AP Chemistry Summer Study Guide
... Dipole-Dipole: Permanent IMF present in polar molecules Direct Relationship: Relationship between two variables where when one changes, the other changes in the same manner Dissociate: To break into ions Dissolve: To break into smaller pieces Distillation: Process of separating liquids based on diff ...
... Dipole-Dipole: Permanent IMF present in polar molecules Direct Relationship: Relationship between two variables where when one changes, the other changes in the same manner Dissociate: To break into ions Dissolve: To break into smaller pieces Distillation: Process of separating liquids based on diff ...
10.4: Helium Atom - PhysWiki
... Hence, we conclude that in excited states of helium the spin singlet state has a higher energy than the spin triplet state. Incidentally, helium in the spin singlet state is known as para-helium, whereas helium in the triplet state is called ortho-helium. As we have seen, for the ground state, only ...
... Hence, we conclude that in excited states of helium the spin singlet state has a higher energy than the spin triplet state. Incidentally, helium in the spin singlet state is known as para-helium, whereas helium in the triplet state is called ortho-helium. As we have seen, for the ground state, only ...
Chapter 10_Handouts_6
... specific ratio by mass according to the law of definite proportions. In a mixture, the components are not present in a specific ratio by mass. ...
... specific ratio by mass according to the law of definite proportions. In a mixture, the components are not present in a specific ratio by mass. ...
Chapter 10 Handouts_1
... 10-7. The Periodic Table The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the periodic law about 1869 which states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular intervals. The periodic table is a listing of the eleme ...
... 10-7. The Periodic Table The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the periodic law about 1869 which states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular intervals. The periodic table is a listing of the eleme ...
Chapter 9 – Many Electron Atoms
... All permutations can be written as a product of transpositions p = TijTklTmj .... either odd or even. Hence action of all Tij determines action of P for any permutation. ...
... All permutations can be written as a product of transpositions p = TijTklTmj .... either odd or even. Hence action of all Tij determines action of P for any permutation. ...
Ms - cloudfront.net
... Bonding 18. Describe how a cation and an anion is formed. 19. What do metals typically do when they become ions? What about nonmetals? 20. What type of elements bond together in ionic bonds? covalent bonds? metallic bonds? 21. How do electrons in ionic bonding interact? Covalent bonding? 22. How doe ...
... Bonding 18. Describe how a cation and an anion is formed. 19. What do metals typically do when they become ions? What about nonmetals? 20. What type of elements bond together in ionic bonds? covalent bonds? metallic bonds? 21. How do electrons in ionic bonding interact? Covalent bonding? 22. How doe ...
Atomic Emission Spectra, Electron Configuration, Periodicity
... book refers to these groups as 1A-8A, and 3B-7B. TRANSLATE THESE INTO GROUPS 1-18! 2. Which group numbers correspond to the representative elements, and why are they given that name? 3. Define atomic radius. What is the trend across a period for the atomic radius of an atom? 4. Define ionization ene ...
... book refers to these groups as 1A-8A, and 3B-7B. TRANSLATE THESE INTO GROUPS 1-18! 2. Which group numbers correspond to the representative elements, and why are they given that name? 3. Define atomic radius. What is the trend across a period for the atomic radius of an atom? 4. Define ionization ene ...
bonding, structure, properties and energy changes
... © ESA Publications (NZ) Ltd – ISBN 978-0-908340-11-8 – Copying or scanning from ESA workbooks is limited to 3% under the NZ Copyright Act. ...
... © ESA Publications (NZ) Ltd – ISBN 978-0-908340-11-8 – Copying or scanning from ESA workbooks is limited to 3% under the NZ Copyright Act. ...
Interaction of Photons with Matter - Faculty
... The Standard Model of Particle Physics D. Atomic Physics: The Role of Quantum Numbers. 1. As mentioned above, the energy, orbital angular momentum, and spin angular momentum do not vary in a continuous way for electrons that are bound in atoms and molecules. Instead, they can only have values that a ...
... The Standard Model of Particle Physics D. Atomic Physics: The Role of Quantum Numbers. 1. As mentioned above, the energy, orbital angular momentum, and spin angular momentum do not vary in a continuous way for electrons that are bound in atoms and molecules. Instead, they can only have values that a ...
2013 Final Exam Answers
... a) closer to C because carbon has a larger radius and thus exerts greater control over the shared electron pair. ...
... a) closer to C because carbon has a larger radius and thus exerts greater control over the shared electron pair. ...
3. Atomic and molecular structure
... out. We now consider the disconcerting fact that despite all the effort we have gone to, we do not really know what we have on our hands. Wavefunctions have no physical significance as such. In order to interpret them, we have to do some further calculations. When introducing his theory, Schrödinger ...
... out. We now consider the disconcerting fact that despite all the effort we have gone to, we do not really know what we have on our hands. Wavefunctions have no physical significance as such. In order to interpret them, we have to do some further calculations. When introducing his theory, Schrödinger ...
Answers to Critical Thinking Questions 4
... a) 1s22s22p63s23p44s1 – the 3p orbitals were not completely filled before electrons were added to 4s (violating the Aufbau principle). The correct configuration is 1s22s22p63s23p5 b) 1s22s22p63s23p7 – the maximum number of electrons in 3p is 6 (violating the Pauli exclusion principle). The correct c ...
... a) 1s22s22p63s23p44s1 – the 3p orbitals were not completely filled before electrons were added to 4s (violating the Aufbau principle). The correct configuration is 1s22s22p63s23p5 b) 1s22s22p63s23p7 – the maximum number of electrons in 3p is 6 (violating the Pauli exclusion principle). The correct c ...
Chemistry 2011-2012
... SC1a. Relate the role of nuclear fusion in producing essentially all elements heavier than helium. SC1b. Identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. SC2 Students will relate how the Law of Conservation of Matter is used to determine chemical composition in compounds and chemical r ...
... SC1a. Relate the role of nuclear fusion in producing essentially all elements heavier than helium. SC1b. Identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. SC2 Students will relate how the Law of Conservation of Matter is used to determine chemical composition in compounds and chemical r ...
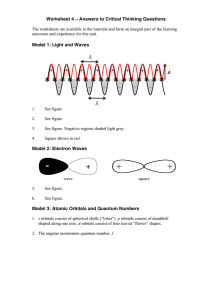
Answers to Critical Thinking Questions 4
... The 2s has one radial node and the 3s has two radial nodes. 3p have one radial node. In general, the number of radial nodes is equal to n – l - 1. ...
... The 2s has one radial node and the 3s has two radial nodes. 3p have one radial node. In general, the number of radial nodes is equal to n – l - 1. ...
Week 6 Review 2014-15
... (constant) composition and unique properties. Contains only 1 type element or compound; homogeneous ...
... (constant) composition and unique properties. Contains only 1 type element or compound; homogeneous ...