PREPARATORY PROBLEMS (Theoretical)
... The natural tendency of any chemical reaction to proceed in a certain direction at constant temperature and pressure is determined by the sign of the Gibbs energy of the reaction, DG. This is the universal principle. If DG < 0, the reaction can proceed predominantly in the forward direction (a produ ...
... The natural tendency of any chemical reaction to proceed in a certain direction at constant temperature and pressure is determined by the sign of the Gibbs energy of the reaction, DG. This is the universal principle. If DG < 0, the reaction can proceed predominantly in the forward direction (a produ ...
Chapter 7 Lecture
... of heat is classified occurs in as a combustion reaction. the cylinders of the engine Combustion reactions are a subclass of Oxidation-Reduction reactions ...
... of heat is classified occurs in as a combustion reaction. the cylinders of the engine Combustion reactions are a subclass of Oxidation-Reduction reactions ...
CHEMISTRY
... An introduction to theory and practice of organic chemistry through study of structural principles, reaction mechanisms, and synthesis leading toward end of second term, when complex molecules of biological interest are discussed. Basic goals of course are to develop appreciation and skill in method ...
... An introduction to theory and practice of organic chemistry through study of structural principles, reaction mechanisms, and synthesis leading toward end of second term, when complex molecules of biological interest are discussed. Basic goals of course are to develop appreciation and skill in method ...
Chemical Technology - Engineers Institute of India
... using pulverized coal directly in the smelter burners or working with secondary combustion gases after ash has been removed must be resulted. ...
... using pulverized coal directly in the smelter burners or working with secondary combustion gases after ash has been removed must be resulted. ...
Head-Gordon`s
... branch of electronic structure theory, namely, that based on seeking tractable approximations to the exact waVe function. However, it has been known for three decades that the exact energy is in fact a functional of only the electron density (a function of only 3, rather than 3n, variables). The onl ...
... branch of electronic structure theory, namely, that based on seeking tractable approximations to the exact waVe function. However, it has been known for three decades that the exact energy is in fact a functional of only the electron density (a function of only 3, rather than 3n, variables). The onl ...
An enquiry into theoretical bioinorganic chemistry: How heuristic is
... Bioinorganic chemistry is a very complex and diverse field. Structures with different types of ligands ranging from chelate co-factors to full proteins, with a varying number of interacting (transition) metals provide the stage for the most complex chemical transformations and for intricate reaction ...
... Bioinorganic chemistry is a very complex and diverse field. Structures with different types of ligands ranging from chelate co-factors to full proteins, with a varying number of interacting (transition) metals provide the stage for the most complex chemical transformations and for intricate reaction ...
CHEM_01A_ExptD_Copper_Cycle_F14
... All steps in this experiment will be performed under the fume hood. Your instructor will turn on the fume hoods before you begin the experiment. Be sure to wear your safety goggles and lab jacket ...
... All steps in this experiment will be performed under the fume hood. Your instructor will turn on the fume hoods before you begin the experiment. Be sure to wear your safety goggles and lab jacket ...
FREE Sample Here
... D) the chemical stability of the elements E) both the relative abundances of the elements and the emergent properties of the compounds made from these elements Answer: E Topic: Concept 2.1 Skill: Synthesis/Evaluation 5) Why is each element unique and different from other elements in chemical propert ...
... D) the chemical stability of the elements E) both the relative abundances of the elements and the emergent properties of the compounds made from these elements Answer: E Topic: Concept 2.1 Skill: Synthesis/Evaluation 5) Why is each element unique and different from other elements in chemical propert ...
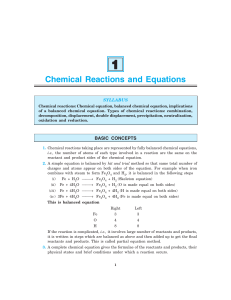
1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
... (ii) Formulae of substances produced in the reaction i.e., products. (iii) The relative number of molecules of reactants and products. (iv) The relative masses of reactants and products. (v) The relative volumes of gaseous substances involved in the reaction. Q. 12. Enlist the limitations of chemica ...
... (ii) Formulae of substances produced in the reaction i.e., products. (iii) The relative number of molecules of reactants and products. (iv) The relative masses of reactants and products. (v) The relative volumes of gaseous substances involved in the reaction. Q. 12. Enlist the limitations of chemica ...
76 kJ/mole
... Using Hess’ Law we can indirectly calculate the heats of formation ∆Hf ∆Hf for methane from its elements is -76 kcal/mol (GOOGLED Value) ...
... Using Hess’ Law we can indirectly calculate the heats of formation ∆Hf ∆Hf for methane from its elements is -76 kcal/mol (GOOGLED Value) ...
Organic Chemical Reactions
... Many millions of organic compounds are known today, either available in Nature (natural products) or prepared by Man (synthesis products). Each of these molecules has been obtained via a chemical reaction through the transformation of other organic molecules. Consequently, many different organic rea ...
... Many millions of organic compounds are known today, either available in Nature (natural products) or prepared by Man (synthesis products). Each of these molecules has been obtained via a chemical reaction through the transformation of other organic molecules. Consequently, many different organic rea ...
MASS RELATIONS and STOICHIOMETRY
... Recall from Chapter 2 that atoms are never created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Consequence: The number of atoms which were present before the reaction must be present after the reaction. A chemical equation which meets this criterion is said to be balanced. Stoichiometry is often used to ba ...
... Recall from Chapter 2 that atoms are never created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Consequence: The number of atoms which were present before the reaction must be present after the reaction. A chemical equation which meets this criterion is said to be balanced. Stoichiometry is often used to ba ...
Chemistry Content Review Notes
... 3. What is the first step that should be taken when a caustic chemical gets into a person’s eye? 4. What is the mass of a substance whose density is 0.2396 g/mL and a volume of 20.0 ml? 5. What is the minimum number of trials needed for a measurement to be reliable? ...
... 3. What is the first step that should be taken when a caustic chemical gets into a person’s eye? 4. What is the mass of a substance whose density is 0.2396 g/mL and a volume of 20.0 ml? 5. What is the minimum number of trials needed for a measurement to be reliable? ...
File
... All metals (on the left side of the periodic table) form cations and nonmetals (on the left side of the periodic table) form anions primarily. In order to determine the formula of the compound they create you must make sure their ions sum to zero. For example, table salt is sodium chloride. Using th ...
... All metals (on the left side of the periodic table) form cations and nonmetals (on the left side of the periodic table) form anions primarily. In order to determine the formula of the compound they create you must make sure their ions sum to zero. For example, table salt is sodium chloride. Using th ...
Honors Chemistry Unit 02
... and smaller pieces, you would eventually cut it down to a particle which could not be subdivided any further. He called these particles atoms (from the Greek atomos, “uncuttable”) • Aristotle (384-322 BC) believed that matter was continuous, and elaborated the idea that everything was composed for f ...
... and smaller pieces, you would eventually cut it down to a particle which could not be subdivided any further. He called these particles atoms (from the Greek atomos, “uncuttable”) • Aristotle (384-322 BC) believed that matter was continuous, and elaborated the idea that everything was composed for f ...
chapt 2
... In a chemical reaction the elements remain the same, but the compounds they form and their properties are different. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... In a chemical reaction the elements remain the same, but the compounds they form and their properties are different. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
FREE Sample Here
... 2) Trace elements are those required by an organism in only minute quantities. Which of the following is a trace element that is required by humans and other vertebrates, but not by other organisms such as bacteria or plants? A) nitrogen B) calcium C) iodine D) sodium E) phosphorus Answer: C Topic: ...
... 2) Trace elements are those required by an organism in only minute quantities. Which of the following is a trace element that is required by humans and other vertebrates, but not by other organisms such as bacteria or plants? A) nitrogen B) calcium C) iodine D) sodium E) phosphorus Answer: C Topic: ...
Measurements - Effingham County Schools
... o Gas state, matter has neither definite volume nor definite ...
... o Gas state, matter has neither definite volume nor definite ...
Comparing Free Energies
... substances involved in a chemical reaction is useful in qualitatively predicting the directionality of chemical reactions. However, given the often competing effects between changes in internal potential energy and entropy during chemical processes, we need to find a systematic way to make reliable ...
... substances involved in a chemical reaction is useful in qualitatively predicting the directionality of chemical reactions. However, given the often competing effects between changes in internal potential energy and entropy during chemical processes, we need to find a systematic way to make reliable ...
C - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... A. Atoms contain electrons. B. Practically all the mass of an atom is contained in its nucleus. C. Atoms contain protons, neutrons, and electrons. D. Atoms have a positively charged nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. E. No two electrons in one atom can have the same four quantum numbers. 65. T ...
... A. Atoms contain electrons. B. Practically all the mass of an atom is contained in its nucleus. C. Atoms contain protons, neutrons, and electrons. D. Atoms have a positively charged nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. E. No two electrons in one atom can have the same four quantum numbers. 65. T ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.