Small Wonders: Taurus
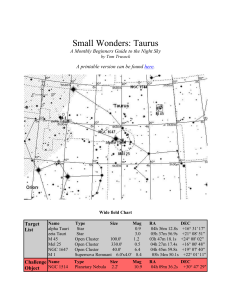
... obviously orange in color - even to the naked eye. Shining at 150 times the suns brightness, it's relative closeness to Earth translates it into the 13th brightest star in the night sky. Aldebaran is thought to have a large planetary companion which masses around 11 Jupiters and orbits at a distance ...
... obviously orange in color - even to the naked eye. Shining at 150 times the suns brightness, it's relative closeness to Earth translates it into the 13th brightest star in the night sky. Aldebaran is thought to have a large planetary companion which masses around 11 Jupiters and orbits at a distance ...
RP 4E1 Earth in the Universe - NC Science Wiki
... By the end of grade 2. Patterns of the motion of the sun, moon, and stars in the sky can be observed, described, and predicted. At night one can see the light coming from many stars with the naked eye, but telescopes make it possible to see many more and to observe them and the moon and planets in ...
... By the end of grade 2. Patterns of the motion of the sun, moon, and stars in the sky can be observed, described, and predicted. At night one can see the light coming from many stars with the naked eye, but telescopes make it possible to see many more and to observe them and the moon and planets in ...
SM_Taurus - Cloudy Nights
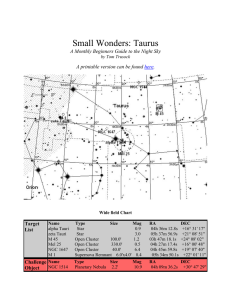
... obviously orange in color - even to the naked eye. Shining at 150 times the suns brightness, it's relative closeness to Earth translates it into the 13th brightest star in the night sky. Aldebaran is thought to have a large planetary companion which masses around 11 Jupiters and orbits at a distance ...
... obviously orange in color - even to the naked eye. Shining at 150 times the suns brightness, it's relative closeness to Earth translates it into the 13th brightest star in the night sky. Aldebaran is thought to have a large planetary companion which masses around 11 Jupiters and orbits at a distance ...
Optics student outline
... a. Provide examples of ideas and theories of light used in the past to explain observed properties. (Pythagoras, Michelson) (132-134) b. Compare the Speed of Light vs. Sound using thunder and lightning as an example. ...
... a. Provide examples of ideas and theories of light used in the past to explain observed properties. (Pythagoras, Michelson) (132-134) b. Compare the Speed of Light vs. Sound using thunder and lightning as an example. ...
A Spectroscopic Study of the RV Tauri Stars TT Oph... Guillermo Hernandez , Donald K. Walter , Jennifer Cash
... TT and UZ Orphiuchus are listed as RV Tauri types in the General Catalog of Variable Stars, although Percy and Mohammed (2004, JAAVSO, 32, 9) question this classification. We have acquired spectra of these objects with the Coude Feed Telescope at KPNO over the past decade. In this study we have phas ...
... TT and UZ Orphiuchus are listed as RV Tauri types in the General Catalog of Variable Stars, although Percy and Mohammed (2004, JAAVSO, 32, 9) question this classification. We have acquired spectra of these objects with the Coude Feed Telescope at KPNO over the past decade. In this study we have phas ...
The magnitude scale, parallax, the parsec, and Cepheid distances
... astronomers use a logarithmic-‐based scale magnitudes – a 'logical' scale would be 1 → 30 – but we actually use a magnitude scale derived from ancient Greek astronomers… ...
... astronomers use a logarithmic-‐based scale magnitudes – a 'logical' scale would be 1 → 30 – but we actually use a magnitude scale derived from ancient Greek astronomers… ...
Astronomy Unit 4 Galaxies
... 37. The distribution of galaxies in the universe is not ___________________, but clusters of galaxies lie within structures called ___________________ which surround empty regions called __________________. 38. Galaxies that are brighter than normal are called __________________________ and emit mos ...
... 37. The distribution of galaxies in the universe is not ___________________, but clusters of galaxies lie within structures called ___________________ which surround empty regions called __________________. 38. Galaxies that are brighter than normal are called __________________________ and emit mos ...
Our Universe - E Natural Health Center
... 30 km (18.6 miles). Only the most massive stars—those of more than three solar masses—become black holes at the end of their lives. Stars with a smaller amount of mass evolve into less compressed bodies, either white dwarfs (白矮星) or neutron stars (中子星). Black holes are difficult to observe on accoun ...
... 30 km (18.6 miles). Only the most massive stars—those of more than three solar masses—become black holes at the end of their lives. Stars with a smaller amount of mass evolve into less compressed bodies, either white dwarfs (白矮星) or neutron stars (中子星). Black holes are difficult to observe on accoun ...
Optics in the Nineteenth Century
... consumer market for optics. Photography depends on light-sensitive materials, and early processes for exposing and developing such materials had been complex, requiring bulky cameras, heavy glass plates, and chemical processing. That changed after a Rochester bookkeeper named George Eastman took up ...
... consumer market for optics. Photography depends on light-sensitive materials, and early processes for exposing and developing such materials had been complex, requiring bulky cameras, heavy glass plates, and chemical processing. That changed after a Rochester bookkeeper named George Eastman took up ...
Life in the Universe
... International Astronomy Union (IAU) divided the entire night sky into 88 constellations. Helpers to find a way around the sky. Connection to the ancient astronomy, and good tool to naming stars (e.g., alpha Orioni the brightest star in Orion) stars in a constellation only appear to be clos ...
... International Astronomy Union (IAU) divided the entire night sky into 88 constellations. Helpers to find a way around the sky. Connection to the ancient astronomy, and good tool to naming stars (e.g., alpha Orioni the brightest star in Orion) stars in a constellation only appear to be clos ...
Beyond the Solar System Homework for Geology 8
... 61. The brightness of a star when viewed from Earth is called its ____________ magnitude. 62. The true brightness of a star, which takes into account the distance from the Earth by using a standard distance, is called its ____________ magnitude. 63. A 1st (first) magnitude star is approximately ____ ...
... 61. The brightness of a star when viewed from Earth is called its ____________ magnitude. 62. The true brightness of a star, which takes into account the distance from the Earth by using a standard distance, is called its ____________ magnitude. 63. A 1st (first) magnitude star is approximately ____ ...
Teacher Guide - Astronomy Outreach at UT Austin
... which these stars differ as they progress through their various stages of life and death. A star, like our Sun, is an enormous and complex system. In order to model and understand their properties and how they change with time, astronomers and astrophysicists apply the basic ideas in physics to math ...
... which these stars differ as they progress through their various stages of life and death. A star, like our Sun, is an enormous and complex system. In order to model and understand their properties and how they change with time, astronomers and astrophysicists apply the basic ideas in physics to math ...
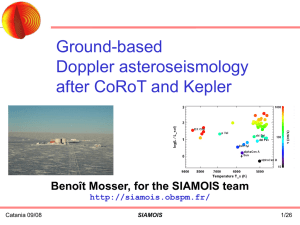
targets - siamois
... -stellar magnitude < 8.5 for solar-like oscillations - increase of the number of reachable targets possibility to achieve specific observations in selected targets ...
... -stellar magnitude < 8.5 for solar-like oscillations - increase of the number of reachable targets possibility to achieve specific observations in selected targets ...
Constellations and Asterisms
... the shapes of microscopes and telescopes. As you can probably infer, these sets are so drastically different in shape from each other reflecting who was looking up into the sky. The early constellations were most likely seen by the naked eye by cultures wanting to see these creatures mapped in the s ...
... the shapes of microscopes and telescopes. As you can probably infer, these sets are so drastically different in shape from each other reflecting who was looking up into the sky. The early constellations were most likely seen by the naked eye by cultures wanting to see these creatures mapped in the s ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • We identify a star cluster that is close enough to determine its distance by parallax • We plots its H-R diagram • Since we know the distances to the cluster stars • We can determine their luminosities ...
... • We identify a star cluster that is close enough to determine its distance by parallax • We plots its H-R diagram • Since we know the distances to the cluster stars • We can determine their luminosities ...
Last time: Star Clusters (sec. 19.6)
... 20-2.) The star is also pulsating (period ~years). Eventually so much of the envelope is lost that the last bit of envelope gets ejected as a more or less spherical shell of gas called a planetary nebula. (see pretty images, pp. 526527) (Note: “planetary” has nothing to do with planets; just a histo ...
... 20-2.) The star is also pulsating (period ~years). Eventually so much of the envelope is lost that the last bit of envelope gets ejected as a more or less spherical shell of gas called a planetary nebula. (see pretty images, pp. 526527) (Note: “planetary” has nothing to do with planets; just a histo ...
How many stars are in the Milky Way Galaxy?
... views, showing the major components. Indicate the approximate dimensions of the components and note the location of the Sun in each diagram. 2: Describe the galactic distribution of general interstellar material, nebulae, and open and globular star clusters. Specify the defining physical characteris ...
... views, showing the major components. Indicate the approximate dimensions of the components and note the location of the Sun in each diagram. 2: Describe the galactic distribution of general interstellar material, nebulae, and open and globular star clusters. Specify the defining physical characteris ...
THE BIG BANG THEORY
... • physicists calculated that roughly 1/4 of mass was converted into helium during the big bang, while the rest remained as hydrogen. • 1970s: spectroscopic studies of other galaxies have confirmed that the majority of the observed helium did exist before any star formation. ...
... • physicists calculated that roughly 1/4 of mass was converted into helium during the big bang, while the rest remained as hydrogen. • 1970s: spectroscopic studies of other galaxies have confirmed that the majority of the observed helium did exist before any star formation. ...
scope buyer`s guide - Astronomy Magazine
... 12.5, the MK67 is a serious planetary observer’s scope. One of the highlights of this telescope is its low weight — only 9.5 pounds. The optical tube assembly has a carry handle, and it also comes with a padded travel bag. A 2" Crayford focuser is standard, as is a 7x35mm straight-through finder sco ...
... 12.5, the MK67 is a serious planetary observer’s scope. One of the highlights of this telescope is its low weight — only 9.5 pounds. The optical tube assembly has a carry handle, and it also comes with a padded travel bag. A 2" Crayford focuser is standard, as is a 7x35mm straight-through finder sco ...
Alignment of the 1.6 meter off-axis New Solar Telescope at Big Bear
... Keywords: Telescope, Alignment, Wave front sensor, Solar observation ...
... Keywords: Telescope, Alignment, Wave front sensor, Solar observation ...
Introduction to Occultations and How to Observe and Record Them
... find is that the program will begin on the local Fox TV station at 8:00 p.m. on March 9. Check your listings, as they say, because this may change. ...
... find is that the program will begin on the local Fox TV station at 8:00 p.m. on March 9. Check your listings, as they say, because this may change. ...
tut44 Making A Mirror Grinding Tool
... their own telescopes. In the good old days, building your own telescope was the only way to get an affordable large aperture telescope. Back in the day, owning your own 10” telescope was huge. Today, with the low-cost imported telescopes, making your own telescope may not save you any money, but you ...
... their own telescopes. In the good old days, building your own telescope was the only way to get an affordable large aperture telescope. Back in the day, owning your own 10” telescope was huge. Today, with the low-cost imported telescopes, making your own telescope may not save you any money, but you ...
Slide 1
... Example: h Carinae: Binary system of a 60 Msun and 70 Msun star. Dramatic mass loss; major eruption in 1843 created double lobes. ...
... Example: h Carinae: Binary system of a 60 Msun and 70 Msun star. Dramatic mass loss; major eruption in 1843 created double lobes. ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.