CMC Chapter 05
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
CMC Chapter 05
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
C. - Elliott County Schools
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t ...
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t ...
Slide 1
... The principal quantum number (n) describes the size of the orbital. Orbitals for which n = 2 are larger than those for which n = 1, for example. Because they have opposite electrical charges, electrons are attracted to the nucleus of the atom. Energy must therefore be absorbed to excite an electron ...
... The principal quantum number (n) describes the size of the orbital. Orbitals for which n = 2 are larger than those for which n = 1, for example. Because they have opposite electrical charges, electrons are attracted to the nucleus of the atom. Energy must therefore be absorbed to excite an electron ...
Chapter 6. Electronic Structure of Atoms.
... 1. Only orbits with definite radii are permitted 2. An electron in a specific orbit has an allowed energy 3. Energy is emitted or absorbed only when it changes from one state to another. ...
... 1. Only orbits with definite radii are permitted 2. An electron in a specific orbit has an allowed energy 3. Energy is emitted or absorbed only when it changes from one state to another. ...
Gen Chem Ch 5 notes
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
Electronic Structure of Atoms
... Particle behavior E = h Wave behavior Wave and particle behavior h mc 2 hc mc 2 ...
... Particle behavior E = h Wave behavior Wave and particle behavior h mc 2 hc mc 2 ...
NIELS BOHR power point22222
... Manchester in March 1912 and joined Ernest Rutherford's group studying the structure of the atom. ...
... Manchester in March 1912 and joined Ernest Rutherford's group studying the structure of the atom. ...
Chapter 4-2 The Quantum Model of the Atom
... Werner Heisenberg proposed an idea that involved the detection of electrons. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. ...
... Werner Heisenberg proposed an idea that involved the detection of electrons. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. ...
amu (atomic mass unit): a unit used to express very small masses
... sun. Bohr's first paper in this field dealt with the hydrogen atom, which he described as a single electron rotating in an orbit about a relatively heavy nucleus. He applied the concept of energy quanta, proposed in 1900 by the German physicist Max Planck (1858-1947) to the observed spectra of hydro ...
... sun. Bohr's first paper in this field dealt with the hydrogen atom, which he described as a single electron rotating in an orbit about a relatively heavy nucleus. He applied the concept of energy quanta, proposed in 1900 by the German physicist Max Planck (1858-1947) to the observed spectra of hydro ...
elements in a family have the same number of
... Atoms in this family have 3 valence electrons. This family includes a metalloid (boron), and the rest are metals. This family includes the most abundant metal in the earth’s crust (aluminum). ...
... Atoms in this family have 3 valence electrons. This family includes a metalloid (boron), and the rest are metals. This family includes the most abundant metal in the earth’s crust (aluminum). ...
The quantum theory was used to show how the wavelike behavior of
... experimental key to atomic structure: analyze light emitted by high temperature gaseous elements o experimental setup: spectroscopy ...
... experimental key to atomic structure: analyze light emitted by high temperature gaseous elements o experimental setup: spectroscopy ...
Modern Physics – Fall 2016 Prof. Akhavan Sharif University of
... In a muonic atom, the electron is replaced by a negatively charged particle called the muon. The muon mass is 207 times the electron mass. (a) What is the radius of the first Bohr orbit of a muonic lead(Z = 82) atom? (b) Calculate the magnitude of the lowest energy state for this atom. (c) Ignoring ...
... In a muonic atom, the electron is replaced by a negatively charged particle called the muon. The muon mass is 207 times the electron mass. (a) What is the radius of the first Bohr orbit of a muonic lead(Z = 82) atom? (b) Calculate the magnitude of the lowest energy state for this atom. (c) Ignoring ...
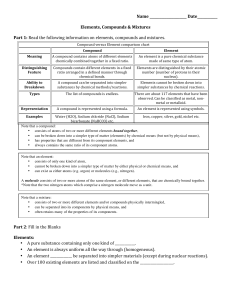
Compound vs Element chart
... • consists of atoms of two or more different elements bound together, • can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (elements) by chemical means (but not by physical means), • has properties that are different from its component elements, and • always contains the same ratio of its component at ...
... • consists of atoms of two or more different elements bound together, • can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (elements) by chemical means (but not by physical means), • has properties that are different from its component elements, and • always contains the same ratio of its component at ...
From Last Time… - High Energy Physics
... • Circular motion of orbiting electrons causes them to emit electromagnetic radiation with frequency equal to orbital frequency. • Same mechanism by which radio waves are emitted by electrons in a radio transmitting antenna. ...
... • Circular motion of orbiting electrons causes them to emit electromagnetic radiation with frequency equal to orbital frequency. • Same mechanism by which radio waves are emitted by electrons in a radio transmitting antenna. ...