Test 4 Review
... Covalent Bonds. Covalent bonds are bonds formed by sharing electrons. The electrons of one atom are attracted to the protons of another, but neither atom pulls strongly enough to remove an electron from the other. Covalent bonds form when the electronegativity difference between the elements is less ...
... Covalent Bonds. Covalent bonds are bonds formed by sharing electrons. The electrons of one atom are attracted to the protons of another, but neither atom pulls strongly enough to remove an electron from the other. Covalent bonds form when the electronegativity difference between the elements is less ...
The Chemical Bond John Murrell Early Ideas Atoms come together
... We can use Lewis theory to understand some features of molecular structure if we analyse the consequences of electrostatic repulsion. We start by adopting the principle that electron pairing is an important feature of the chemical bond, and count the number of electron pairs around an atom. Consider ...
... We can use Lewis theory to understand some features of molecular structure if we analyse the consequences of electrostatic repulsion. We start by adopting the principle that electron pairing is an important feature of the chemical bond, and count the number of electron pairs around an atom. Consider ...
FACTORS AFFECT
... VALENCE BOND THEORY This theory was developed by Linus Pauling. According to this theory the bonding in metal complexes arises when a filled ligand orbital containing a pair of electrons overlaps with a vacant hybrid orbital on the metal atom. The VBT assumes the bonding between the metal atom an ...
... VALENCE BOND THEORY This theory was developed by Linus Pauling. According to this theory the bonding in metal complexes arises when a filled ligand orbital containing a pair of electrons overlaps with a vacant hybrid orbital on the metal atom. The VBT assumes the bonding between the metal atom an ...
Chemistry basics powerpoint Chapter 2
... bonding partners An example is the transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine After the transfer of an electron, both atoms have ...
... bonding partners An example is the transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine After the transfer of an electron, both atoms have ...
24 Sept 08 - Seattle Central College
... – KHSO4 … K+ + HSO4- potassium hydrogen sulfate – NH4C2H3O2 … NH4+ + C2H3O2- ammonium acetate – NaH2PO3 ... Na+ + H2PO3- sodium dihydrogen phosphite ...
... – KHSO4 … K+ + HSO4- potassium hydrogen sulfate – NH4C2H3O2 … NH4+ + C2H3O2- ammonium acetate – NaH2PO3 ... Na+ + H2PO3- sodium dihydrogen phosphite ...
Transition Metals & Complex ions
... Less common shape = tetrahedral ( 4 coordinate bonds) BOND ANGLE = all 109.5o ...
... Less common shape = tetrahedral ( 4 coordinate bonds) BOND ANGLE = all 109.5o ...
Chemistry for BIOS 302
... Rule: Carbon and hydrogen share electrons equally. Oxygen and nitrogen also share equally. But, oxygen and nitrogen attract electrons more strongly than carbon or hydrogen. – That is, oxygen and nitrogen are more electronegative than carbon and hydrogen. – Or: in a covalent bond, an oxygen or nitrog ...
... Rule: Carbon and hydrogen share electrons equally. Oxygen and nitrogen also share equally. But, oxygen and nitrogen attract electrons more strongly than carbon or hydrogen. – That is, oxygen and nitrogen are more electronegative than carbon and hydrogen. – Or: in a covalent bond, an oxygen or nitrog ...
chapter 7-Chemical Bonding
... • Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons. It Occurs when the electronegativity difference between elements (atoms) is zero or relativity small (電負度幾乎沒差) • The bonds between atoms within a molecule (intramolecular bonds 分子內鍵結) are relatively strong, but the force of attraction between m ...
... • Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons. It Occurs when the electronegativity difference between elements (atoms) is zero or relativity small (電負度幾乎沒差) • The bonds between atoms within a molecule (intramolecular bonds 分子內鍵結) are relatively strong, but the force of attraction between m ...
Investigation of Zr-C, Zr-N, and Potential Agostic Interactions in an
... σ-bond complexes is directly and fundamentally related to the oxidative addition process,9,10 and therefore also to many other types of important bond activation reactions11 and to processes of major technical significance (e.g., olefin polymerizations12-17), an understanding of the interactions whi ...
... σ-bond complexes is directly and fundamentally related to the oxidative addition process,9,10 and therefore also to many other types of important bond activation reactions11 and to processes of major technical significance (e.g., olefin polymerizations12-17), an understanding of the interactions whi ...
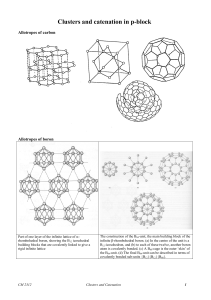
Clusters
... Additional H atoms are placed either around the B-B edges of an open face of the cluster or in extra terminal positions, usually if a boron atom is of particularly low connectivity. In arachno structures vacant vertices are usually adjacent. Cluster symmetry is generally kept as high as possible. Wh ...
... Additional H atoms are placed either around the B-B edges of an open face of the cluster or in extra terminal positions, usually if a boron atom is of particularly low connectivity. In arachno structures vacant vertices are usually adjacent. Cluster symmetry is generally kept as high as possible. Wh ...
Stoichiometry - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... brittleness, high melting and boiling points, and the ability to conduct electricity when molten or in aqueous solution using the theory of metallic bonding, explain why metals are malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity, and have a wide range of melting and boiling points co ...
... brittleness, high melting and boiling points, and the ability to conduct electricity when molten or in aqueous solution using the theory of metallic bonding, explain why metals are malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity, and have a wide range of melting and boiling points co ...
The format of this test is MULTIPLE CHOICE
... a. Metals are found primarily on the __left__ side of the periodic table (with the exception of __Al, ____). Nonmetals are found on the __right__ side of the table. b. Columns in the periodic table are called __groups________ and the rows are called ___periods_______. c. The _alkali metals____ are f ...
... a. Metals are found primarily on the __left__ side of the periodic table (with the exception of __Al, ____). Nonmetals are found on the __right__ side of the table. b. Columns in the periodic table are called __groups________ and the rows are called ___periods_______. c. The _alkali metals____ are f ...
Semester I CP Chemistry Review
... 34. For each of the following pairs which atom/ion will have the HIGHER ionization energy? Explain. a. Ca or Ba? - Ca is higher because it has only 4 energy levels so its valence electrons are closer to its nucleus b. Al or Cl? – Cl, they both have 3 energy levels but Cl has more protons attracti ...
... 34. For each of the following pairs which atom/ion will have the HIGHER ionization energy? Explain. a. Ca or Ba? - Ca is higher because it has only 4 energy levels so its valence electrons are closer to its nucleus b. Al or Cl? – Cl, they both have 3 energy levels but Cl has more protons attracti ...
Topics • Introduction • Molecular Structure and Bonding • Molecular
... – 2. Use two to form each bond between atoms – 3. Distribute the electrons in pairs so that each atom has an octet of valence electrons from a combination of lone pairs and bonds. ...
... – 2. Use two to form each bond between atoms – 3. Distribute the electrons in pairs so that each atom has an octet of valence electrons from a combination of lone pairs and bonds. ...
The format of this test is MULTIPLE CHOICE
... 6. Which nonmetal elements can form triple bonds? Nitrogen family 7. Which nonmetal elements can only form single bond? Halogens 8. What major assumption of the VSEPR theory means that bond angles will be as large as possible and that compound will exist in 3 dimensional space? Unpaired electron clo ...
... 6. Which nonmetal elements can form triple bonds? Nitrogen family 7. Which nonmetal elements can only form single bond? Halogens 8. What major assumption of the VSEPR theory means that bond angles will be as large as possible and that compound will exist in 3 dimensional space? Unpaired electron clo ...
Gupta 2014 Credit: Google Images for the pictures Chapter 1
... both may be a complex. (Follow standard nomenclature for noncomplexes.) 2. Within each complex (neutral or ion), name all ligands before the metal. -Name ligands in alphabetical order -If more than one of the same ligand is present, use a numerical prefix: di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, … -Ignore nume ...
... both may be a complex. (Follow standard nomenclature for noncomplexes.) 2. Within each complex (neutral or ion), name all ligands before the metal. -Name ligands in alphabetical order -If more than one of the same ligand is present, use a numerical prefix: di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, … -Ignore nume ...
Hon Chem Year Outline
... will recognize “cations” and “anions” in binary compounds. will draw Lewis structures for atoms. will relate Roman numerals on the periodic table to valence electrons and Lewis structures. will relate Lewis structures to auf bau notation. will relate valence electrons to oxidation number. ...
... will recognize “cations” and “anions” in binary compounds. will draw Lewis structures for atoms. will relate Roman numerals on the periodic table to valence electrons and Lewis structures. will relate Lewis structures to auf bau notation. will relate valence electrons to oxidation number. ...
What is Chemistry? Chemistry
... o Atoms that gain electrons to form compounds are called anions. Anions have a _________________________________. o Naming Anions: Drop the last few letters of the element name and add “ide”. o E.g. Group 17 (Halogens) gain electrons easily and release lots of energy in the process highly reactive ...
... o Atoms that gain electrons to form compounds are called anions. Anions have a _________________________________. o Naming Anions: Drop the last few letters of the element name and add “ide”. o E.g. Group 17 (Halogens) gain electrons easily and release lots of energy in the process highly reactive ...
Name: Period:______ PHYSICAL SCIENCE 1st Semester Final
... According to Rutherford’s model, all of an atom’s positive charge is located in its nucleus. Protons, electrons, and neutrons can be distinguished by mass, charge, and location in an atom. Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but different mass numbers because they have different ...
... According to Rutherford’s model, all of an atom’s positive charge is located in its nucleus. Protons, electrons, and neutrons can be distinguished by mass, charge, and location in an atom. Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but different mass numbers because they have different ...
2 Bonding and Structure
... elements after the 3rd period, the number of covalent bonds is sometimes five (e.g. PCl5) or six (e.g. SF6), and the central atom of these molecules shows hypervalency. In this case, because s and p electrons run short to form more than four 2-electron covalent bonds, it was once believed that d el ...
... elements after the 3rd period, the number of covalent bonds is sometimes five (e.g. PCl5) or six (e.g. SF6), and the central atom of these molecules shows hypervalency. In this case, because s and p electrons run short to form more than four 2-electron covalent bonds, it was once believed that d el ...
Electronegativity and Bond Type: Predicting
... Changing the coordinates from differences and averages of EN to the unfunctionalized EN terms themselves (12) successfully normalizes the graphical presentation, as shown in Figure 2. Binary compounds are positioned on this graph by locating the value of the element of lower EN along the ordinate an ...
... Changing the coordinates from differences and averages of EN to the unfunctionalized EN terms themselves (12) successfully normalizes the graphical presentation, as shown in Figure 2. Binary compounds are positioned on this graph by locating the value of the element of lower EN along the ordinate an ...
Adv review key
... _Group/Family 15_7. Name of the chemical family containing Nitrogen _P,As,Sb,Bi__8. Name of another element in the same family with Nitrogen _Li,Be,B,C,O,F,Ne____9. Name of another element in the same period with Nitrogen Ionic bonding A) Electrons are transferred between atoms B) Valence electrons- ...
... _Group/Family 15_7. Name of the chemical family containing Nitrogen _P,As,Sb,Bi__8. Name of another element in the same family with Nitrogen _Li,Be,B,C,O,F,Ne____9. Name of another element in the same period with Nitrogen Ionic bonding A) Electrons are transferred between atoms B) Valence electrons- ...
APS 1st semester exam review 2016
... _Group/Family 15_7. Name of the chemical family containing Nitrogen _P,As,Sb,Bi__8. Name of another element in the same family with Nitrogen _Li,Be,B,C,O,F,Ne____9. Name of another element in the same period with Nitrogen Ionic bonding A) Electrons are transferred between atoms B) Valence electrons- ...
... _Group/Family 15_7. Name of the chemical family containing Nitrogen _P,As,Sb,Bi__8. Name of another element in the same family with Nitrogen _Li,Be,B,C,O,F,Ne____9. Name of another element in the same period with Nitrogen Ionic bonding A) Electrons are transferred between atoms B) Valence electrons- ...
ch14
... All boron compounds are covalent, and B forms a variety of network covalent compounds with other elements. Boron is often electron-deficient in compounds, and acts effectively as a Lewis acid since it can accept an e- pair. BF3(g) + :NH3(g) → F3B–NH3(g) Boron forms bridge bonds, in which one pair of ...
... All boron compounds are covalent, and B forms a variety of network covalent compounds with other elements. Boron is often electron-deficient in compounds, and acts effectively as a Lewis acid since it can accept an e- pair. BF3(g) + :NH3(g) → F3B–NH3(g) Boron forms bridge bonds, in which one pair of ...