Secrets of the Sun
... The orbits of Earth around the sun and of the moon around Earth, together with the rotation of Earth about an axis between its North and South poles, cause observable patterns. These include day and night; daily changes in the length and direction of shadows; and different positions of the sun, moon ...
... The orbits of Earth around the sun and of the moon around Earth, together with the rotation of Earth about an axis between its North and South poles, cause observable patterns. These include day and night; daily changes in the length and direction of shadows; and different positions of the sun, moon ...
Galaxies Galaxies M81
... This image shows the spiral galaxy NGC 4319 and the quasar Markarian 205. The distance to NGC is 80 million light years, which Mkn 205 is 14 times farther away at a distance of 1 billion light year. The very distant quasar is nearly as bright as the much closer galaxy. The extraordinary brightness o ...
... This image shows the spiral galaxy NGC 4319 and the quasar Markarian 205. The distance to NGC is 80 million light years, which Mkn 205 is 14 times farther away at a distance of 1 billion light year. The very distant quasar is nearly as bright as the much closer galaxy. The extraordinary brightness o ...
Long Ago and Far Away
... Light travels very fast, but not infinitely fast. For example, it takes light from the Sun about 8 minutes to reach Earth. So a telescope is like a time machine – objects appear as they were when the light we see left them, not as they are right now. When we look at the distant universe, we see gala ...
... Light travels very fast, but not infinitely fast. For example, it takes light from the Sun about 8 minutes to reach Earth. So a telescope is like a time machine – objects appear as they were when the light we see left them, not as they are right now. When we look at the distant universe, we see gala ...
Our Place in the Cosmos Elective Course Autumn 2006
... backwards • In the same way, light from a distant star appears to be coming from a slightly different direction due to Earth’s motion through space • Over the course of a year stars appear to trace out a loop - aberration of starlight ...
... backwards • In the same way, light from a distant star appears to be coming from a slightly different direction due to Earth’s motion through space • Over the course of a year stars appear to trace out a loop - aberration of starlight ...
planet_tute
... Most of the stars in this constellation look much the same when viewed through the “telescope” (they still look like dots of light, only brighter). The middle star of the cross, however, the one that moves with respect to the others, ...
... Most of the stars in this constellation look much the same when viewed through the “telescope” (they still look like dots of light, only brighter). The middle star of the cross, however, the one that moves with respect to the others, ...
PSC100 Summary Chapters 1 to Chapter 9
... light from the next nearest star, Alpha Centauri, takes well over 4 years. The farther away an object is from us in space, the longer it takes for the light from that source to reach us. Our current telescopes can pick up light from objects that we believe to be about 10 billion light years away fro ...
... light from the next nearest star, Alpha Centauri, takes well over 4 years. The farther away an object is from us in space, the longer it takes for the light from that source to reach us. Our current telescopes can pick up light from objects that we believe to be about 10 billion light years away fro ...
PPT
... -Hints that there may be z>6 galaxies similar (Egami lens). Mobasher source - z=6.5??? (probably lower-z) -Turn now to larger samples, to provide stellar mass density in first Gyr with Spitzer -- In Stark, Bunker, Ellis et al. (2006) we look at vdrops (z~5) in the GOODS-South -21 have spectroscopic ...
... -Hints that there may be z>6 galaxies similar (Egami lens). Mobasher source - z=6.5??? (probably lower-z) -Turn now to larger samples, to provide stellar mass density in first Gyr with Spitzer -- In Stark, Bunker, Ellis et al. (2006) we look at vdrops (z~5) in the GOODS-South -21 have spectroscopic ...
Gravity-mod
... • Gravity is a force pulling together all matter (which is anything you can physically ...
... • Gravity is a force pulling together all matter (which is anything you can physically ...
S T A R S
... What is the distance from the earth ? There are different ways of measuring interstellar distances. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. In light years, Alpha Centuri is 4.2 light years away. The speed of light is about 3 x 10 to the 8th power m/s or 186 000 miles per second. ...
... What is the distance from the earth ? There are different ways of measuring interstellar distances. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. In light years, Alpha Centuri is 4.2 light years away. The speed of light is about 3 x 10 to the 8th power m/s or 186 000 miles per second. ...
104-cm Sampurnanand Telescope
... We describe below the operation of the 104-cm telescope and the back-end instruments with special reference to the Wrights 2k CCD camera. It should be noted that the 40-inch telescope has been in operation since last 30 years and as a result its operation is becoming critical day by day and requires ...
... We describe below the operation of the 104-cm telescope and the back-end instruments with special reference to the Wrights 2k CCD camera. It should be noted that the 40-inch telescope has been in operation since last 30 years and as a result its operation is becoming critical day by day and requires ...
Scientific Investigation and Reasoning Scientific Investigations
... Spectroscopes are devices that separate electromagnetic radiation into different wavelengths. These devices can be used for many purposes. In astronomy, spectroscopes are used to determine what planets, stars, and other objects are made of. For example, scientists use spectroscopes to separate visib ...
... Spectroscopes are devices that separate electromagnetic radiation into different wavelengths. These devices can be used for many purposes. In astronomy, spectroscopes are used to determine what planets, stars, and other objects are made of. For example, scientists use spectroscopes to separate visib ...
22DistanceMotion
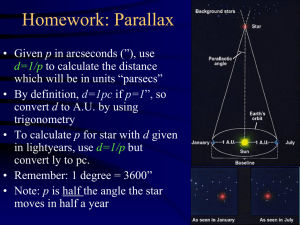
... • If we know intrinsic brightness and measure apparent brightness, we can measure distance • But how do we know intrinsic brightness of astronomical objects? – Conversely, if you know distance and measure apparent brightness you can measure intrinsic brightness • Use parallax for nearby objects to m ...
... • If we know intrinsic brightness and measure apparent brightness, we can measure distance • But how do we know intrinsic brightness of astronomical objects? – Conversely, if you know distance and measure apparent brightness you can measure intrinsic brightness • Use parallax for nearby objects to m ...
Monday, April 15
... – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
... – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
Lecture (Powerpoint)
... the mass of the Sun, or ~80 Jupiter masses) never ``turn on'' Central temperatures never get hot enough for nuclear burning to begin in earnest Nuclear burning is what powers the star through its life Star sits around as a brown dwarf – too big and hot to be a planet, too small and cold to be a real ...
... the mass of the Sun, or ~80 Jupiter masses) never ``turn on'' Central temperatures never get hot enough for nuclear burning to begin in earnest Nuclear burning is what powers the star through its life Star sits around as a brown dwarf – too big and hot to be a planet, too small and cold to be a real ...
29-1
... _______________________________________________________________ 23. How does the mass of the sun compare with the mass of Earth? _______________________________________________________________ 24. What is the most common nuclear reaction inside the sun? ______________________________________________ ...
... _______________________________________________________________ 23. How does the mass of the sun compare with the mass of Earth? _______________________________________________________________ 24. What is the most common nuclear reaction inside the sun? ______________________________________________ ...
2. A giant hand took one of the planets discovered
... 2. A giant hand took one of the planets discovered around other stars and put it in the solar system at the same distance from the sun as from its star. The mass of the planet is approximately that of Jupiter and the orbit is approximately that of Earth. These are the “hot Jupiters”, as big as Jupit ...
... 2. A giant hand took one of the planets discovered around other stars and put it in the solar system at the same distance from the sun as from its star. The mass of the planet is approximately that of Jupiter and the orbit is approximately that of Earth. These are the “hot Jupiters”, as big as Jupit ...
Lecture 2a
... • Kepler figured out correct orbital shape and determined some relationships between the orbits of different planets • A big step was realizing that Earth’s orbit about the Sun also wasn’t a circle – mostly he used relative location of Mars after repeated orbits around the Sun (Mars is close and s ...
... • Kepler figured out correct orbital shape and determined some relationships between the orbits of different planets • A big step was realizing that Earth’s orbit about the Sun also wasn’t a circle – mostly he used relative location of Mars after repeated orbits around the Sun (Mars is close and s ...
1. The diagram shows the concave mirror of a Cassegrain reflecting
... The diagram shows the concave mirror of a Cassegrain reflecting telescope, together with the eyepiece lens. Complete the diagram of the telescope and mark on it the focal point of the concave mirror. Draw a ray diagram for two rays from a star, parallel to the principal axis, passing through the tel ...
... The diagram shows the concave mirror of a Cassegrain reflecting telescope, together with the eyepiece lens. Complete the diagram of the telescope and mark on it the focal point of the concave mirror. Draw a ray diagram for two rays from a star, parallel to the principal axis, passing through the tel ...
Wien`s law - Uplift Education
... • If two stars have the same absolute magnitude but different apparent magnitude they would have the same brightness if they were both at distance of 10 pc from Earth, so we conclude they have the same luminosity, but are at different distances from Earth !!!!!!!!!!!!!! • Every one step in absolute ...
... • If two stars have the same absolute magnitude but different apparent magnitude they would have the same brightness if they were both at distance of 10 pc from Earth, so we conclude they have the same luminosity, but are at different distances from Earth !!!!!!!!!!!!!! • Every one step in absolute ...
newsletter - Thanet Astronomy Group
... direction visible from the side of the Earth that faces away from the Sun, the planets can be observed in the night sky all at the same time. This is exactly what is happening now. The planets that have aligned are Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. These are the five planets that are visible ...
... direction visible from the side of the Earth that faces away from the Sun, the planets can be observed in the night sky all at the same time. This is exactly what is happening now. The planets that have aligned are Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. These are the five planets that are visible ...
Part II: Ideas in Conflict.
... are a very large number of stars – many are invisible to the naked eye. Most stars appear to move in fixed groups (called constellations) with the same basic daily motion as the Sun and Moon, moving from East to West. Stars are seen only at night (although the brightest ones are seen just before ...
... are a very large number of stars – many are invisible to the naked eye. Most stars appear to move in fixed groups (called constellations) with the same basic daily motion as the Sun and Moon, moving from East to West. Stars are seen only at night (although the brightest ones are seen just before ...
GET WORKSHEETS FROM MY ASSIGNMENTS PAGE Mrs
... hottest, dimmest stars? coolest, dimmest stars? brightest, hottest stars? brightest, coolest stars? ...
... hottest, dimmest stars? coolest, dimmest stars? brightest, hottest stars? brightest, coolest stars? ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.