How did “World of Warcraft” help advance virus research?
... virus into the game called "corrupted blood" [source: Wired]. The virtual virus was intended to test the best players of the game, but it succeeded so well that it became an infectious disease that killed off many weaker characters in the virtual world of the game. Some of the players avoided the in ...
... virus into the game called "corrupted blood" [source: Wired]. The virtual virus was intended to test the best players of the game, but it succeeded so well that it became an infectious disease that killed off many weaker characters in the virtual world of the game. Some of the players avoided the in ...
Epidemiology and pathogenesis of Ebola viruses
... populations have been suggested: either direct contact to a reservoir or contact to other wildlife that also contracts EBOV from the reservoir [17]. Epidemiologic observations showed that chimpanzees were the source of one human case in two recently described outbreaks (Coˆte d’Ivoire in 1994 and Ga ...
... populations have been suggested: either direct contact to a reservoir or contact to other wildlife that also contracts EBOV from the reservoir [17]. Epidemiologic observations showed that chimpanzees were the source of one human case in two recently described outbreaks (Coˆte d’Ivoire in 1994 and Ga ...
Global and Community Health
... Emerging infectious diseases cab defined as infectious that have newly appeared in the population, or have existed but are rapidly increasing in incidence or ...
... Emerging infectious diseases cab defined as infectious that have newly appeared in the population, or have existed but are rapidly increasing in incidence or ...
Clinical Progression of Ebola
... Provide rehydration therapy to prevent volume depletion. Correct abnormal electrolytes. Proton pump inhibitors should be administered for dyspepsia and gastrointestinal bleed prophylaxis. Administer antiemetics for nausea/vomiting. Monitor for dehydration. ...
... Provide rehydration therapy to prevent volume depletion. Correct abnormal electrolytes. Proton pump inhibitors should be administered for dyspepsia and gastrointestinal bleed prophylaxis. Administer antiemetics for nausea/vomiting. Monitor for dehydration. ...
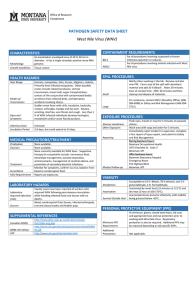
PATHOGEN SAFETY DATA SHEET West Nile Virus (WNV)
... An icosahedral, enveloped virus of 40 to 50 nm in diameter. It has a single stranded, positive-sense RNA genome. Tissue culture ...
... An icosahedral, enveloped virus of 40 to 50 nm in diameter. It has a single stranded, positive-sense RNA genome. Tissue culture ...
jeoprady review communicable and non - 9
... A disease transmitted through protozoans that is parasitic. The disease affects the liver and attacks red blood cells. Results include an enlarged liver and spleen. ...
... A disease transmitted through protozoans that is parasitic. The disease affects the liver and attacks red blood cells. Results include an enlarged liver and spleen. ...
The Diocesan Harvest Appeal for 2015/16 MLN (Maize Lethal
... wiped out the maize harvest and pushed many subsistence farmers and their families deeper into poverty. The Diocese of Nyahururu is doing its best to help provide food and seeds. MLN is a viral disease affecting maize. It arrived in East Africa in 2011. MLN is highly infectious. It attacks the leave ...
... wiped out the maize harvest and pushed many subsistence farmers and their families deeper into poverty. The Diocese of Nyahururu is doing its best to help provide food and seeds. MLN is a viral disease affecting maize. It arrived in East Africa in 2011. MLN is highly infectious. It attacks the leave ...
- Diocese of Chichester
... many health care workers unwittingly caught the disease when treating patients. The severe impact on the region’s fragile health care caused an increase in deaths from preventable diseases have risen. In the recent outbreak around 28,000 contracted Ebola mainly in Liberia, Guinea and Sierra Leone an ...
... many health care workers unwittingly caught the disease when treating patients. The severe impact on the region’s fragile health care caused an increase in deaths from preventable diseases have risen. In the recent outbreak around 28,000 contracted Ebola mainly in Liberia, Guinea and Sierra Leone an ...
The immune system project - Town of Mansfield, Connecticut
... Within a few days of high fever, headache, sore throat, hiccups, becoming infected with muscle aches, rash, red and itchy the virus: ...
... Within a few days of high fever, headache, sore throat, hiccups, becoming infected with muscle aches, rash, red and itchy the virus: ...
review worksheet... Comm disease
... 1. ________ Diseases can enter the body though the openings in the ears? 2. ________ A cold is caused by bacteria? 3. ________ Antigens produce a “code” that allows the body to detect certain pathogens? 4. ________ T cells and B cells are part of specific resistance? 5. ________ Ringworm is caused b ...
... 1. ________ Diseases can enter the body though the openings in the ears? 2. ________ A cold is caused by bacteria? 3. ________ Antigens produce a “code” that allows the body to detect certain pathogens? 4. ________ T cells and B cells are part of specific resistance? 5. ________ Ringworm is caused b ...
Infectious disease control: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and
... (FHI) has recommended what a basic personal protective equipment “kit” for infectious disease control should include. Such products are widely available internationally. This type of products and measures are used by primary health care representatives in their daily work in many countries. The main ...
... (FHI) has recommended what a basic personal protective equipment “kit” for infectious disease control should include. Such products are widely available internationally. This type of products and measures are used by primary health care representatives in their daily work in many countries. The main ...
スライド 1
... Attention travelers to regions with outbreaks (travel caution) • Take precautions against mosquito bites in outbreak regions, such as wearing long sleeves and pants, and regularly applying insect repellant. • Consider the risk of sexually-transmitted infections during your stay in outbreak areas, an ...
... Attention travelers to regions with outbreaks (travel caution) • Take precautions against mosquito bites in outbreak regions, such as wearing long sleeves and pants, and regularly applying insect repellant. • Consider the risk of sexually-transmitted infections during your stay in outbreak areas, an ...
Bloodborne Pathogens
... bloodborne disease Symptoms range from flu-like to none at all No symptoms - person is infectious and can spread the disease Hepatitis infects about 300,000 people in USA annually ...
... bloodborne disease Symptoms range from flu-like to none at all No symptoms - person is infectious and can spread the disease Hepatitis infects about 300,000 people in USA annually ...
CYTOMEGALOVIRUS FACT SHEET
... CYTOMEGALOVIRUS FACT SHEET Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a viral infection which can affect body tissues such as mucous membranes, body organs, and body fluids such as blood, human milk, urine and saliva. The majority of cases are mild, and occur without symptoms. Because CMV is in the herpes virus famil ...
... CYTOMEGALOVIRUS FACT SHEET Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a viral infection which can affect body tissues such as mucous membranes, body organs, and body fluids such as blood, human milk, urine and saliva. The majority of cases are mild, and occur without symptoms. Because CMV is in the herpes virus famil ...
Clinical Case Management Guidelines of Ebola Virus Disease (EVD)
... increase in survival time, though it did not reduce mortality significantly. These findings suggest that early postexposure interferon-beta therapy may be a promising adjunct in the treatment of Ebola virus infection. 3. Passive immunity has been attempted by using equine-derived hyperimmune globuli ...
... increase in survival time, though it did not reduce mortality significantly. These findings suggest that early postexposure interferon-beta therapy may be a promising adjunct in the treatment of Ebola virus infection. 3. Passive immunity has been attempted by using equine-derived hyperimmune globuli ...
Unit 8: Communicable/Infectious Diseases
... Bits of genetic material that can only be seen by an electron microscope and take over body cells Can only live outside the body for a short time but must multiply inside the body Examples: Rabies, Polio, Common Cold, Hepatitis, Mumps, Mononucleosis, Small Pox, Chicken Pox, Shingles, and Warts ...
... Bits of genetic material that can only be seen by an electron microscope and take over body cells Can only live outside the body for a short time but must multiply inside the body Examples: Rabies, Polio, Common Cold, Hepatitis, Mumps, Mononucleosis, Small Pox, Chicken Pox, Shingles, and Warts ...
US Scientists See Long Fight Against Ebola
... capital of Liberia — gravely complicating efforts to control the spread of the disease. Alessandro Vespignani, a professor of computational sciences at Northeastern University who has been involved in the computer modeling of Ebola’s spread, said that if the case count reaches hundreds of thousands, ...
... capital of Liberia — gravely complicating efforts to control the spread of the disease. Alessandro Vespignani, a professor of computational sciences at Northeastern University who has been involved in the computer modeling of Ebola’s spread, said that if the case count reaches hundreds of thousands, ...
notes chap. 24 virsuses - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... onto host cell membrane. b. Entry – DNA/RNA is injected into cell. c. Replication – viral DNA/RNA tells host cell to make more viruses d. Assembly – making of more viruses e. Lysis (release) – host cell ruptures and releases all viruses to go and infect new cells. -- interferon – chemical released b ...
... onto host cell membrane. b. Entry – DNA/RNA is injected into cell. c. Replication – viral DNA/RNA tells host cell to make more viruses d. Assembly – making of more viruses e. Lysis (release) – host cell ruptures and releases all viruses to go and infect new cells. -- interferon – chemical released b ...
Notes on Infectious Disease backup
... Infectious Disease Definition: Diseases transmitted(spread) by pathogens(germs) ...
... Infectious Disease Definition: Diseases transmitted(spread) by pathogens(germs) ...
Infectious bursal disease virus monoclonal antibody, clone
... Immunogen: Native purified very virulent IBD virus (field strain) derived from infected chicken bursas. Host: Mouse Reactivity: Chicken Applications: ELISA, IHC, S-ELISA, WB (See our web site product page for detailed applications information) Protocols: See our web site at http://www.abnova.com/sup ...
... Immunogen: Native purified very virulent IBD virus (field strain) derived from infected chicken bursas. Host: Mouse Reactivity: Chicken Applications: ELISA, IHC, S-ELISA, WB (See our web site product page for detailed applications information) Protocols: See our web site at http://www.abnova.com/sup ...
Infectious bursal disease virus monoclonal antibody, clone
... Immunogen: Native purified very virulent IBD virus (field strain) derived from infected chicken bursas. Host: Mouse Reactivity: Chicken Applications: ELISA, IHC, S-ELISA, WB (See our web site product page for detailed applications information) Protocols: See our web site at http://www.abnova.com/sup ...
... Immunogen: Native purified very virulent IBD virus (field strain) derived from infected chicken bursas. Host: Mouse Reactivity: Chicken Applications: ELISA, IHC, S-ELISA, WB (See our web site product page for detailed applications information) Protocols: See our web site at http://www.abnova.com/sup ...
Emerging Infectious Diseases with Global Impact
... for the virus is unknown, it is suspected that bats are a carrier and likely reservoir. Within the genus Ebolavirus there are five species, named after the areas the virus was discovered. Bundibugyo ebolavirus, Zaire ebolavirus, Sudan ebolavirus, and Taï Forest ebolavirus infect humans. The fifth, R ...
... for the virus is unknown, it is suspected that bats are a carrier and likely reservoir. Within the genus Ebolavirus there are five species, named after the areas the virus was discovered. Bundibugyo ebolavirus, Zaire ebolavirus, Sudan ebolavirus, and Taï Forest ebolavirus infect humans. The fifth, R ...
12 Filoviruses
... Two viral proteins suppress the type I interferon response VP35 protein inhibits activation of interferon regulatory factor 3 VP24 blocks STAT1 localization to the nucleus Lymphocytes die by apoptosis (and not viral infection) ...
... Two viral proteins suppress the type I interferon response VP35 protein inhibits activation of interferon regulatory factor 3 VP24 blocks STAT1 localization to the nucleus Lymphocytes die by apoptosis (and not viral infection) ...
Marburg hemorrhagic fever
... does not occur during the incubation period.Infection results from contact with blood or other body fluids (faeces, vomitus, urine, saliva, and respiratory secretions) with high virus concentration, especially when these fluids contain blood. Transmission via infected semen can occur; virus has been ...
... does not occur during the incubation period.Infection results from contact with blood or other body fluids (faeces, vomitus, urine, saliva, and respiratory secretions) with high virus concentration, especially when these fluids contain blood. Transmission via infected semen can occur; virus has been ...
Ebola virus disease

Ebola virus disease (EVD; also Ebola hemorrhagic fever, or EHF), or simply Ebola, is a disease of humans and other primates caused by ebolaviruses. Signs and symptoms typically start between two days and three weeks after contracting the virus with a fever, sore throat, muscular pain, and headaches. Then, vomiting, diarrhea and rash usually follow, along with decreased function of the liver and kidneys. At this time some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. The disease has a high risk of death, killing between 25 and 90 percent of those infected, with an average of about 50 percent. This is often due to low blood pressure from fluid loss, and typically follows six to sixteen days after symptoms appear.The virus spreads by direct contact with body fluids, such as blood, of an infected human or other animals. This may also occur through contact with an item recently contaminated with bodily fluids. Spread of the disease through the air between primates, including humans, has not been documented in either laboratory or natural conditions. Semen or breast milk of a person after recovery from EVD may still carry the virus for several weeks to months. Fruit bats are believed to be the normal carrier in nature, able to spread the virus without being affected by it. Other diseases such as malaria, cholera, typhoid fever, meningitis and other viral hemorrhagic fevers may resemble EVD. Blood samples are tested for viral RNA, viral antibodies or for the virus itself to confirm the diagnosis.Control of outbreaks requires coordinated medical services, alongside a certain level of community engagement. The medical services include rapid detection of cases of disease, contact tracing of those who have come into contact with infected individuals, quick access to laboratory services, proper healthcare for those who are infected, and proper disposal of the dead through cremation or burial. Samples of body fluids and tissues from people with the disease should be handled with special caution. Prevention includes limiting the spread of disease from infected animals to humans. This may be done by handling potentially infected bush meat only while wearing protective clothing and by thoroughly cooking it before eating it. It also includes wearing proper protective clothing and washing hands when around a person with the disease. No specific treatment or vaccine for the virus is available, although a number of potential treatments are being studied. Supportive efforts, however, improve outcomes. This includes either oral rehydration therapy (drinking slightly sweetened and salty water) or giving intravenous fluids as well as treating symptoms.The disease was first identified in 1976 in two simultaneous outbreaks, one in Nzara, and the other in Yambuku, a village near the Ebola River from which the disease takes its name. EVD outbreaks occur intermittently in tropical regions of sub-Saharan Africa. Between 1976 and 2013, the World Health Organization reports a total of 24 outbreaks involving 1,716 cases. The largest outbreak is the ongoing epidemic in West Africa, still affecting Guinea and Sierra Leone. {{#section:Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa|casesasof}}, this outbreak has {{#section:Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa|cases}} reported cases resulting in {{#section:Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa|deaths}} deaths.{{#section:Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa|caserefs}}