Telescope Consisting of Two Converging Lenses
... The last refracting telescope that could be called ‘the largest optical telescope in the world’ was one with an objective lens of diameter 0.90 m. It was superseded in 1889 by a reflecting telescope with an objective mirror of diameter 1.52 m. (a) ...
... The last refracting telescope that could be called ‘the largest optical telescope in the world’ was one with an objective lens of diameter 0.90 m. It was superseded in 1889 by a reflecting telescope with an objective mirror of diameter 1.52 m. (a) ...
View - Rutgers Physics
... 13. Light of wavelength 520 nm passes through a double slit, yielding the interference pattern of intensity I versus deflection angle θ shown. What is the separation, d, between the slits? a) ...
... 13. Light of wavelength 520 nm passes through a double slit, yielding the interference pattern of intensity I versus deflection angle θ shown. What is the separation, d, between the slits? a) ...
Galileo, Brahe, and Kepler - Pennsylvania State University
... resolution than any previous IR telescope. It will focus on the first stars and galaxies, as well as planets around other stars. ...
... resolution than any previous IR telescope. It will focus on the first stars and galaxies, as well as planets around other stars. ...
Paper Title - Mees Solar Observatory
... The past few decades have witnessed several abortive attempts to field a new, large aperture solar facility. Projects such as LEST and CLEAR have come and gone and the McMath and Dunn Solar Telescope at the National Solar Observatory remain among the largest solar apertures available even though the ...
... The past few decades have witnessed several abortive attempts to field a new, large aperture solar facility. Projects such as LEST and CLEAR have come and gone and the McMath and Dunn Solar Telescope at the National Solar Observatory remain among the largest solar apertures available even though the ...
How Technology is Used to Observe Objects in Outer Space
... A radio telescope collects radio waves instead of light. ...
... A radio telescope collects radio waves instead of light. ...
Lecture Outline: Chapter 5: Telescopes
... This will be proportional to the area of the collector, so ∝ D2 where D is the diameter of the telescope. Read text on largest telescopes, future designs, etc. How much fainter a star can you see with a 6 meter telescope than a 2 meter telescope? Angular resolution You must get used to angular measu ...
... This will be proportional to the area of the collector, so ∝ D2 where D is the diameter of the telescope. Read text on largest telescopes, future designs, etc. How much fainter a star can you see with a 6 meter telescope than a 2 meter telescope? Angular resolution You must get used to angular measu ...
Telescope Lab - Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
... Taking an image. Explain to students that they will control the robotic telescope remotely. They will select the target star and several observing times. At night, the telescope will automatically point to ...
... Taking an image. Explain to students that they will control the robotic telescope remotely. They will select the target star and several observing times. At night, the telescope will automatically point to ...
Omegon MightyMak 90
... The telescope tube employs a Maksutov-Cassegrain design for exquisite views of Solar System targets while the ringed giant stole the show at magnitude +0.8. While the view of Saturn was small in the field of view, the planet’s majestic rings blew us away. Although conditions weren’t favourable enoug ...
... The telescope tube employs a Maksutov-Cassegrain design for exquisite views of Solar System targets while the ringed giant stole the show at magnitude +0.8. While the view of Saturn was small in the field of view, the planet’s majestic rings blew us away. Although conditions weren’t favourable enoug ...
Galileo Galilei - cloudfront.net
... 1. What could Galileo conclude after his observations of Jupiter’s moons? 2. What was Galileo able to propose for testing (hypothesis) after observing the phases of the planet Venus? 3. Ultimately, what could Galileo conclude from all of his telescope observations? ...
... 1. What could Galileo conclude after his observations of Jupiter’s moons? 2. What was Galileo able to propose for testing (hypothesis) after observing the phases of the planet Venus? 3. Ultimately, what could Galileo conclude from all of his telescope observations? ...
2011Aug26_SVP_forPub..
... bird watching from the bottom of a swimming pool." -Remington P. S. Stone ...
... bird watching from the bottom of a swimming pool." -Remington P. S. Stone ...
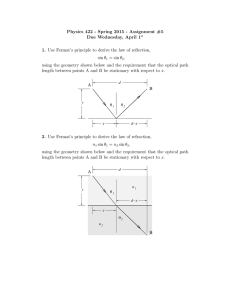
Physics 422 - Spring 2015 - Assignment #5
... 3. (a) Calculate the distance to the object focal point, fo , and the image focal point fi for a single spherical concave refracting surface with radius of curvature R = −10 cm, made of a material with index of refraction n2 = 1.5, and with air (n1 = 1) on the object side. (b) Calculate fo and fi f ...
... 3. (a) Calculate the distance to the object focal point, fo , and the image focal point fi for a single spherical concave refracting surface with radius of curvature R = −10 cm, made of a material with index of refraction n2 = 1.5, and with air (n1 = 1) on the object side. (b) Calculate fo and fi f ...
Unit 5 Review Key - Grande Cache Community High School
... This is a method used to find distance far away objects are using 2 different reference points. (aka parallax technique) When something’s image is distorted due to the angle of observation. This is a telescope that uses radio waves instead of visible light to obtain images of distant celestial objec ...
... This is a method used to find distance far away objects are using 2 different reference points. (aka parallax technique) When something’s image is distorted due to the angle of observation. This is a telescope that uses radio waves instead of visible light to obtain images of distant celestial objec ...
Large telescopes and why we need them Transcript
... Whilst many small amateur telescopes still use this design, it becomes less effective with progressively larger telescopes. The eyepiece is located at the far end of the tube from the objective mirror, making access to the image increasingly inconvenient as the tube gets longer and further from the ...
... Whilst many small amateur telescopes still use this design, it becomes less effective with progressively larger telescopes. The eyepiece is located at the far end of the tube from the objective mirror, making access to the image increasingly inconvenient as the tube gets longer and further from the ...
Seeing stars in a big way
... McCray has relied on written documentation and interviews with the key players in the Gemini programme to tell his story. The ...
... McCray has relied on written documentation and interviews with the key players in the Gemini programme to tell his story. The ...
Chapter 5: Telescopes - University of Texas Astronomy Home Page
... Radio waves can get into the atmosphere without being blocked. But a problem is that their wavelengths are so large that their diffraction limit on resolution is also very large. If radio telescopes were the size of optical telescopes, the radio sky would look like one big blur. ...
... Radio waves can get into the atmosphere without being blocked. But a problem is that their wavelengths are so large that their diffraction limit on resolution is also very large. If radio telescopes were the size of optical telescopes, the radio sky would look like one big blur. ...
Optics student outline
... a. Describe how three incident rays refract through concave lenses. Include the following incident rays: (a) traveling parallel to the principal axis (b) traveling through the optical centre (c) traveling through the focus b. Construct ray diagrams to describe the image properties (SPOT) in a double ...
... a. Describe how three incident rays refract through concave lenses. Include the following incident rays: (a) traveling parallel to the principal axis (b) traveling through the optical centre (c) traveling through the focus b. Construct ray diagrams to describe the image properties (SPOT) in a double ...
The Industrial Revolution in Astronomy
... • Nathan Hill • PPARC Industry Coordinator These short talks will be followed by a drinks reception and buffet. Professor Longair's Plenary will begin at 6.30 p.m. and last approximately 45mins. There will then be an opportunity for attendees to tour the SPIE Industry exhibition free of charge. ...
... • Nathan Hill • PPARC Industry Coordinator These short talks will be followed by a drinks reception and buffet. Professor Longair's Plenary will begin at 6.30 p.m. and last approximately 45mins. There will then be an opportunity for attendees to tour the SPIE Industry exhibition free of charge. ...
Wide field telescope using spherical mirrors
... the corrector plate and because of the required length. Transmissive (glass) correctors suffer from chromatic effects and limitations from self-weight deflection. Reflective designs can be scaled up, but the large reflective corrector is extremely difficult to manufacture. Currently, the LAMOST proj ...
... the corrector plate and because of the required length. Transmissive (glass) correctors suffer from chromatic effects and limitations from self-weight deflection. Reflective designs can be scaled up, but the large reflective corrector is extremely difficult to manufacture. Currently, the LAMOST proj ...
Design Considerations for Large Detector Arrays on Submillimeter
... relative sideband gain, the distinction between telescope efficiency and aperture efficiency, digitization and data processing corrections: these introduce factors of order unity which have been considered in Table 1 but which can be neglected in the present plausibility argument. We assume that the ...
... relative sideband gain, the distinction between telescope efficiency and aperture efficiency, digitization and data processing corrections: these introduce factors of order unity which have been considered in Table 1 but which can be neglected in the present plausibility argument. We assume that the ...
Curved mirrors - schoolphysics
... When they bend inwards they are called CONCAVE MIRRORS and when they bend outwards they are called CONVEX MIRRORS. Describe how your face appears in each type of mirror. Experiment Two Use the two large curved plastic mirrors which should be mounted vertically in the lab. Walk towards each mirror an ...
... When they bend inwards they are called CONCAVE MIRRORS and when they bend outwards they are called CONVEX MIRRORS. Describe how your face appears in each type of mirror. Experiment Two Use the two large curved plastic mirrors which should be mounted vertically in the lab. Walk towards each mirror an ...
Chapter 3 - AstroStop
... Orion as Seen in Visible, Ultraviolet, and Infrared Wavelengths (a) This is an ordinary optical photograph of the constellation Orion. (b) This is an ultraviolet image of Orion obtained during a brief rocket flight on December 5, 1975. The 100-s exposure captured wavelengths ranging from 125 to 200 ...
... Orion as Seen in Visible, Ultraviolet, and Infrared Wavelengths (a) This is an ordinary optical photograph of the constellation Orion. (b) This is an ultraviolet image of Orion obtained during a brief rocket flight on December 5, 1975. The 100-s exposure captured wavelengths ranging from 125 to 200 ...
Light and Other Forms of Radiation
... Reflecting Telescope: Concave Mirror focuses light onto the focal plane ...
... Reflecting Telescope: Concave Mirror focuses light onto the focal plane ...
Telescope Lending Program brochure - Hamilton
... It might be best to hold your observation session in a dark area such as a park or atop a hill where a large portion of the night sky is visible. If observing from your back yard, turn off or dim lights to maximize darkness. Use skymaps.com to print an easy-to-use map to help identify planets, stars ...
... It might be best to hold your observation session in a dark area such as a park or atop a hill where a large portion of the night sky is visible. If observing from your back yard, turn off or dim lights to maximize darkness. Use skymaps.com to print an easy-to-use map to help identify planets, stars ...
Reflecting telescope

A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is an optical telescope which uses a single or combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Reflecting telescopes come in many design variations and may employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a ""catoptric"" telescope.