Lecture 18
... to be reasonable soluble in water so that it can be transported through the blood. Since amines are weak bases, they are often converted to salts with some acid and therefore may oral drugs have amine salts as part of their structure. One reason for their presence is that they confer some water solu ...
... to be reasonable soluble in water so that it can be transported through the blood. Since amines are weak bases, they are often converted to salts with some acid and therefore may oral drugs have amine salts as part of their structure. One reason for their presence is that they confer some water solu ...
Week - Syllabus | Chaminade
... This is the first part of a two-semester course in organic chemistry, where carbon compounds are studied on the basis of their functional groups. Following a review of basic principles in general chemistry, acid-base reactions will be investigated with an emphasis on electron pair transfers and the ...
... This is the first part of a two-semester course in organic chemistry, where carbon compounds are studied on the basis of their functional groups. Following a review of basic principles in general chemistry, acid-base reactions will be investigated with an emphasis on electron pair transfers and the ...
Chem 3.5 Answers #3
... The presence of the OH group on propanol allows hydrogen bonding to occur between propanol molecules. The attractions between propane molecules are weak Van der Waals forces and so the energy needed to separate its molecules from each other is much less giving a lower B. Pt. The OH bond allows the a ...
... The presence of the OH group on propanol allows hydrogen bonding to occur between propanol molecules. The attractions between propane molecules are weak Van der Waals forces and so the energy needed to separate its molecules from each other is much less giving a lower B. Pt. The OH bond allows the a ...
Naming Organic Compounds
... Originally compounds were named based on their source or use Many organic compounds were given common names which are still in use However many ambiguities resulted With the large number of organic compounds, a method for systematically naming them is very important ...
... Originally compounds were named based on their source or use Many organic compounds were given common names which are still in use However many ambiguities resulted With the large number of organic compounds, a method for systematically naming them is very important ...
KEY - Practice Qs
... bonds with other carbon atoms (2) the carbon atom readily forms ionic bonds with other carbon atoms (3) the carbon atom readily combines with oxygen (4) the carbon atom readily dissolves in water 5. Atoms of which element can bond to each other to form chains, rings, and networks? (1) carbon (3) hyd ...
... bonds with other carbon atoms (2) the carbon atom readily forms ionic bonds with other carbon atoms (3) the carbon atom readily combines with oxygen (4) the carbon atom readily dissolves in water 5. Atoms of which element can bond to each other to form chains, rings, and networks? (1) carbon (3) hyd ...
11.1 Organic Chemistry
... • In alkenes with groups other than hydrogen, two different molecules are possible with the same formulas. Trans isomers have the groups diagonally opposite while cis isomers have the groups on the same side of a molecular axis. ...
... • In alkenes with groups other than hydrogen, two different molecules are possible with the same formulas. Trans isomers have the groups diagonally opposite while cis isomers have the groups on the same side of a molecular axis. ...
organic chemistry - Madison County Schools
... A group of atoms that give characteristics and properties to organic compounds. These functional groups may be aldehydes, alcohols, ethers, ketones, amino acids, amides, and others. We will study the alcohols because of their wide use in combustion reactions. ...
... A group of atoms that give characteristics and properties to organic compounds. These functional groups may be aldehydes, alcohols, ethers, ketones, amino acids, amides, and others. We will study the alcohols because of their wide use in combustion reactions. ...
A New Method for Halodecarboxylation of Acids Using Lead(IV
... to a solution of the acid and lead(1V) acetate in benzene. The mixture is swept with nitrogen and heated to 80" with stirring. With LiCl and CaC12, though initially heterogeneous, the reaction is complete within a few minutes. The very insoluble KC1 and NaCl require longer heating. Acetonitrile and ...
... to a solution of the acid and lead(1V) acetate in benzene. The mixture is swept with nitrogen and heated to 80" with stirring. With LiCl and CaC12, though initially heterogeneous, the reaction is complete within a few minutes. The very insoluble KC1 and NaCl require longer heating. Acetonitrile and ...
Microsoft Word - Final Exam Study Guide
... substitution reactions, SN1 mechanism, SN2 mechanism, alkene classifications, alkene stability, elimination reactions, Zaitsev’s rule, E1 mechanism, E2 mechanism, antiperiplanar, comparing substitution and elimination mechanisms, synthesis of ethers, alcohols, and epoxides, dehydration of alcohols, ...
... substitution reactions, SN1 mechanism, SN2 mechanism, alkene classifications, alkene stability, elimination reactions, Zaitsev’s rule, E1 mechanism, E2 mechanism, antiperiplanar, comparing substitution and elimination mechanisms, synthesis of ethers, alcohols, and epoxides, dehydration of alcohols, ...
Group G
... This article discusses how many people take the use of over the counter (OTC) drugs too lightly. These drugs in high doses or with frequent use can carry certain harmful effects on the body. One example cited is the use of the chemical phenylpropanolamine (PPA) in many OTC drugs. Recently a study at ...
... This article discusses how many people take the use of over the counter (OTC) drugs too lightly. These drugs in high doses or with frequent use can carry certain harmful effects on the body. One example cited is the use of the chemical phenylpropanolamine (PPA) in many OTC drugs. Recently a study at ...
Mr. Kent`s Organic Chemistry Unit Notes B. ______ will not only
... A. HYDROCARBONS 1. Contain only ____________ and _____________ atoms. 2. Homologous Series (see table ____)- each sample of a homologous series differs by the previous by ___ carbon and _____hydrogen atoms 3. Boiling Points- As the number of carbon atoms increases the boiling points ___________ due ...
... A. HYDROCARBONS 1. Contain only ____________ and _____________ atoms. 2. Homologous Series (see table ____)- each sample of a homologous series differs by the previous by ___ carbon and _____hydrogen atoms 3. Boiling Points- As the number of carbon atoms increases the boiling points ___________ due ...
Inorganic Reaction Mechanisms at the Molecular Level Oxford
... strongest “oxidants” should most efficiently catalyze “oxidation” reactions. However, this reasoning only holds if the rate determining steps in the reaction mechanisms involve reactions, such as hydrogen atom abstraction or outer-sphere electron transfer reactions and others that correlate with red ...
... strongest “oxidants” should most efficiently catalyze “oxidation” reactions. However, this reasoning only holds if the rate determining steps in the reaction mechanisms involve reactions, such as hydrogen atom abstraction or outer-sphere electron transfer reactions and others that correlate with red ...
Notes
... Definition/Functional group: contain at least one benzene ring, often with other groups added (“substituted” for hydrogen). Benzene exists as a resonance structure. It is also a carcinogen. Prefix: Benz Examples Benzene Benzaldehyde ...
... Definition/Functional group: contain at least one benzene ring, often with other groups added (“substituted” for hydrogen). Benzene exists as a resonance structure. It is also a carcinogen. Prefix: Benz Examples Benzene Benzaldehyde ...
Physical Organic Chemistry
... without substituted with another atom or group. The elimination of HX molecule from alkyl derivatives. While X is a halogen or ester… etc. the hydrogen atom on adjacent carbon with X Elimination reactions and nucleophilic substitution are similar in cases of affecting factors. Hence it’s a com ...
... without substituted with another atom or group. The elimination of HX molecule from alkyl derivatives. While X is a halogen or ester… etc. the hydrogen atom on adjacent carbon with X Elimination reactions and nucleophilic substitution are similar in cases of affecting factors. Hence it’s a com ...
+ H 2 O(g)
... Info on Decomp Reactions • Energy is usually need to make these reactions happen • Often hard to predict products unless the substance breaks into its ...
... Info on Decomp Reactions • Energy is usually need to make these reactions happen • Often hard to predict products unless the substance breaks into its ...
Alcohols
... If the carbon containing the hydroxyl group bonds to one other carbon atom it is primary; two other carbon atoms – secondary and three carbon atoms – tertiary. Properties of Alcohols The hydroxyl group in an alcohol is polar therefore hydrogen bonding occurs. “Like dissolves Like” therefore th ...
... If the carbon containing the hydroxyl group bonds to one other carbon atom it is primary; two other carbon atoms – secondary and three carbon atoms – tertiary. Properties of Alcohols The hydroxyl group in an alcohol is polar therefore hydrogen bonding occurs. “Like dissolves Like” therefore th ...
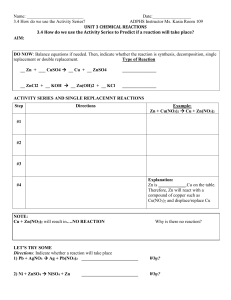
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... F2 + 2NaCl Cl2 + 2NaF 1. What is the most reactive nonmetal according to the table?___________________________________ 2. ______________________will react with anything below it 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction ...
... F2 + 2NaCl Cl2 + 2NaF 1. What is the most reactive nonmetal according to the table?___________________________________ 2. ______________________will react with anything below it 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction ...
Regular Evening08-11-2013Tuition
... Topics Solutions Electrochemistry Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Section A ...
... Topics Solutions Electrochemistry Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Section A ...
Lecture 15a - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... • Acetylene, carbon monoxide and alcohols are reacted in the presence of a catalyst like Ni(CO)4, HCo(CO)4 or Fe(CO)5 to yield acrylic acid esters • If water is used instead of alcohols, the carboxylic acid is obtained (i.e., acrylic acid) • The BHC process to synthesize of ibuprofen uses a palladiu ...
... • Acetylene, carbon monoxide and alcohols are reacted in the presence of a catalyst like Ni(CO)4, HCo(CO)4 or Fe(CO)5 to yield acrylic acid esters • If water is used instead of alcohols, the carboxylic acid is obtained (i.e., acrylic acid) • The BHC process to synthesize of ibuprofen uses a palladiu ...
Alcohols - Miller, Jonathan
... Primary alcohols can be oxidised to either aldehydes or carboxylic acids depending on the reaction conditions. In the case of the formation of carboxylic acids, the alcohol is first oxidised to an aldehyde which is then oxidised further to the acid. Note that the orange chromate(VI) is reduced to gr ...
... Primary alcohols can be oxidised to either aldehydes or carboxylic acids depending on the reaction conditions. In the case of the formation of carboxylic acids, the alcohol is first oxidised to an aldehyde which is then oxidised further to the acid. Note that the orange chromate(VI) is reduced to gr ...
Answers
... forced back to the left? (Hint: What is the byproduct of the reaction?) This equilibrium is possible through the addition of acid to the electrophile, making it a better electrophile. This means it does not need as strong of a nucleophile to react. The reaction could be forced back to the left is wa ...
... forced back to the left? (Hint: What is the byproduct of the reaction?) This equilibrium is possible through the addition of acid to the electrophile, making it a better electrophile. This means it does not need as strong of a nucleophile to react. The reaction could be forced back to the left is wa ...
Chapter 26 Functional Groups and Organic Reactions
... –1st: alkyl attached to single bonded oxygen from alcohol –2nd: take the acid name, remove the -ic acid, add -ate example on top of page 791 ...
... –1st: alkyl attached to single bonded oxygen from alcohol –2nd: take the acid name, remove the -ic acid, add -ate example on top of page 791 ...
UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS
... or haloalkanes (alkyl halides). 1. By the dehydration of alcohols Alkenes are obtained by the dehydration of alcohols. The dehydration of alcohols can be affected by two common methods. - By passing the vapors of an alcohol over heated alumina. - By heating an alcohol with concentrated mineral acid, ...
... or haloalkanes (alkyl halides). 1. By the dehydration of alcohols Alkenes are obtained by the dehydration of alcohols. The dehydration of alcohols can be affected by two common methods. - By passing the vapors of an alcohol over heated alumina. - By heating an alcohol with concentrated mineral acid, ...
DEHYDRATION - ALKENE TEST EXERCISES
... 4. Why is the formation of substitution products involving displacement of water by attack of bisulfate or of dihydrogen phosphate upon a protonated alcohol not a reaction of concern in these procedures ? ...
... 4. Why is the formation of substitution products involving displacement of water by attack of bisulfate or of dihydrogen phosphate upon a protonated alcohol not a reaction of concern in these procedures ? ...
Organic Chemistry:
... Carbon has 4 unpaired electrons. It can form 4 covalent bonds. Note: C can form only 3 bonds to any other single C atom. ...
... Carbon has 4 unpaired electrons. It can form 4 covalent bonds. Note: C can form only 3 bonds to any other single C atom. ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.