Chapter 8 and 9
... Lysine is an amino acid which has the following elemental composition: C, H, O, N. In one experiment, 2.175 g of lysine was combusted to produce 3.94 g of CO2 and 1.89 g H2O. In a separate experiment, 1.873 g of lysine was burned to produce 0.436 g of NH2. The molar mass of lysine is 150 g/mol. Dete ...
... Lysine is an amino acid which has the following elemental composition: C, H, O, N. In one experiment, 2.175 g of lysine was combusted to produce 3.94 g of CO2 and 1.89 g H2O. In a separate experiment, 1.873 g of lysine was burned to produce 0.436 g of NH2. The molar mass of lysine is 150 g/mol. Dete ...
Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations
... First of all, water is a liquid rather than a gas at room temperature, and its boiling point is hundreds of degrees above the boiling points of hydrogen and oxygen. Second, instead of being flammable (like hydrogen gas) or supporting combustion (like oxygen gas), water actually smothers flames. Wate ...
... First of all, water is a liquid rather than a gas at room temperature, and its boiling point is hundreds of degrees above the boiling points of hydrogen and oxygen. Second, instead of being flammable (like hydrogen gas) or supporting combustion (like oxygen gas), water actually smothers flames. Wate ...
L-11 Chemical thermodynamics
... You know that hot tea/milk (let us call it a system) kept in a stoppered thermos flask remains hot for a couple of hours. If this flask is made of perfect insulating material, then there would be no exchange of matter or energy between the system and the surroundings. We call such a system an isolat ...
... You know that hot tea/milk (let us call it a system) kept in a stoppered thermos flask remains hot for a couple of hours. If this flask is made of perfect insulating material, then there would be no exchange of matter or energy between the system and the surroundings. We call such a system an isolat ...
CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2: Organic
... mathematical functions for the two 1s orbitals that come together to form this molecule. A molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behaviour of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of ...
... mathematical functions for the two 1s orbitals that come together to form this molecule. A molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behaviour of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of ...
Introduction to Chemistry
... B.C. - 347 B.C.), and Aristotle (384 B.C. - 322 B.C.) are among the most famous of the Greek philosophers. Plato was a student of Socrates, and Aristotle was a student of Plato. These three were probably the greatest thinkers of their time. Aristotle's views on physical science profoundly shaped med ...
... B.C. - 347 B.C.), and Aristotle (384 B.C. - 322 B.C.) are among the most famous of the Greek philosophers. Plato was a student of Socrates, and Aristotle was a student of Plato. These three were probably the greatest thinkers of their time. Aristotle's views on physical science profoundly shaped med ...
Year 11 C2 Mock Exam Revision Questions
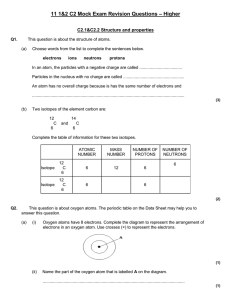
... Phosphorus and fluorine form a covalent compound, phosphorus trifluoride. Complete the sentences below which are about this compound. Phosphorus trifluoride is made up of phosphorus and fluorine ................................ These are joined together by sharing pairs of .......................... ...
... Phosphorus and fluorine form a covalent compound, phosphorus trifluoride. Complete the sentences below which are about this compound. Phosphorus trifluoride is made up of phosphorus and fluorine ................................ These are joined together by sharing pairs of .......................... ...
Massachusetts Tests for Educator Licensure (MTEL ) www.mtel
... fume exhaust hood to study the reaction between the elements copper and sulfur. Before beginning the experiment, the teacher will review with the class the proper use of the exhaust hood. Which of the following instructions should be included in this discussion? A. ...
... fume exhaust hood to study the reaction between the elements copper and sulfur. Before beginning the experiment, the teacher will review with the class the proper use of the exhaust hood. Which of the following instructions should be included in this discussion? A. ...
The mole and calculations
... Another type of chemical reaction to be aware of is the combustion reaction. Combustion is used to measure the amount of hydrogen and carbon in an organic substance as it burns in the presence of oxygen. All of the hydrogen is converted or H2O, while all of the carbon is converted to CO2. If the ...
... Another type of chemical reaction to be aware of is the combustion reaction. Combustion is used to measure the amount of hydrogen and carbon in an organic substance as it burns in the presence of oxygen. All of the hydrogen is converted or H2O, while all of the carbon is converted to CO2. If the ...
Document
... Heating value of a fuel • Lower heating value at constant pressure = symmetric of the standard enthalpy of combustion, per unit mass of fuel, when there is water vapour in the combustion products (always positive) • Lower heating value at constant volume = symmetric of the standard internal energy ...
... Heating value of a fuel • Lower heating value at constant pressure = symmetric of the standard enthalpy of combustion, per unit mass of fuel, when there is water vapour in the combustion products (always positive) • Lower heating value at constant volume = symmetric of the standard internal energy ...
Chemical Reactions
... Word Equations • Word Equations: an equation in which the reactants and products in a chemical reaction are represented by words instead of chemical formulas. • The problem with word equations is they do not actually show the number of atoms or molecules of each substance… formulas would have to be ...
... Word Equations • Word Equations: an equation in which the reactants and products in a chemical reaction are represented by words instead of chemical formulas. • The problem with word equations is they do not actually show the number of atoms or molecules of each substance… formulas would have to be ...
DCY1B - Manonmaniam Sundaranar University
... Titanium group elements have the general electronic configuration (n-1 ) d2 ns2. (iii) Oxidation states: The most common and most stable oxidation state of titanium group elements is +4. In this oxidation state, the elements have d° configuration and hence the compounds are colourless and diamagneti ...
... Titanium group elements have the general electronic configuration (n-1 ) d2 ns2. (iii) Oxidation states: The most common and most stable oxidation state of titanium group elements is +4. In this oxidation state, the elements have d° configuration and hence the compounds are colourless and diamagneti ...
2014_S4_CHM_NORMAL (ALL)
... 53. Element X (atomic number 11) reacts with element Y (atomic number 16) to form an ionic compound. Each atom of X loses one electron and each atom of Y accepts two electrons to form a compound with formula X2Y. 54. Consider the following information: ...
... 53. Element X (atomic number 11) reacts with element Y (atomic number 16) to form an ionic compound. Each atom of X loses one electron and each atom of Y accepts two electrons to form a compound with formula X2Y. 54. Consider the following information: ...
key for Unit 1 pp 21
... The element discussed in question number one is a halogen. As a pure element, it exists as a diatomic molecule (at room temperature and 1 atm pressure it is most stable as a liquid). (a) What is the average mass of each of these diatomic molecules (in amu)? ans.: if two average atoms combine they wi ...
... The element discussed in question number one is a halogen. As a pure element, it exists as a diatomic molecule (at room temperature and 1 atm pressure it is most stable as a liquid). (a) What is the average mass of each of these diatomic molecules (in amu)? ans.: if two average atoms combine they wi ...
Table of Contents Pages Unit 1- Matter and Change 1
... called filtering. Some simple methods also exist for separating homogeneous mixtures. A solid dissolved in a liquid solution can be separated by letting it dry out in the process of ___________________. Mixtures are separated into pure _____________________. A pure substance always has the same comp ...
... called filtering. Some simple methods also exist for separating homogeneous mixtures. A solid dissolved in a liquid solution can be separated by letting it dry out in the process of ___________________. Mixtures are separated into pure _____________________. A pure substance always has the same comp ...
Chemistry – 5071
... on the understanding and application of scientific concepts and principles. This approach has been adopted in recognition of the need of students to develop skills that will be of long term value in an increasing technological world rather than focusing on large quantities of actual material which m ...
... on the understanding and application of scientific concepts and principles. This approach has been adopted in recognition of the need of students to develop skills that will be of long term value in an increasing technological world rather than focusing on large quantities of actual material which m ...
03_Worked_Examples
... An inventory of atoms on each side of the equation shows that there are one N and three O on the left side of the arrow and one N and two O on the right. To balance O we must increase the number of O atoms on the right while keeping the coefficients for NO and NO2 equal. Sometimes a trial-and-error ...
... An inventory of atoms on each side of the equation shows that there are one N and three O on the left side of the arrow and one N and two O on the right. To balance O we must increase the number of O atoms on the right while keeping the coefficients for NO and NO2 equal. Sometimes a trial-and-error ...
Pesticides, Chemical Regulation, and Right-to
... 696 is essentially the same legislation introduced by Senator Lautenberg as the Safe Chemicals Act of 2011 (S. 847).) If TSCA reform is to be realized any time soon, it is possible it would be through movement to the Senate floor of an amended version of one of these two bills. If so, how likely is ...
... 696 is essentially the same legislation introduced by Senator Lautenberg as the Safe Chemicals Act of 2011 (S. 847).) If TSCA reform is to be realized any time soon, it is possible it would be through movement to the Senate floor of an amended version of one of these two bills. If so, how likely is ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.