxo- group. ...
Chapter 4 – Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... 1. The hydroxyl group -If you see a structural diagram of a molecule and hanging off one end is –OH, it implies that the oxygen and hydrogen are attached by a covalent bond. Another example would be something like –CH3 which means the three hydrogens are covalently bound to the carbon (there is no o ...
... 1. The hydroxyl group -If you see a structural diagram of a molecule and hanging off one end is –OH, it implies that the oxygen and hydrogen are attached by a covalent bond. Another example would be something like –CH3 which means the three hydrogens are covalently bound to the carbon (there is no o ...
Functional Groups
... • A functional group is an atom or a group of atoms with characteristic chemical and physical properties. It is the reactive part of a molecule. • Organic compounds having only C—C and C—H bonds are called Hydrocarbons. There are four classes of hydrocarbons: alkanes, alkenes, akynes and aromatics. ...
... • A functional group is an atom or a group of atoms with characteristic chemical and physical properties. It is the reactive part of a molecule. • Organic compounds having only C—C and C—H bonds are called Hydrocarbons. There are four classes of hydrocarbons: alkanes, alkenes, akynes and aromatics. ...
Handout V
... A. Common Name In common name, the suffix –amine is given after the names of the alkyl groups bonded to nitrogen. The prefixes di-, tri-, and tetra- are used to describe two, three, or four identical substituents. Aromatic and heterocyclic amines are known by historical names ...
... A. Common Name In common name, the suffix –amine is given after the names of the alkyl groups bonded to nitrogen. The prefixes di-, tri-, and tetra- are used to describe two, three, or four identical substituents. Aromatic and heterocyclic amines are known by historical names ...
3-MO theory(U).pptx
... The electron location in H2 is identical between valence bond theory and molecular orbital theory (due to there only being one bond in H2 and thus the electrons must be located on the two atoms) ...
... The electron location in H2 is identical between valence bond theory and molecular orbital theory (due to there only being one bond in H2 and thus the electrons must be located on the two atoms) ...
Ultimate Analysis - Cheresources.com
... double bonds. The remaining single valence of each carbon holds one hydrogen atom at each corner of the hexagon. The benzene ring is highly symmetrical & is very less reactive than would be expected from the presence of the three unsaturated linkages. If one or more of the hydrogens of benzene are r ...
... double bonds. The remaining single valence of each carbon holds one hydrogen atom at each corner of the hexagon. The benzene ring is highly symmetrical & is very less reactive than would be expected from the presence of the three unsaturated linkages. If one or more of the hydrogens of benzene are r ...
4.9 Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols and Hydrogen Halides
... by positively charged carbon because the s orbital can overlap with the empty 2p orbital of positively charged carbon ...
... by positively charged carbon because the s orbital can overlap with the empty 2p orbital of positively charged carbon ...
23.1 Introduction to Functional Groups
... Organic reactions often proceed more slowly than inorganic reactions because organic reactions commonly involve the breaking of relatively strong covalent bonds. • They often require catalysts. • Many organic reactions are complex, and they usually produce a mixture of products. – The desired produc ...
... Organic reactions often proceed more slowly than inorganic reactions because organic reactions commonly involve the breaking of relatively strong covalent bonds. • They often require catalysts. • Many organic reactions are complex, and they usually produce a mixture of products. – The desired produc ...
Grignard Reagents brochure
... react with a broad range of electrophilic substrates. The reactions with aldehydes, ketones27, esters, acids49 and acid chlorides is one of the most useful reaction in organic chemistry for the formation of C-C-bonds50,51,52. The reaction has a very broad scope, and the Grignard reagent can be aliph ...
... react with a broad range of electrophilic substrates. The reactions with aldehydes, ketones27, esters, acids49 and acid chlorides is one of the most useful reaction in organic chemistry for the formation of C-C-bonds50,51,52. The reaction has a very broad scope, and the Grignard reagent can be aliph ...
Cerium(IV) Ammonium Nitrate as a Catalyst in
... UCM in 1988, under the supervision of Dr. Mónica M. Söllhuber. In August 1988, he joined the group of Professor Steven V. Ley at Imperial College, London, where he worked on the total synthesis of the natural ionophoric antibiotic routiennocin. In September 1989, he returned as a Profesor Titular ...
... UCM in 1988, under the supervision of Dr. Mónica M. Söllhuber. In August 1988, he joined the group of Professor Steven V. Ley at Imperial College, London, where he worked on the total synthesis of the natural ionophoric antibiotic routiennocin. In September 1989, he returned as a Profesor Titular ...
Amines
... none bonding electrons at nitrogen atom to form bond with an acid. • The more easier the lone pair electrons formed bond with the acid, will make the amines a stronger base. • Factors that effect the basicity of the amines: i) substitution by alkyl groups - the presence of alkyl groups (electron-don ...
... none bonding electrons at nitrogen atom to form bond with an acid. • The more easier the lone pair electrons formed bond with the acid, will make the amines a stronger base. • Factors that effect the basicity of the amines: i) substitution by alkyl groups - the presence of alkyl groups (electron-don ...
Catalytic, Enantioselective Alkylations of N,O- and
... addition. The alkylations of N,O-acetals could potentially play an important role especially when the corresponding imines are difficult or impossible to synthesize and store. When X is an electron-withdrawing group, we found that racemic hemiacetals l a - l h (R = H) possessing a flexible range of ...
... addition. The alkylations of N,O-acetals could potentially play an important role especially when the corresponding imines are difficult or impossible to synthesize and store. When X is an electron-withdrawing group, we found that racemic hemiacetals l a - l h (R = H) possessing a flexible range of ...
Alcohols
... Formation of Phenoxide Ion Phenol reacts with hydroxide ions to form phenoxide ions - no redox is necessary. O ...
... Formation of Phenoxide Ion Phenol reacts with hydroxide ions to form phenoxide ions - no redox is necessary. O ...
Polymerization Lab
... 2) Initiation: Using an oxygen atom, in this case, representing a free radical, initiate the polymerization by breaking one of the double bonds and connecting it to the oxygen free radical. a. Remember that a free radical is an atom that has an unpaired electron. So, of the two electrons in the bond ...
... 2) Initiation: Using an oxygen atom, in this case, representing a free radical, initiate the polymerization by breaking one of the double bonds and connecting it to the oxygen free radical. a. Remember that a free radical is an atom that has an unpaired electron. So, of the two electrons in the bond ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.