
Lecture 13 - UD Physics
... can be arranged in an n × n matrix. The Dik are therefore called electric-dipole matrix elements. If some of the matrix elements are zero, the corresponding transition does not occur. One says that this transition is “not allowed” but “forbidden”, or electric-dipole forbidden. Note that the absolute ...
... can be arranged in an n × n matrix. The Dik are therefore called electric-dipole matrix elements. If some of the matrix elements are zero, the corresponding transition does not occur. One says that this transition is “not allowed” but “forbidden”, or electric-dipole forbidden. Note that the absolute ...
No Slide Title
... The problem with classical physics of the time was that an electron orbiting a nucleus would lose energy & eventually collapse into the nucleus. In Bohr’s model, an electron can travel around a nucleus without radiating energy. Furthermore, an electron in a given orbit has a certain definite amount ...
... The problem with classical physics of the time was that an electron orbiting a nucleus would lose energy & eventually collapse into the nucleus. In Bohr’s model, an electron can travel around a nucleus without radiating energy. Furthermore, an electron in a given orbit has a certain definite amount ...
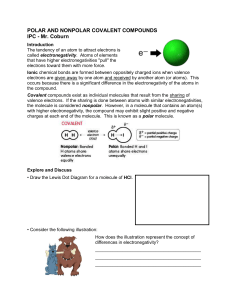
Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Compounds
... Recall that polarity refers to an unequal sharing of electrons resulting from differences in electronegativity. There is a distinction between polar bonds and polar molecules. A polar covalent bond occurs when bonding electrons are more attracted to an atom with a higher electronegativity. The polar ...
... Recall that polarity refers to an unequal sharing of electrons resulting from differences in electronegativity. There is a distinction between polar bonds and polar molecules. A polar covalent bond occurs when bonding electrons are more attracted to an atom with a higher electronegativity. The polar ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... Answer all questions in this part. Directions (1–30): For each statement or question, record on your separate answer sheet the number of the word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question. Some questions may require the use of the 2011 Edition Reference ...
... Answer all questions in this part. Directions (1–30): For each statement or question, record on your separate answer sheet the number of the word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question. Some questions may require the use of the 2011 Edition Reference ...
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context
... A) carbon, sodium, hydrogen, nitrogen B) carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, hydrogen C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, nitrogen D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen E) carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, calcium 2) Trace elements are those required by an organism in only minute quantities. Which of the following is a t ...
... A) carbon, sodium, hydrogen, nitrogen B) carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, hydrogen C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, nitrogen D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen E) carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, calcium 2) Trace elements are those required by an organism in only minute quantities. Which of the following is a t ...
Chapter 7: ELECTRONS IN ATOMS AND PERIODIC PROPERTIES
... orbital occupancy indicated...that is, electrons that occupy the same orbital appear as paired dots. ...
... orbital occupancy indicated...that is, electrons that occupy the same orbital appear as paired dots. ...
orbit - Seattle Central College
... orbital occupancy indicated...that is, electrons that occupy the same orbital appear as paired dots. ...
... orbital occupancy indicated...that is, electrons that occupy the same orbital appear as paired dots. ...
Chapter 11
... Quanta - the amount of energy needed to move from one energy level to another. Quantum leap in energy. Schrödinger derived an equation that described the energy and position of the electrons in an atom Treated electrons as waves ...
... Quanta - the amount of energy needed to move from one energy level to another. Quantum leap in energy. Schrödinger derived an equation that described the energy and position of the electrons in an atom Treated electrons as waves ...
Chapter 6.2 Notes
... - have ionic bonds – an attractive force between oppositely charged ions, which form when electrons are transferred from one to another - one atom loses one or more electrons and another atom or atoms gains them - the oppositely charged ions are then attracted to each other and form an ionic bond ...
... - have ionic bonds – an attractive force between oppositely charged ions, which form when electrons are transferred from one to another - one atom loses one or more electrons and another atom or atoms gains them - the oppositely charged ions are then attracted to each other and form an ionic bond ...
C2_revision_slides_V3_+_questions_+_MS_-_H[1]
... delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of positive ions with electrons between the ions holding them together by strong electrostatic attractions. • Metals conduct heat and electricity because of the delocalised electrons in their structures. • The layers of atoms ...
... delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of positive ions with electrons between the ions holding them together by strong electrostatic attractions. • Metals conduct heat and electricity because of the delocalised electrons in their structures. • The layers of atoms ...
Ionic bonding
... Positive ions in a sea of delocalised electrons Metals • Metals consist of giant structures of atoms arranged in a regular pattern. • The electrons in the highest occupied energy levels (outer shell) of metal atoms are delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of pos ...
... Positive ions in a sea of delocalised electrons Metals • Metals consist of giant structures of atoms arranged in a regular pattern. • The electrons in the highest occupied energy levels (outer shell) of metal atoms are delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of pos ...
C2 revision slides V3 + questions + MS
... Positive ions in a sea of delocalised electrons Metals • Metals consist of giant structures of atoms arranged in a regular pattern. • The electrons in the highest occupied energy levels (outer shell) of metal atoms are delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of pos ...
... Positive ions in a sea of delocalised electrons Metals • Metals consist of giant structures of atoms arranged in a regular pattern. • The electrons in the highest occupied energy levels (outer shell) of metal atoms are delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of pos ...
Ionic bonding - Animated Science
... delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of positive ions with electrons between the ions holding them together by strong electrostatic attractions. • Metals conduct heat and electricity because of the delocalised electrons in their structures. • The layers of atoms ...
... delocalised and so free to move through the whole structure. • a structure of positive ions with electrons between the ions holding them together by strong electrostatic attractions. • Metals conduct heat and electricity because of the delocalised electrons in their structures. • The layers of atoms ...
Chemistry - School District of Springfield Township
... Unit III: The Organization of Matter • The Periodic Table evolved over time as scientists discovered more useful ways to compare and organize the elements. o Elements with similar properties have been placed into groups. o The physical and chemical properties of the elements repeat in a regular patt ...
... Unit III: The Organization of Matter • The Periodic Table evolved over time as scientists discovered more useful ways to compare and organize the elements. o Elements with similar properties have been placed into groups. o The physical and chemical properties of the elements repeat in a regular patt ...
Sample Exercise 2.1 Illustrating the Size of an Atom
... Each compound is ionic and is named using the guidelines we have already discussed. In naming ionic compounds, it is important to recognize polyatomic ions and to determine the charge of cations with variable charge. (a) The cation in this compound is K+, and the anion is SO42–. (If you thought the ...
... Each compound is ionic and is named using the guidelines we have already discussed. In naming ionic compounds, it is important to recognize polyatomic ions and to determine the charge of cations with variable charge. (a) The cation in this compound is K+, and the anion is SO42–. (If you thought the ...
















![C2_revision_slides_V3_+_questions_+_MS_-_H[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000092833_1-97fb33725e7f1ef12029ed42751d3dca-300x300.png)





