Models of the Atom
... • Each electron state labeled by 4 numbers: n = principal quantum number (1, 2, 3, …) l = angular momentum (0, 1, 2, … n-1) ml = component of l (-l < ml < l) Quantum ms = spin (-½ , +½) Numbers ...
... • Each electron state labeled by 4 numbers: n = principal quantum number (1, 2, 3, …) l = angular momentum (0, 1, 2, … n-1) ml = component of l (-l < ml < l) Quantum ms = spin (-½ , +½) Numbers ...
Chapter Excerpt
... Noble gases (group 18 elements) have no color or odor and exist as individual gas atoms that experience London forces. These attractions also increase with period number as shown by the circular data points in the figures on the previous page. Noble gases are nearly chemically inert. The heavier nob ...
... Noble gases (group 18 elements) have no color or odor and exist as individual gas atoms that experience London forces. These attractions also increase with period number as shown by the circular data points in the figures on the previous page. Noble gases are nearly chemically inert. The heavier nob ...
Exercises. 1.1 The power delivered to a photodetector which collects
... was proposed by Bohr. It has been displaced by quantum mechanics, but by a remarkable coincidence (not the only one where the Coulomb potential is concerned) the energies it predicts agree exactly with those obtained from the Schrödinger equation. The Bohr atom is imagined as an electron circulating ...
... was proposed by Bohr. It has been displaced by quantum mechanics, but by a remarkable coincidence (not the only one where the Coulomb potential is concerned) the energies it predicts agree exactly with those obtained from the Schrödinger equation. The Bohr atom is imagined as an electron circulating ...
Common Chemical Formula List
... of the equation. (But it is usually a good idea to leave hydrogen and oxygen until you've done the others first.) To balance that element, multiply the chemical species on the side which doesn't have enough atoms of that type by the number required to bring it up to the same as the other side. The n ...
... of the equation. (But it is usually a good idea to leave hydrogen and oxygen until you've done the others first.) To balance that element, multiply the chemical species on the side which doesn't have enough atoms of that type by the number required to bring it up to the same as the other side. The n ...
Hydrogen Atom Simulator – Exercises
... fraction of atoms in the Hydrogen exist at a certain energy level. This next section will explore what conditions one might expect to have if a “red” cloud of Hydrogen gas is observed in space. ...
... fraction of atoms in the Hydrogen exist at a certain energy level. This next section will explore what conditions one might expect to have if a “red” cloud of Hydrogen gas is observed in space. ...
Chapter 8: Periodic Properties of the Elements
... C. The magnetic quantum number, ml, identifies the three dimensional orientation in space. For an s orbital it is 0, for p it can be -1, 0, +1, d has 5 orientations, f has 7 Three quantum numbers are required to specify an orbital: principle, azimuthal and magnetic. An orbital is a place in an atom ...
... C. The magnetic quantum number, ml, identifies the three dimensional orientation in space. For an s orbital it is 0, for p it can be -1, 0, +1, d has 5 orientations, f has 7 Three quantum numbers are required to specify an orbital: principle, azimuthal and magnetic. An orbital is a place in an atom ...
Fermion Mixtures in an Optical Lattice
... Competition between kinetic and repulsive energy Bose-Einstein Condensate: kinetic energy wins ...
... Competition between kinetic and repulsive energy Bose-Einstein Condensate: kinetic energy wins ...
PPT | 485.4 KB
... In atomtronics scientists construct circuit elements using ultra-cold atomic gases where the atoms take the role of electrons. PFC scientists have developed an experiment that not only generates persistent superfluid currents--frictionless flow; this quantum fluid can be configured to switch atom-cu ...
... In atomtronics scientists construct circuit elements using ultra-cold atomic gases where the atoms take the role of electrons. PFC scientists have developed an experiment that not only generates persistent superfluid currents--frictionless flow; this quantum fluid can be configured to switch atom-cu ...
Boltzmann/Saha Equation Problems/Questions
... A) For a gas of neutral hydrogen (gn =2n2 ), at what temperature is the number of atoms in the first excited state only 1% of the number of atoms in the ground state? B) At what temperature is the number of atoms in the first excited state equal to 10% of the number in the ground state? C) For a gas ...
... A) For a gas of neutral hydrogen (gn =2n2 ), at what temperature is the number of atoms in the first excited state only 1% of the number of atoms in the ground state? B) At what temperature is the number of atoms in the first excited state equal to 10% of the number in the ground state? C) For a gas ...
Chapter 8 - Clayton State University
... The array of colors is called the emission spectrum of the element. Why are only certain colors emitted by each atom? Each atom has a distinctive electron structure. Figure 8-21 Figure 8-23 Bohr not only described the structure of atoms, but also explained the patterns of light found in atomic spect ...
... The array of colors is called the emission spectrum of the element. Why are only certain colors emitted by each atom? Each atom has a distinctive electron structure. Figure 8-21 Figure 8-23 Bohr not only described the structure of atoms, but also explained the patterns of light found in atomic spect ...
Unit 3 Spiraling
... -An ion is an atom that has a charge because it has gained or lost electrons. Positive ions (cations) have lost electrons; negative ions (anions) have gained electrons. The amount of charge is equal to the number of electrons lost or gained. -Max Planck discovered that atoms in a flame could absorb ...
... -An ion is an atom that has a charge because it has gained or lost electrons. Positive ions (cations) have lost electrons; negative ions (anions) have gained electrons. The amount of charge is equal to the number of electrons lost or gained. -Max Planck discovered that atoms in a flame could absorb ...
AP B - Unit 11 - 2013
... solid - x-rays are part of the electromagnetic spectrum →frequencies higher than those of ultraviolet radiation →can penetrate most materials with relative ease - x-rays are produced when high-speed electrons are suddenly decelerated →when a metal target is struck by electrons that have been acceler ...
... solid - x-rays are part of the electromagnetic spectrum →frequencies higher than those of ultraviolet radiation →can penetrate most materials with relative ease - x-rays are produced when high-speed electrons are suddenly decelerated →when a metal target is struck by electrons that have been acceler ...
genchem study guide test_4a
... B Only a max of 2 electrons in each orbital and they must have opposite spins C Subdivision of energy level; the numeric value of energy level is equal to the total number of these in that energy level D Empty Bus Seat Rule; electrons occupy equal‐ energy orbitals so that a maximum number of u ...
... B Only a max of 2 electrons in each orbital and they must have opposite spins C Subdivision of energy level; the numeric value of energy level is equal to the total number of these in that energy level D Empty Bus Seat Rule; electrons occupy equal‐ energy orbitals so that a maximum number of u ...
QUANTUM CLAUSTROPHOBIA
... the stuff of neutron stars, in an ultracold gas Deep down, the world is made of fermions. The familiar proton and neutron are fermions, and so are their constituent quarks. The fermionic nature of electrons underlies the structure of the periodic table of elements (and hence all of chemistry). Their ...
... the stuff of neutron stars, in an ultracold gas Deep down, the world is made of fermions. The familiar proton and neutron are fermions, and so are their constituent quarks. The fermionic nature of electrons underlies the structure of the periodic table of elements (and hence all of chemistry). Their ...
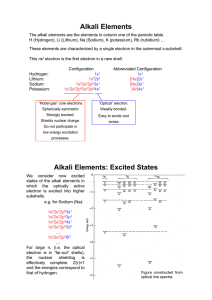
Alkali Elements Alkali Elements: Excited States
... Spin-Orbit Coupling: As before, the magnetic interaction between orbital- and spinmagnetic moments. However, now we have multiple electrons to consider (each with an orbital and an spin moment). ...
... Spin-Orbit Coupling: As before, the magnetic interaction between orbital- and spinmagnetic moments. However, now we have multiple electrons to consider (each with an orbital and an spin moment). ...
Slides from lecture 4.
... Now put 18 people (electrons) in the auditorium (atom). Note that no two people (electrons) can occupy the same seat (state)! So, when one row is filled, a new row is started. This is a fundamental property of quantum mechanics, i.e., no two electrons in an atom can exist in the same state. It is ca ...
... Now put 18 people (electrons) in the auditorium (atom). Note that no two people (electrons) can occupy the same seat (state)! So, when one row is filled, a new row is started. This is a fundamental property of quantum mechanics, i.e., no two electrons in an atom can exist in the same state. It is ca ...