Lecture Notes V: Spin, Pauli Exclusion Principle, Symmetric
... other source of magnetic dipole: With field on, atoms will deflect in “all” directions. (The “funny” shape is due to the magnet geometry.) ...
... other source of magnetic dipole: With field on, atoms will deflect in “all” directions. (The “funny” shape is due to the magnet geometry.) ...
Chemistry: Nuclear Reactions Guided Inquiry + n → + + 3 n +
... have 4 hydrogen atoms and 2 oxygen atoms. Nuclear reactions are reactions that affect the nucleus of an atom. In nature, unstable nuclei undergo nuclear reactions to form more stable nuclei. Stable ...
... have 4 hydrogen atoms and 2 oxygen atoms. Nuclear reactions are reactions that affect the nucleus of an atom. In nature, unstable nuclei undergo nuclear reactions to form more stable nuclei. Stable ...
AP Chemistry Summer Work Packet I have read and understand the i
... SO WHAT IS THE SUMMER WORK? All work should be done neatly and clearly on paper and organized in the order it was assigned. All work for every problem including units throughout is necessary for AP. This is an expectation on the AP exam in the spring and we want to get into the good habit early ____ ...
... SO WHAT IS THE SUMMER WORK? All work should be done neatly and clearly on paper and organized in the order it was assigned. All work for every problem including units throughout is necessary for AP. This is an expectation on the AP exam in the spring and we want to get into the good habit early ____ ...
Advanced Chemical Physics
... In the molecular orbitals (MO) approach is to consider the nuclei, without their electrons, at a distance apart which equal to the internuclear equilibrium distance, and to construct MOs around them from linear combination of the atomic orbitals (AO). Electrons are then fed into the MOs in pairs. He ...
... In the molecular orbitals (MO) approach is to consider the nuclei, without their electrons, at a distance apart which equal to the internuclear equilibrium distance, and to construct MOs around them from linear combination of the atomic orbitals (AO). Electrons are then fed into the MOs in pairs. He ...
Experimental evidence for shell model
... Relative to H-atom terms, alkali terms lie at lower energies. This shift increases the smaller l is. ...
... Relative to H-atom terms, alkali terms lie at lower energies. This shift increases the smaller l is. ...
Excitations
... faster due to their higher energy E=ћ. The center of a wave packet moves with the group velocity vg . That determines how fast a signal pulse propagates. Solitons In a non-linear medium, the phase velocity depends on the amplitude. The spread of a wave packet due to dispersion can be compensated by ...
... faster due to their higher energy E=ћ. The center of a wave packet moves with the group velocity vg . That determines how fast a signal pulse propagates. Solitons In a non-linear medium, the phase velocity depends on the amplitude. The spread of a wave packet due to dispersion can be compensated by ...
Electrons in Atoms
... The smaller the orbit, the lower the energy state The larger the orbit, the higher the energy state Bohr assigned numbers to these orbits based on their radius The number are called quantum numbers (n) n = 1 : first energy level, radius 0.0529 nm n = 2 : second energy level, radius 0.212 ...
... The smaller the orbit, the lower the energy state The larger the orbit, the higher the energy state Bohr assigned numbers to these orbits based on their radius The number are called quantum numbers (n) n = 1 : first energy level, radius 0.0529 nm n = 2 : second energy level, radius 0.212 ...
Exam 2 Sol/81/F01
... possible. Let’s call the oscillator coordinate x. The ground state wavefunction for the harmonic oscillator is an even function of x, but the first excited state wavefunc– tion is an odd function (one node right at x = 0). But that’s OK—the dipole operator, –ex, is also an odd function of x. Thus, t ...
... possible. Let’s call the oscillator coordinate x. The ground state wavefunction for the harmonic oscillator is an even function of x, but the first excited state wavefunc– tion is an odd function (one node right at x = 0). But that’s OK—the dipole operator, –ex, is also an odd function of x. Thus, t ...
Periodic Properties of the Elements Effective Nuclear Charge, Zeff
... Effective Nuclear Charge, Zeff The splitting of the principle energy level into the s, p, d, and f energy sublevels is best explained by using the concept of “effective” nuclear charge, Zeff. An electron in a higher energy level is “screened” from seeing 100% (all the protons) of the nuclear charge ...
... Effective Nuclear Charge, Zeff The splitting of the principle energy level into the s, p, d, and f energy sublevels is best explained by using the concept of “effective” nuclear charge, Zeff. An electron in a higher energy level is “screened” from seeing 100% (all the protons) of the nuclear charge ...
Grade 10 NSC Chemistry Curriculum
... sharing of electrons in the formation of a covalent bond, single, double and triple bonds electron diagrams of simple covalent molecules, names and formulae of covalent compounds. • Ionic bonding: transfer of electrons in the formation of ionic bonding, cations and anions, electron diagrams of simpl ...
... sharing of electrons in the formation of a covalent bond, single, double and triple bonds electron diagrams of simple covalent molecules, names and formulae of covalent compounds. • Ionic bonding: transfer of electrons in the formation of ionic bonding, cations and anions, electron diagrams of simpl ...
CHEM 115 EXAM #1
... A basketball has a diameter of 9.4 inches. The Earth has a surface area of 196,935,000 sq miles. How many basketballs are required to cover the Earth with a single layer of basketballs? (note: if your calculator does not have a key for π, try using 22/7) ...
... A basketball has a diameter of 9.4 inches. The Earth has a surface area of 196,935,000 sq miles. How many basketballs are required to cover the Earth with a single layer of basketballs? (note: if your calculator does not have a key for π, try using 22/7) ...
Quantum mechanical model of atom, Orbitals and Quantum Numbers
... The relative energy various orbitals can be obtained by using (n + l) rule. The energy value of orbital increases as its (n + l) value increases. for Ex: (n + l) value of 1S orbital is 1+0=1 and that of 2S orbital is 2+0=2.Hence energy of 1S<2S If two orbitals have the same value for (n + l), the or ...
... The relative energy various orbitals can be obtained by using (n + l) rule. The energy value of orbital increases as its (n + l) value increases. for Ex: (n + l) value of 1S orbital is 1+0=1 and that of 2S orbital is 2+0=2.Hence energy of 1S<2S If two orbitals have the same value for (n + l), the or ...
The Atom Board - ETC Montessori
... Why Teach with the Bohr Model? We designed the atom board based on the Bohr Model. So why did we chose the Bohr Model if its not the most recent conception of the atom? The “real” model is very complicated and abstract for middle school students, and even some high school students. Bohr’s model may ...
... Why Teach with the Bohr Model? We designed the atom board based on the Bohr Model. So why did we chose the Bohr Model if its not the most recent conception of the atom? The “real” model is very complicated and abstract for middle school students, and even some high school students. Bohr’s model may ...
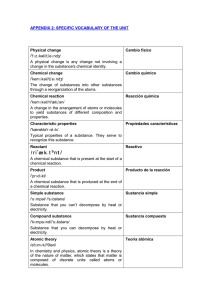
Unit 11: The Mole
... SOME VOCABULARY … Percent Composition: The percent by mass of each element in a compound. Empirical Formula: The formula with the smallest whole number ratio of the elements. ...
... SOME VOCABULARY … Percent Composition: The percent by mass of each element in a compound. Empirical Formula: The formula with the smallest whole number ratio of the elements. ...
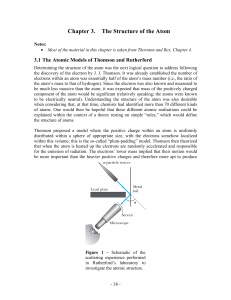
Chapter 3. The Structure of the Atom
... determination of the scattering angles confirmed that it is massive and concentrated). Although these results clearly excluded Thomson’s plum-pudding model, it did not completely rule out a classical model. Indeed, Thomson had previously considered a “planetary model” with a positively charged nucle ...
... determination of the scattering angles confirmed that it is massive and concentrated). Although these results clearly excluded Thomson’s plum-pudding model, it did not completely rule out a classical model. Indeed, Thomson had previously considered a “planetary model” with a positively charged nucle ...
Chem Regents 2015 A Few Things
... In BOTH types of cell the same types of reaction occur at the same electrode: ANode — OXidation ...
... In BOTH types of cell the same types of reaction occur at the same electrode: ANode — OXidation ...
Solutions of the Schrödinger equation for the ground helium by finite
... helium by finite element method by Jiahua Guo 1. Introduction Multi-body Coulomb problems are traditional challenging problems [1]. The failure of theory to describe precisely the system stimulated many mathematicians and physicists to devote themselves in using various methods to obtain the energie ...
... helium by finite element method by Jiahua Guo 1. Introduction Multi-body Coulomb problems are traditional challenging problems [1]. The failure of theory to describe precisely the system stimulated many mathematicians and physicists to devote themselves in using various methods to obtain the energie ...