Chromatic and Monochromatic Aberrations
... The tangential axis appears to have greater curvature and hence focuses the light earlier to form a horizontal line focus. The sagittal axis appears to have less curvature and causes the vertical line focus that is further away. The difference in focal distances gives rise to a phenomena called curv ...
... The tangential axis appears to have greater curvature and hence focuses the light earlier to form a horizontal line focus. The sagittal axis appears to have less curvature and causes the vertical line focus that is further away. The difference in focal distances gives rise to a phenomena called curv ...
Polar Winter Differential image motion monitor (PWD)
... want to get the information during winter, we will have to operate the telescope remotely. • fully remote operation Tohoku-DIMM, which was put on the entrance of AIRT40 and was used for seeing measurement in 2010/2011 campaign, is not available because AIRT40 will be used for Infrared observation ne ...
... want to get the information during winter, we will have to operate the telescope remotely. • fully remote operation Tohoku-DIMM, which was put on the entrance of AIRT40 and was used for seeing measurement in 2010/2011 campaign, is not available because AIRT40 will be used for Infrared observation ne ...
The achromatic design of an atmospheric dispersion corrector for
... The linear ADC was originally proposed by Beckers in 1997 [13]. It contains two identical thin prisms (wedges) W1 and W2 with opposite orientation. The amount of longitudinal dispersion produced by the LADC is proportional to their axial separation. One of the wedges can move along the optical axis ...
... The linear ADC was originally proposed by Beckers in 1997 [13]. It contains two identical thin prisms (wedges) W1 and W2 with opposite orientation. The amount of longitudinal dispersion produced by the LADC is proportional to their axial separation. One of the wedges can move along the optical axis ...
File
... thinner in the centre than at the edges. As parallel light rays pass through a concave lens, they are refracted away from the principal axis. The light rays diverge and they will never meet on the other side of the lens. The image formed is always upright, virtual and smaller than the object ...
... thinner in the centre than at the edges. As parallel light rays pass through a concave lens, they are refracted away from the principal axis. The light rays diverge and they will never meet on the other side of the lens. The image formed is always upright, virtual and smaller than the object ...
History of the Telescope
... As it is known, the effect of a telescope is not dependent on its length, but on the aperture of its object glass, so that with equal perfection that telescope, which has double the size of a comparable one, has twice the effect. The difficulties which are to be faced when making larger, equally go ...
... As it is known, the effect of a telescope is not dependent on its length, but on the aperture of its object glass, so that with equal perfection that telescope, which has double the size of a comparable one, has twice the effect. The difficulties which are to be faced when making larger, equally go ...
The Very precise Echelle SpectroPolarimeter on the Araki telescope
... polarization generated by the upstream lenses and/or the other optical elements forward of the modulator often degrades the final polarization accuracy. With these multi-purpose spectropolarimeters mounted on the Cassegrain focus, it is difficult to achieve both high dispersion and wide wavelength c ...
... polarization generated by the upstream lenses and/or the other optical elements forward of the modulator often degrades the final polarization accuracy. With these multi-purpose spectropolarimeters mounted on the Cassegrain focus, it is difficult to achieve both high dispersion and wide wavelength c ...
laser room - CERN Indico
... Compressor and Telescope are at the merging point Flat-top beam focusing profiles Focusing of a 430 mJ flat-top beam 25 m downstream to the middle of the plasma. At the ideal Gaussian waist Wmax = 6.84 J/cm2 and FWHM = 2.35 mm. Flat-top beam focusing has been optimized to obtain the same maximum fl ...
... Compressor and Telescope are at the merging point Flat-top beam focusing profiles Focusing of a 430 mJ flat-top beam 25 m downstream to the middle of the plasma. At the ideal Gaussian waist Wmax = 6.84 J/cm2 and FWHM = 2.35 mm. Flat-top beam focusing has been optimized to obtain the same maximum fl ...
Astronomers Select Top Ten Most Amazing Pictures Taken by
... After correcting an initial problem with the lens, when the Hubble Space Telescope was first launched in 1990, the floating astro-observatory began to relay back to Earth, incredible snapshots of the 'final frontier' it was perusing. Recently, astronauts voted on the top photographs taken by Hubble, ...
... After correcting an initial problem with the lens, when the Hubble Space Telescope was first launched in 1990, the floating astro-observatory began to relay back to Earth, incredible snapshots of the 'final frontier' it was perusing. Recently, astronauts voted on the top photographs taken by Hubble, ...
Relativistic corrections in displacement measuring
... these errors to the subnanometer level. In our ongoing studies of errors that degrade interferometer performance we noticed that so far no attention has been paid to relativistic effects, presumably due to the comparatively small stage velocities involved. However, high sample stage velocities are d ...
... these errors to the subnanometer level. In our ongoing studies of errors that degrade interferometer performance we noticed that so far no attention has been paid to relativistic effects, presumably due to the comparatively small stage velocities involved. However, high sample stage velocities are d ...
- Lorentz Center
... for fine gimbal tip/tilt and focus adjustment Simple box construction with cross-bracing cables to increase structural stiffness Measured 64% of output laser power to sky ...
... for fine gimbal tip/tilt and focus adjustment Simple box construction with cross-bracing cables to increase structural stiffness Measured 64% of output laser power to sky ...
Beyond the Hubble Space Telescope: Early
... closely on the HST and at the time Astronomer Royal for Scotland, carried this idea further when in 1983 he argued that many “exciting projects are being converted from gleams in the eye of the astronomer into feasible astronomical projects, the only limits being those of the imagination of the astr ...
... closely on the HST and at the time Astronomer Royal for Scotland, carried this idea further when in 1983 he argued that many “exciting projects are being converted from gleams in the eye of the astronomer into feasible astronomical projects, the only limits being those of the imagination of the astr ...
SIMG-716 Linear Imaging Mathematics I 01 - Motivation 1
... • Each source point emits spherical waves of e-m radiation — propagates outward from the source at velocity of light. — radiation at all points on one wave surface emitted at same instant of time in a direction perpendicular to wave surface, thus corresponding to the ray in the simpler model. • Rays ...
... • Each source point emits spherical waves of e-m radiation — propagates outward from the source at velocity of light. — radiation at all points on one wave surface emitted at same instant of time in a direction perpendicular to wave surface, thus corresponding to the ray in the simpler model. • Rays ...
as a PDF
... corrected, because the light has followed a different path. If, instead, the phase delay at each point in the atmosphere within some field of view could be reproduced with opposite sign at a conjugate point in a three-dimensional correcting optic, perfect imaging would be restored across the field. ...
... corrected, because the light has followed a different path. If, instead, the phase delay at each point in the atmosphere within some field of view could be reproduced with opposite sign at a conjugate point in a three-dimensional correcting optic, perfect imaging would be restored across the field. ...
Measurement of radiation-pressure
... First we consider the pendular mode with oscillation frequency, ⍀0 = 2 ⫻ 1 Hz, and with M eff ⬅ = 0.125 kg, the reduced mass of the two mirror system. For sufficient detuning ␦, the optical restoring force will be much larger than the mechanical restoring force, i.e., K Ⰷ ⍀20. In this regime ⍀ Ⰶ ...
... First we consider the pendular mode with oscillation frequency, ⍀0 = 2 ⫻ 1 Hz, and with M eff ⬅ = 0.125 kg, the reduced mass of the two mirror system. For sufficient detuning ␦, the optical restoring force will be much larger than the mechanical restoring force, i.e., K Ⰷ ⍀20. In this regime ⍀ Ⰶ ...
Optics Refraction Dispersion
... beam containing red and violet wavelengths is on a slab of quartz at an angle of incidence The index of refraction of quartz is 1.455 at 1 its index of refraction is 1.468 (red light), and ...
... beam containing red and violet wavelengths is on a slab of quartz at an angle of incidence The index of refraction of quartz is 1.455 at 1 its index of refraction is 1.468 (red light), and ...
OSA6Challenges and opportunities - DU Portfolio
... To appreciate the opportunities afforded by the Mt. Evans site, a review of local astronomy history is appropriate. In 1880, Herbert A. Howe arrived from the Cincinnati Observatory as a new professor of mathematics and astronomy at the University of Denver. By the end of that decade, a patron enabl ...
... To appreciate the opportunities afforded by the Mt. Evans site, a review of local astronomy history is appropriate. In 1880, Herbert A. Howe arrived from the Cincinnati Observatory as a new professor of mathematics and astronomy at the University of Denver. By the end of that decade, a patron enabl ...
Learning material
... The section shows a small bundle of rays that enter the eye that originate form the object at B, but are traced back apparently from the image at B’. Since the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence the triangles BQP and B’QP are similar, and since QP is a common side, they are congruent. ...
... The section shows a small bundle of rays that enter the eye that originate form the object at B, but are traced back apparently from the image at B’. Since the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence the triangles BQP and B’QP are similar, and since QP is a common side, they are congruent. ...
Atmospheric Spatial and Temporal Seeing Monitor Using Portable
... One popular seeing monitor is the Differential Image Motion Monitor (DIMM) of Fried 1 where a two-hole aperture mask is placed in front of a slightly defocused telescope that is aimed at a bright star. The relative motion due to seeing of the two resulting images is measured, while common-mode effec ...
... One popular seeing monitor is the Differential Image Motion Monitor (DIMM) of Fried 1 where a two-hole aperture mask is placed in front of a slightly defocused telescope that is aimed at a bright star. The relative motion due to seeing of the two resulting images is measured, while common-mode effec ...
The Effects of Atmospheric Turbulence on Simulated
... light exceeds the light from the planet (Figure 2). Therefore, coronagraphy will be effective only for the closest stars. Nulling interferometry uses destructive interference to cancel light directly from a star. The residual pattern created by a nulling interferometer falls off faster with angle than ...
... light exceeds the light from the planet (Figure 2). Therefore, coronagraphy will be effective only for the closest stars. Nulling interferometry uses destructive interference to cancel light directly from a star. The residual pattern created by a nulling interferometer falls off faster with angle than ...
ray optics and optical instruments
... the image A′B′ (in this case, real) of an object A B formed by a concave mirror. It does not mean that only three rays emanate from the point A. An infinite number of rays emanate from any source, in all directions. Thus, point A′ is image point of A if every ray originating at point A and falling o ...
... the image A′B′ (in this case, real) of an object A B formed by a concave mirror. It does not mean that only three rays emanate from the point A. An infinite number of rays emanate from any source, in all directions. Thus, point A′ is image point of A if every ray originating at point A and falling o ...
Christiaan Huygens and his telescopes
... (also known as an ‘object glass’) with a focal length of 10 Rhineland feet (about 337 cm). The eyepiece he used was a single-lens of 3 Rhineland inches (79 mm) focal length, resulting in a magnification of about 43x. Christiaan himself writes that he used a telescope of 12 Rhineland feet, but at tha ...
... (also known as an ‘object glass’) with a focal length of 10 Rhineland feet (about 337 cm). The eyepiece he used was a single-lens of 3 Rhineland inches (79 mm) focal length, resulting in a magnification of about 43x. Christiaan himself writes that he used a telescope of 12 Rhineland feet, but at tha ...
Michelson interferometer
... A difference in refractive index between the two paths means that the speed of light is different, thus retarding one path and causing a time delay that results in a relative phase difference.4 The reduction of the speed of light in a medium compared to that in vacuum is determined in a complicated ...
... A difference in refractive index between the two paths means that the speed of light is different, thus retarding one path and causing a time delay that results in a relative phase difference.4 The reduction of the speed of light in a medium compared to that in vacuum is determined in a complicated ...
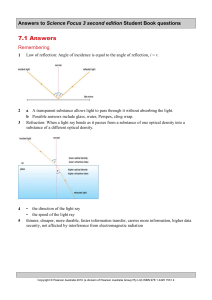
7.1 textbook answers - aiss-science-9
... will never produce an enlarged image of the Moon because the Moon is so far away. It will always be further than one focal length away from the lens. ...
... will never produce an enlarged image of the Moon because the Moon is so far away. It will always be further than one focal length away from the lens. ...
Paper
... the samples up within each interferogram. Second of all, our high spatial resolution on our servo control of the scanning mirror allows us to hold the mirror at zero OPD where we record a simple broadband IR image no different from an IR ...
... the samples up within each interferogram. Second of all, our high spatial resolution on our servo control of the scanning mirror allows us to hold the mirror at zero OPD where we record a simple broadband IR image no different from an IR ...
Reflecting telescope

A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is an optical telescope which uses a single or combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Reflecting telescopes come in many design variations and may employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a ""catoptric"" telescope.