Ethanol as a solvent
... the carbon the –OH group is attached to joins one other carbon (i.e. on the end of a carbon chain) the carbon the –OH group is attached to joins two other carbons (i.e. in the middle of a carbon chain) the carbon the –OH group is attached to joins three other carbons (i.e. in the middle of a carbon ...
... the carbon the –OH group is attached to joins one other carbon (i.e. on the end of a carbon chain) the carbon the –OH group is attached to joins two other carbons (i.e. in the middle of a carbon chain) the carbon the –OH group is attached to joins three other carbons (i.e. in the middle of a carbon ...
AS Definitions
... Elimination free-radical Nucleophile 2.15 Alkenes Addition polymerisation Alkene Biodegradable Electrophile Geometrical isomers (E-Z isomers) Stereoisomerism 2.16 Alcohols Biofuel carbon neutral ...
... Elimination free-radical Nucleophile 2.15 Alkenes Addition polymerisation Alkene Biodegradable Electrophile Geometrical isomers (E-Z isomers) Stereoisomerism 2.16 Alcohols Biofuel carbon neutral ...
File
... stereoisomerism, in terms of restricted rotation about a double bond and the requirement for two different groups to be attached to each carbon atom of the C=C group, cis-trans isomerism; a special case of E/Z isomerism in which two of the substituent groups are the same; describe a ‘curly arrow’ as ...
... stereoisomerism, in terms of restricted rotation about a double bond and the requirement for two different groups to be attached to each carbon atom of the C=C group, cis-trans isomerism; a special case of E/Z isomerism in which two of the substituent groups are the same; describe a ‘curly arrow’ as ...
11/29 Lecture
... • Nature of Carbon – Carbon Bonds – Carbon is one of the few elements that form fairly stable bonds with itself – Most alkanes (hydrocarbons with only single bonds), while combustible in air (more stable as CO2 + H2O), have negative DGfº – Carbon “likes to” form 4 bonds ([He]2s22p2, but mostly forms ...
... • Nature of Carbon – Carbon Bonds – Carbon is one of the few elements that form fairly stable bonds with itself – Most alkanes (hydrocarbons with only single bonds), while combustible in air (more stable as CO2 + H2O), have negative DGfº – Carbon “likes to” form 4 bonds ([He]2s22p2, but mostly forms ...
Unit 12 pdf notes - Chemistry Notes Lecture
... Ex. 8) Draw 2-bromo-5-chloro-6,6-diethyl-3-methyl-4-tert-butyl nonane ...
... Ex. 8) Draw 2-bromo-5-chloro-6,6-diethyl-3-methyl-4-tert-butyl nonane ...
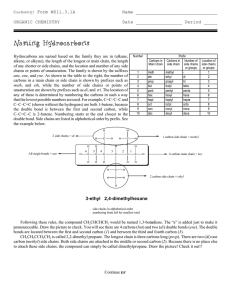
Naming Hydrocarbons
... of any shorter or side chains, and the location and number of any side chains or points of unsaturation. The family is shown by the suffixes ane, ene, and yne. As shown in the table to the right, the number of carbons in a main chain or side chain is shown by prefixes such as meth, and eth, while th ...
... of any shorter or side chains, and the location and number of any side chains or points of unsaturation. The family is shown by the suffixes ane, ene, and yne. As shown in the table to the right, the number of carbons in a main chain or side chain is shown by prefixes such as meth, and eth, while th ...
File - Mrs. Mintz`s Flipped Chemistry Classroom
... When(naming(alkenes(you(must(give(the(location(of(the(double(bond(in(the(name(when( there(are(more(than(3(carbon(atoms(in(the(compound.((You(do(this(by(numbering(the( carbon(atoms(and(stating(which(number(carbon(the(double(bond(is(on.(((You(can( number(the(carbon(atoms(from'left'to'right(or(right'to ...
... When(naming(alkenes(you(must(give(the(location(of(the(double(bond(in(the(name(when( there(are(more(than(3(carbon(atoms(in(the(compound.((You(do(this(by(numbering(the( carbon(atoms(and(stating(which(number(carbon(the(double(bond(is(on.(((You(can( number(the(carbon(atoms(from'left'to'right(or(right'to ...
REDOX REACTIONS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... There are a variety of ways for calculating oxidation numbers for organic chemistry. In single C compounds, we use the same (rigorous) procedure used for inorganic chemistry, i.e., assign ox. #’s to all atoms other than C based on their EN values and calculate the ox. # of C from these with the aid ...
... There are a variety of ways for calculating oxidation numbers for organic chemistry. In single C compounds, we use the same (rigorous) procedure used for inorganic chemistry, i.e., assign ox. #’s to all atoms other than C based on their EN values and calculate the ox. # of C from these with the aid ...
Chapter 11
... disproved the idea of “vital force.” - previously, it was thought that there were two types of matter (based on heating): melting/freezing cooking (required “vital force”) Carbon Atoms •Carbon atoms generally form 4 bonds (think about their electron configuration) •In “organic” compounds these bonds ...
... disproved the idea of “vital force.” - previously, it was thought that there were two types of matter (based on heating): melting/freezing cooking (required “vital force”) Carbon Atoms •Carbon atoms generally form 4 bonds (think about their electron configuration) •In “organic” compounds these bonds ...
CAN YOU …
... use IUPAC rules to name and draw alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes identify the physical properties of alkanes identify a functional group name and draw compounds with functional groups such as esters, ethers, aldehydes, alcohols, ketones, haloalkanes, carboxylic acids, amines and….using IUPAC rules des ...
... use IUPAC rules to name and draw alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes identify the physical properties of alkanes identify a functional group name and draw compounds with functional groups such as esters, ethers, aldehydes, alcohols, ketones, haloalkanes, carboxylic acids, amines and….using IUPAC rules des ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... b) PCC = pyridinium chlorochromate, pyridine, and CH2Cl2 conditions ...
... b) PCC = pyridinium chlorochromate, pyridine, and CH2Cl2 conditions ...
Organic Chemistry
... What does it mean to be organic? To be an organic compound means that you contain carbon ...
... What does it mean to be organic? To be an organic compound means that you contain carbon ...
Chapter 4,5
... sulfur bonded to H; thiols • Phosphate Group phosphate ion; covalently attached by 1 of its O to the C skeleton; ...
... sulfur bonded to H; thiols • Phosphate Group phosphate ion; covalently attached by 1 of its O to the C skeleton; ...
Chapter 11 Intermolecular Forces
... They can take on conformations in which their bond angles are very close to the tetrahedral angle. Smaller rings are quite strained. ...
... They can take on conformations in which their bond angles are very close to the tetrahedral angle. Smaller rings are quite strained. ...
organic chemistry - Assignment Point
... soluble in both nonpolar alkanes and water. – If an alcohol contains two OH groups it is a diol (sometimes called a glycol). – An alcohol with three OH groups is called a triol (sometimes called a glycerol). ...
... soluble in both nonpolar alkanes and water. – If an alcohol contains two OH groups it is a diol (sometimes called a glycol). – An alcohol with three OH groups is called a triol (sometimes called a glycerol). ...
Quarter 3: Post Test Review
... 44. ________ mmHg = __________torr = _________Pascals = __________kilopascals Convert 2983.4 mmHg into torr. ___________________ convert in Pascals ________________ E. Bonding and Electron Configurations 45. Besides metallic, what are the other two types of bonding. _____________ and __________ b. d ...
... 44. ________ mmHg = __________torr = _________Pascals = __________kilopascals Convert 2983.4 mmHg into torr. ___________________ convert in Pascals ________________ E. Bonding and Electron Configurations 45. Besides metallic, what are the other two types of bonding. _____________ and __________ b. d ...
Geoffrey Wilkinson - Nobel Lecture
... are being transformed or synthesised industrially in processes which at some stage involve a transition metal to carbon bond. The nonchemist will probably be most familiar with polyethylene or polypropylene in the form of domestic utensils, packaging materials, children’s toys and so on. These mater ...
... are being transformed or synthesised industrially in processes which at some stage involve a transition metal to carbon bond. The nonchemist will probably be most familiar with polyethylene or polypropylene in the form of domestic utensils, packaging materials, children’s toys and so on. These mater ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Valence Bond Theory Structure
... carbon always has four bonds • In 1874 van't Hoff and Le Bel proposed that the four bonds of carbon have specific spatial directions • van't Hoff suggested that the four atoms surround carbon as corners of a tetrahedron Note that a dashed line indicates a bond is behind the page Note that a wedge in ...
... carbon always has four bonds • In 1874 van't Hoff and Le Bel proposed that the four bonds of carbon have specific spatial directions • van't Hoff suggested that the four atoms surround carbon as corners of a tetrahedron Note that a dashed line indicates a bond is behind the page Note that a wedge in ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.