Organic Naming Notes
... - In this example there is a chain with 9 (nonane) 2. Number the chain starting with one that will give the attached groups (substituent group) the lowest number. 3. Add numbers of the parent chain carbon bonded to the names of the substituent group ...
... - In this example there is a chain with 9 (nonane) 2. Number the chain starting with one that will give the attached groups (substituent group) the lowest number. 3. Add numbers of the parent chain carbon bonded to the names of the substituent group ...
Year 9 Homework Task 9E-5 Reactions 5-7
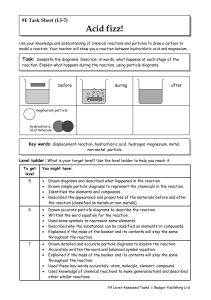
... Task: Complete the diagrams. Describe, in words, what happens at each stage of the reaction. Explain what happens during the reaction, using particle diagrams. ...
... Task: Complete the diagrams. Describe, in words, what happens at each stage of the reaction. Explain what happens during the reaction, using particle diagrams. ...
2nd Semester Final Exam Review
... 3. If a 35.00% solution of NaCl contained 90.0 grams of NaCl, how many grams of water was it dissolved in? 4. How many grams of KBr are needed to make 750.0 ml of a .500 M solution? 5. What is the effect on the number of dissolved particles on: vapor pressure, freezing point, and boiling point? Coll ...
... 3. If a 35.00% solution of NaCl contained 90.0 grams of NaCl, how many grams of water was it dissolved in? 4. How many grams of KBr are needed to make 750.0 ml of a .500 M solution? 5. What is the effect on the number of dissolved particles on: vapor pressure, freezing point, and boiling point? Coll ...
Reaction Predictions
... The “driving force” in these reactions is the removal of at least one pair of ions from solution. This removal of ions happens with the formation of a precipitate, gas, or molecular species. When a double replacement reaction doesn’t go to completion, it is a reversible reaction (no ions have been ...
... The “driving force” in these reactions is the removal of at least one pair of ions from solution. This removal of ions happens with the formation of a precipitate, gas, or molecular species. When a double replacement reaction doesn’t go to completion, it is a reversible reaction (no ions have been ...
Chemistry in engineering curriculum Prisedsky V.V. (DonNTU
... Role of Mathematics. Mathematics is a universal symbolic language of science and in this role is widely used in such quantitative areas of chemistry as thermodynamics, kinetics, electrochemistry [1,3,4]. Using chemical laws and definitions generally involves algebraic calculation and manipulation, i ...
... Role of Mathematics. Mathematics is a universal symbolic language of science and in this role is widely used in such quantitative areas of chemistry as thermodynamics, kinetics, electrochemistry [1,3,4]. Using chemical laws and definitions generally involves algebraic calculation and manipulation, i ...
File
... A. Heterogeneous mixture B. Homogenous compound C. Heterogeneous substance D. Homogenous mixture ...
... A. Heterogeneous mixture B. Homogenous compound C. Heterogeneous substance D. Homogenous mixture ...
+2 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... • Oxidation numbers are numbers assigned to the atoms in a molecular compound or ion that indicates the general distribution of electrons among bonded atoms. • Oxidation numbers are not actual charges. • Oxidation numbers can be useful in naming compounds and writing formulas. ...
... • Oxidation numbers are numbers assigned to the atoms in a molecular compound or ion that indicates the general distribution of electrons among bonded atoms. • Oxidation numbers are not actual charges. • Oxidation numbers can be useful in naming compounds and writing formulas. ...
Ionic bonding - Nidderdale High School
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
Chemical Equations
... A. Combination or Synthesis • where 2 or more simple substances (elements or compounds) combine to form ONE complex substance • 8Fe + S8 8FeS • 2Sr + O2 2SrO ...
... A. Combination or Synthesis • where 2 or more simple substances (elements or compounds) combine to form ONE complex substance • 8Fe + S8 8FeS • 2Sr + O2 2SrO ...
AP Chemistry - School Webmasters
... ___________________________________ number of ____________________________________________ in the original measurements *Significant Figures Rules only apply to measured values. Please show your work using the underline or circle method. Remember that significant figures rules only apply to measurem ...
... ___________________________________ number of ____________________________________________ in the original measurements *Significant Figures Rules only apply to measured values. Please show your work using the underline or circle method. Remember that significant figures rules only apply to measurem ...
8.P.1.1Homework for Website
... B. It cannot combine with other substances, liquid at room temperature, and cannot be changed into simpler substances. C. It is solid at room temperature, can be broken down from compounds by chemical changes, and composed of one kind of atom. 7. Which is a homogeneous mixture? A. woven fabric B. co ...
... B. It cannot combine with other substances, liquid at room temperature, and cannot be changed into simpler substances. C. It is solid at room temperature, can be broken down from compounds by chemical changes, and composed of one kind of atom. 7. Which is a homogeneous mixture? A. woven fabric B. co ...
Chemistry in Biology
... COMPOUNDS II. Composition of Matter A. Elements—pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler kinds of matter • Made of one type of atom • More than 100 elements (92 naturally occurring) • 90% of the mass of an organism is composed of 4 elements (oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen) • E ...
... COMPOUNDS II. Composition of Matter A. Elements—pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler kinds of matter • Made of one type of atom • More than 100 elements (92 naturally occurring) • 90% of the mass of an organism is composed of 4 elements (oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen) • E ...
Single-Replacement Reactions
... A, B = elements or compounds AB = compound consisting of A and B This is the only type of chemical reaction in which there is a single product formed. This single product is always more complex than the reactants. ...
... A, B = elements or compounds AB = compound consisting of A and B This is the only type of chemical reaction in which there is a single product formed. This single product is always more complex than the reactants. ...
Test Booklet
... D the strong electrostatic attraction between Na+ and Cl− What is the state of the substance at point I ? ...
... D the strong electrostatic attraction between Na+ and Cl− What is the state of the substance at point I ? ...
34.) Write out the set of four quantum numbers for the last electron
... 6.) What is the mass of 15 nickels? 7.) What is the density of 15 nickels? Unit 2 * Classify as element, compound, solution, or heterogeneous mixture. 8.) Flat soda 9.) Potassium iodide 10.) Iodine 11.) Potassium iodide completely dissolved in water 12.) Soil 13.) Chromium * Classify as chemical or ...
... 6.) What is the mass of 15 nickels? 7.) What is the density of 15 nickels? Unit 2 * Classify as element, compound, solution, or heterogeneous mixture. 8.) Flat soda 9.) Potassium iodide 10.) Iodine 11.) Potassium iodide completely dissolved in water 12.) Soil 13.) Chromium * Classify as chemical or ...
Unit 3 - Chemistry
... theories to explain his observations and came up with Dalton’s atomic theory. ...
... theories to explain his observations and came up with Dalton’s atomic theory. ...
AP Chemistry Review Assignment Brown and LeMay: Chemistry the
... The last part of this section, including how to determine the formula of a hydrate, and how to use combustion analyses to determine empirical formulas will be addressed early in the semester, probably Thurs., Aug. 20. 43. Give the empirical formula of each of the following compounds if a sample cont ...
... The last part of this section, including how to determine the formula of a hydrate, and how to use combustion analyses to determine empirical formulas will be addressed early in the semester, probably Thurs., Aug. 20. 43. Give the empirical formula of each of the following compounds if a sample cont ...
Chemistry - Target Publications
... Molarity of the solution. [Given: Density of solution is 1.20 g mL−1 and molar mass of glucose is 180 g mol−1] iii. Resistance of conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 100 ohms. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 520 ohms, calculate the conductiv ...
... Molarity of the solution. [Given: Density of solution is 1.20 g mL−1 and molar mass of glucose is 180 g mol−1] iii. Resistance of conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 100 ohms. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 520 ohms, calculate the conductiv ...
CHAPTER 1 Practice Exercises 1.1 12.3 g Cd 1.3 26.9814 u 1.5
... An orbital is a region in space where there is a non-zero probability of finding an electron. ...
... An orbital is a region in space where there is a non-zero probability of finding an electron. ...
honors final key
... NH4OH NH3 + H2O decomposition, will occur due to increased entropy b. Carbon dioxide and water are formed as a result of the combustion of methane gas. CH4(g) + 2O2 CO2 + 2 H2O combustion, will occur c. A barium sulfate precipitate and aqueous sodium chloride are formed from the metathesis react ...
... NH4OH NH3 + H2O decomposition, will occur due to increased entropy b. Carbon dioxide and water are formed as a result of the combustion of methane gas. CH4(g) + 2O2 CO2 + 2 H2O combustion, will occur c. A barium sulfate precipitate and aqueous sodium chloride are formed from the metathesis react ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.