Schlieren Visualization
... In the first part of the experiment you will be dealing with an open flame. Be very careful not to accidentally ignite anything besides the sterno heater. The gas used for the jet during this laboratory will come from a bottle filled with compressed gas. The bottle is portable and located in the Can ...
... In the first part of the experiment you will be dealing with an open flame. Be very careful not to accidentally ignite anything besides the sterno heater. The gas used for the jet during this laboratory will come from a bottle filled with compressed gas. The bottle is portable and located in the Can ...
Stops: Finite nature of lenses affects the energy and... and imaged by optical systems
... reduce IMD by factor of 100, due to the spiraling effect and indexdependent speed of the Core diameter is less than ~10 μm and typically from 2-9 μm. rays. IMD of 2 ns/km is typical here. ...
... reduce IMD by factor of 100, due to the spiraling effect and indexdependent speed of the Core diameter is less than ~10 μm and typically from 2-9 μm. rays. IMD of 2 ns/km is typical here. ...
Restart Review Presentation
... Is this estimate consistent with NOAO’s planned resources over the duration of the GNIRS project? Have the technical issues (AURA report attached for reference) identified by the AURA review committee been addressed adequately to permit continuation of GNIRS? Does NOAO now have in place an app ...
... Is this estimate consistent with NOAO’s planned resources over the duration of the GNIRS project? Have the technical issues (AURA report attached for reference) identified by the AURA review committee been addressed adequately to permit continuation of GNIRS? Does NOAO now have in place an app ...
Atmospheric-Turbulence Compensation Experiments Using
... SWAT demonstrated what we believe to be the first use of a synthetic beacon to compensate a stellar image for atmospheric turbulence. We also performed the first experiments demonstrating atmospheric compensation of a stellar image by using multiple synthetic beacons. One of the major objectives of ...
... SWAT demonstrated what we believe to be the first use of a synthetic beacon to compensate a stellar image for atmospheric turbulence. We also performed the first experiments demonstrating atmospheric compensation of a stellar image by using multiple synthetic beacons. One of the major objectives of ...
solartele
... This elaborate setup was used most notably during the transit of Mercury on 03 May, 1661. Published calculations predicted a transit between 1 May and 11 May. Hevelius planned 11 days of continuous observation, if need be. The third day was partly cloudy, and at 14:00 the sun appeared for just a few ...
... This elaborate setup was used most notably during the transit of Mercury on 03 May, 1661. Published calculations predicted a transit between 1 May and 11 May. Hevelius planned 11 days of continuous observation, if need be. The third day was partly cloudy, and at 14:00 the sun appeared for just a few ...
Document
... Optical consequences of turbulence • Temperature fluctuations in small patches of air cause changes in index of refraction (like many little lenses) • Light rays are refracted many times (by small amounts) • When they reach telescope they are no longer parallel • Hence rays can’t be focused to a po ...
... Optical consequences of turbulence • Temperature fluctuations in small patches of air cause changes in index of refraction (like many little lenses) • Light rays are refracted many times (by small amounts) • When they reach telescope they are no longer parallel • Hence rays can’t be focused to a po ...
P2830syllSp07
... An investigation of naturally occuring optical phenomena, with an emphasis on observational characteristics and causes. Prerequisites: PHYS 1113 or PHYS 1213 or instructor's permission. Course objectives and learning goals: Optics is an interdisciplinary science, ranging from simple lenses to sophis ...
... An investigation of naturally occuring optical phenomena, with an emphasis on observational characteristics and causes. Prerequisites: PHYS 1113 or PHYS 1213 or instructor's permission. Course objectives and learning goals: Optics is an interdisciplinary science, ranging from simple lenses to sophis ...
Subpixel Scatter in Digital Micromirror Devices
... large numerical aperture, it had a very limited depth of field (about 14μm). Due to this constraint, it was very important to obtain the best possible focus of the projected spot in the center of the field of view. To focus the spot onto the mirrors, the mirrors were moved to their flat state. An iris ...
... large numerical aperture, it had a very limited depth of field (about 14μm). Due to this constraint, it was very important to obtain the best possible focus of the projected spot in the center of the field of view. To focus the spot onto the mirrors, the mirrors were moved to their flat state. An iris ...
Light, Mirrors, and Lenses - Jenkins Independent Schools
... produced a wave much like the one in Figure 1A. A wave is a disturbance that carries energy through matter or space. The matter in this case is the water, and the energy originally comes from the impact of the rock. As the ripples spread out, they carry some of that energy. Light is a type of wave t ...
... produced a wave much like the one in Figure 1A. A wave is a disturbance that carries energy through matter or space. The matter in this case is the water, and the energy originally comes from the impact of the rock. As the ripples spread out, they carry some of that energy. Light is a type of wave t ...
Lowell Observer, Winter 2006, Issue 69
... the galaxy center, turbulence that drops to a low level in the outer part of the disk, a distribution in the local gas density with a dispersion that increases with the level of turbulence, a density threshold for self-gravity to overcome Coriolis and pressure forces (the Toomre model), and a local ...
... the galaxy center, turbulence that drops to a low level in the outer part of the disk, a distribution in the local gas density with a dispersion that increases with the level of turbulence, a density threshold for self-gravity to overcome Coriolis and pressure forces (the Toomre model), and a local ...
8 m Club Meeting - Adaptive optics
... Measurement of zodiacal dust around nearby stars using nulling (TPF) ...
... Measurement of zodiacal dust around nearby stars using nulling (TPF) ...
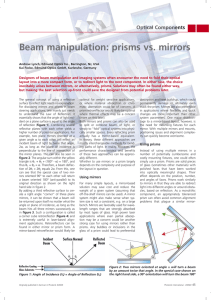
Beam manipulation: prisms vs. mirrors
... Designers of beam manipulation and imaging systems often encounter the need to fold their optical layout into a more compact form, or to redirect light to the next component. In either case, the choice inevitably arises between mirrors, or alternatively, prisms. Solutions may often be found either w ...
... Designers of beam manipulation and imaging systems often encounter the need to fold their optical layout into a more compact form, or to redirect light to the next component. In either case, the choice inevitably arises between mirrors, or alternatively, prisms. Solutions may often be found either w ...
Concave mirrors - Ridgefield School
... – A photographer can choose an object to focus on after the picture has been taken, because the camera effectively focuses on all objects at once. ...
... – A photographer can choose an object to focus on after the picture has been taken, because the camera effectively focuses on all objects at once. ...
The WSO, a world-class observatory for the ultraviolet
... There are several driving principles behind the design of the WSO mission. The plan is to operate a 1-2 meter class telescope in Earth orbit with a spectroscopic and imaging capability specific to the UV wavelength range. The telescope should have a high throughput and the mission optimized for oper ...
... There are several driving principles behind the design of the WSO mission. The plan is to operate a 1-2 meter class telescope in Earth orbit with a spectroscopic and imaging capability specific to the UV wavelength range. The telescope should have a high throughput and the mission optimized for oper ...
External Reflection from Omnidirectional Dielectric Mirror Fibers
... 20. The starting point for the fluid Xe simulations was a tetragonal slab of solid, fcc Xe with a lattice parameter 1.5 times that of Al confined between two walls, 8.06 nm apart, each consisting, in the first instance, of three {111} Al planes. The dimensions of the cell were 8.06 nm, 6.86 nm, and ...
... 20. The starting point for the fluid Xe simulations was a tetragonal slab of solid, fcc Xe with a lattice parameter 1.5 times that of Al confined between two walls, 8.06 nm apart, each consisting, in the first instance, of three {111} Al planes. The dimensions of the cell were 8.06 nm, 6.86 nm, and ...
Nondiffracting Light Beams for Long Ranges
... telescope. For example, outside shape can be linear, where more exact nondiffracting beam is generated although range is reduced [1] . Figure 5(a) is an example of computer simulation, i.e., light beam pattern along the optical axis, where a condition of using a light source of Nd:YAG laser (λ= 0.53 ...
... telescope. For example, outside shape can be linear, where more exact nondiffracting beam is generated although range is reduced [1] . Figure 5(a) is an example of computer simulation, i.e., light beam pattern along the optical axis, where a condition of using a light source of Nd:YAG laser (λ= 0.53 ...
Computer with Internet connection Dr. Dan Reichart and his
... However, PROMPT's control software—called Skynet—is well written and can identify most failures as they occur. If Skynet identifies a failure, either (1) it corrects it itself, or (2) if it cannot, it communicates the failure to Dr. Reichart's group (by both email and text message). Dr. Reichart's g ...
... However, PROMPT's control software—called Skynet—is well written and can identify most failures as they occur. If Skynet identifies a failure, either (1) it corrects it itself, or (2) if it cannot, it communicates the failure to Dr. Reichart's group (by both email and text message). Dr. Reichart's g ...
Optics Image Formation from Mirrors and Lenses
... We are seeing an image of and object that is placed in front of the mirror. The image seems to be the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. The image seems to be the same size as the object. This is not true for all optical devices, but we can work out things about how the ...
... We are seeing an image of and object that is placed in front of the mirror. The image seems to be the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. The image seems to be the same size as the object. This is not true for all optical devices, but we can work out things about how the ...
optical design of an echelle grating based atomic emission
... signal to noise and the simplicity in data acquisition due to the use of a single detector are added advantages. The echelle grating spectrometer is also much more compact than a concave grating polychromator of equivalent resolution. We describe here the optical design and development of an echelle ...
... signal to noise and the simplicity in data acquisition due to the use of a single detector are added advantages. The echelle grating spectrometer is also much more compact than a concave grating polychromator of equivalent resolution. We describe here the optical design and development of an echelle ...
Lab 8 Lenses.pages
... diverging lens. What do you see? Why can you see the image clearly even though it can not be projected onto a surface?! To measure its focal length, we will have to use a converging lens to re-converge the image. We will use the combination lens equation as well as the thin lens equation for this.! ...
... diverging lens. What do you see? Why can you see the image clearly even though it can not be projected onto a surface?! To measure its focal length, we will have to use a converging lens to re-converge the image. We will use the combination lens equation as well as the thin lens equation for this.! ...
Answer Choices
... http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ori on_Nebula,_X_ray_and_Infrared.jpg These objects emit infrared radiation which can be detected with infrared telescopes. This is an infrared image of the Sombrero galaxy. ...
... http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ori on_Nebula,_X_ray_and_Infrared.jpg These objects emit infrared radiation which can be detected with infrared telescopes. This is an infrared image of the Sombrero galaxy. ...
Ultra–large field-of-view two-photon microscopy
... compensation optics to produce a 25-mm diameter beam that fills the back aperture. We utilize a unity-gain telescope to relay the image of the X-scan mirror onto the Y-scan mirror (Fig. 2(a)). This separation of mirrors permits us to separately compensate for scan-induced aberrations along the X- an ...
... compensation optics to produce a 25-mm diameter beam that fills the back aperture. We utilize a unity-gain telescope to relay the image of the X-scan mirror onto the Y-scan mirror (Fig. 2(a)). This separation of mirrors permits us to separately compensate for scan-induced aberrations along the X- an ...
Low cost CCD cameras for amateur astronomy
... striking example is optical counterparts of gamma ray bursts (GRB) discussed in the previous article of this issue [1]. In recent years several small robotic telescopes have been developed [2] to monitor large portion of the sky. Contrary to large telescopes they usually have short focal lengths (10 ...
... striking example is optical counterparts of gamma ray bursts (GRB) discussed in the previous article of this issue [1]. In recent years several small robotic telescopes have been developed [2] to monitor large portion of the sky. Contrary to large telescopes they usually have short focal lengths (10 ...
5 - nptel
... where d is the diffraction angle in the given order and d is the corresponding angular separation of the nearest line. Equation 4 can be used to measure the resolving power of a grating experimentally. Procedure: 1. In the above experiment replace the mercury lamp with the sodium lamp and do the ...
... where d is the diffraction angle in the given order and d is the corresponding angular separation of the nearest line. Equation 4 can be used to measure the resolving power of a grating experimentally. Procedure: 1. In the above experiment replace the mercury lamp with the sodium lamp and do the ...
Reflecting telescope

A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is an optical telescope which uses a single or combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Reflecting telescopes come in many design variations and may employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a ""catoptric"" telescope.