CO 2 - TrimbleChemistry
... Examples: Writing the Formula for Ionic Compounds • Ca and Cl • Ba and F • Na and S ...
... Examples: Writing the Formula for Ionic Compounds • Ca and Cl • Ba and F • Na and S ...
Practice Toxins Mid-Unit Test 08-09
... ______1. What type of reaction is this? Ag (s) + CuI2 (aq) AgI (s) + Cu(s) (A) single displacement (B) double displacement (C) combination reaction (D) decomposition reaction ______2.Calcium Chloride is abbreviated (A) CaCl (C) Ca2Cl (B) CaCl2 (D) Cl2Ca ______3. What is the molarity of 3.5 moles o ...
... ______1. What type of reaction is this? Ag (s) + CuI2 (aq) AgI (s) + Cu(s) (A) single displacement (B) double displacement (C) combination reaction (D) decomposition reaction ______2.Calcium Chloride is abbreviated (A) CaCl (C) Ca2Cl (B) CaCl2 (D) Cl2Ca ______3. What is the molarity of 3.5 moles o ...
Brønsted acid
... In a titration a solution of accurately known concentration is added gradually added to another solution of unknown concentration until the chemical reaction between the two solutions is complete. Equivalence point – the point at which the reaction is complete Indicator – substance that changes colo ...
... In a titration a solution of accurately known concentration is added gradually added to another solution of unknown concentration until the chemical reaction between the two solutions is complete. Equivalence point – the point at which the reaction is complete Indicator – substance that changes colo ...
Compounds
... 46. What must occur to create a combination substitutional/interstitial alloy? 47. Alloying metal requires a large energy input. What are the benefits of metal alloys over pure metal? 48. Some early human tools have been found to be made from meteoric iron, a naturally occurring homogeneous alloy of ...
... 46. What must occur to create a combination substitutional/interstitial alloy? 47. Alloying metal requires a large energy input. What are the benefits of metal alloys over pure metal? 48. Some early human tools have been found to be made from meteoric iron, a naturally occurring homogeneous alloy of ...
Chemistry 21 A - El Camino College
... 1) Does your reaction have oxygen as one of it's reactants and carbon dioxide and water as products? If yes, then it's a combustion reaction 2) Does your reaction have two (or more) chemicals combining to form one chemical? If yes, then it's a synthesis reaction 3) Does your reaction have one large ...
... 1) Does your reaction have oxygen as one of it's reactants and carbon dioxide and water as products? If yes, then it's a combustion reaction 2) Does your reaction have two (or more) chemicals combining to form one chemical? If yes, then it's a synthesis reaction 3) Does your reaction have one large ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... Element “X” is composed of the following naturally occurring isotopes: Isotope ...
... Element “X” is composed of the following naturally occurring isotopes: Isotope ...
Topic guide 9.3: Drug discovery and design
... ‘The essential principle is that we aim to invent safe drugs for unmet medical needs. With modern chemical and computing techniques we can make and investigate a myriad of new compounds. There are so many avenues we could go down, but ultimately we have to take pragmatic decisions to ensure that we ...
... ‘The essential principle is that we aim to invent safe drugs for unmet medical needs. With modern chemical and computing techniques we can make and investigate a myriad of new compounds. There are so many avenues we could go down, but ultimately we have to take pragmatic decisions to ensure that we ...
Ch 7: Reactions
... • 2) Does your reaction have two (or more) chemicals combining to form one chemical? If yes, then it's a synthesis reaction • 3) Does your reaction have one large molecule falling apart to make several small ones? If yes, then it's a decomposition reaction • 4) Does your reaction have any molecules ...
... • 2) Does your reaction have two (or more) chemicals combining to form one chemical? If yes, then it's a synthesis reaction • 3) Does your reaction have one large molecule falling apart to make several small ones? If yes, then it's a decomposition reaction • 4) Does your reaction have any molecules ...
Proposed syllabus and Scheme of Examination B.Sc. (Program) with
... and angular nodes and their significance. Radial distribution functions and the concept of the most probable distance with special reference to 1s and 2s atomic orbitals. Significance of quantum numbers, orbital angular momentum and quantum numbers ml and ms. Shapes of s, p and d atomic orbitals, no ...
... and angular nodes and their significance. Radial distribution functions and the concept of the most probable distance with special reference to 1s and 2s atomic orbitals. Significance of quantum numbers, orbital angular momentum and quantum numbers ml and ms. Shapes of s, p and d atomic orbitals, no ...
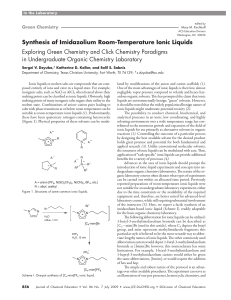
Synthesis of Imidazolium Room-Temperature Ionic
... Department of Chemistry, Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, TX 76129; *[email protected] ...
... Department of Chemistry, Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, TX 76129; *[email protected] ...
Chemistry - Northeastern Illinois University
... CHEM-348. Advanced Organic Chemistry: Bio-Organic Compounds. 3 Hours. The chemistry of complex molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids and carbohydrates is studied from the point of view of their physical properties and their reaction, synthesis and structure-function relationships. Lecture 3 hour ...
... CHEM-348. Advanced Organic Chemistry: Bio-Organic Compounds. 3 Hours. The chemistry of complex molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids and carbohydrates is studied from the point of view of their physical properties and their reaction, synthesis and structure-function relationships. Lecture 3 hour ...
writing chemical equations
... 2. Solid calcium reacts with oxygen gas. 3. Solutions of aluminum chloride & sodium carbonate are mixed. 4. Liquid magnesium bromide is decomposed at high temperature. 5. Solid nickel is reacted with aqueous magnesium sulfate. 6. Chlorine gas is reacted with aqueous potassium bromide. 7. Solid magne ...
... 2. Solid calcium reacts with oxygen gas. 3. Solutions of aluminum chloride & sodium carbonate are mixed. 4. Liquid magnesium bromide is decomposed at high temperature. 5. Solid nickel is reacted with aqueous magnesium sulfate. 6. Chlorine gas is reacted with aqueous potassium bromide. 7. Solid magne ...
An Efficient Oxidation of Benzoins to Benzils by Manganese (II
... donor atoms have shown an exponential increase as inorganic catalysts for various organic transformations. Distinct advantages of such ligands include their low cost, facile syntheses, and convenient incorporation of inexpensive, chiral 1,2-diamines into the ligand backbone. Moreover, the ligands ge ...
... donor atoms have shown an exponential increase as inorganic catalysts for various organic transformations. Distinct advantages of such ligands include their low cost, facile syntheses, and convenient incorporation of inexpensive, chiral 1,2-diamines into the ligand backbone. Moreover, the ligands ge ...
Florida`s - Wavefunction, Inc.
... A. A working definition of matter is that it takes up space, has mass, and has measurable properties. Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, reactivity, and molecular structures. Repeati ...
... A. A working definition of matter is that it takes up space, has mass, and has measurable properties. Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, reactivity, and molecular structures. Repeati ...
System International Base Units
... Lewis structures for compounds Draw element with most unpaired electrons in center Draw other elements around center element (s) such that their unpaired electrons face each other, then connect the unpaired electrons All atoms should have eight electrons around them (remember dashes represent ...
... Lewis structures for compounds Draw element with most unpaired electrons in center Draw other elements around center element (s) such that their unpaired electrons face each other, then connect the unpaired electrons All atoms should have eight electrons around them (remember dashes represent ...
Glossary: Chemical bonds
... CA, CB, CC, CD are concentrations of gaseous or dissolved substances. Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic one, so it can be shifted according to le Chateleu’s principle (principle of counteraction): if an equilibrium system is affected by any factor (change in concentrations, pressure or temperature), ...
... CA, CB, CC, CD are concentrations of gaseous or dissolved substances. Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic one, so it can be shifted according to le Chateleu’s principle (principle of counteraction): if an equilibrium system is affected by any factor (change in concentrations, pressure or temperature), ...
Reporting Category 3: Bonding and Chemical Reactions
... Metals are also malleable, which means that they can be shaped and hammered into thin sheets. A force, such as the strike of a hammer, applied to the solid reshapes the lattice of cations because the cations can move through the “sea” of electrons without breaking the metallic bonds. For this same r ...
... Metals are also malleable, which means that they can be shaped and hammered into thin sheets. A force, such as the strike of a hammer, applied to the solid reshapes the lattice of cations because the cations can move through the “sea” of electrons without breaking the metallic bonds. For this same r ...
chemistry-2nd-edition-julia-burdge-solution
... (b) one green sphere, two red spheres two red spheres (d) two green spheres, one red sphere ...
... (b) one green sphere, two red spheres two red spheres (d) two green spheres, one red sphere ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.