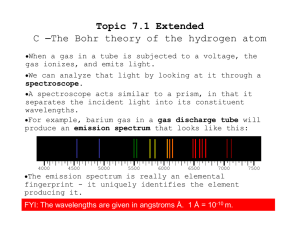
Topic 7_1_Ext C__The Bohr theory of the hydrogen atom
... accelerating charges. Since the hydrogen atom only radiates when its electron "drops" from one excited state to a less energetic state, Bohr postulated that "the hydrogen electron does NOT radiate energy when it is in one of its bound states (allowed by n). It only does so when "dropping" from a hig ...
... accelerating charges. Since the hydrogen atom only radiates when its electron "drops" from one excited state to a less energetic state, Bohr postulated that "the hydrogen electron does NOT radiate energy when it is in one of its bound states (allowed by n). It only does so when "dropping" from a hig ...
Bonding - Berkeley City College
... •The 'd+' and 'd-' symbols indicate partial positive and negative charges. •The arrow indicates the "pull" of electrons off the hydrogen and towards the more electronegative atom. ...
... •The 'd+' and 'd-' symbols indicate partial positive and negative charges. •The arrow indicates the "pull" of electrons off the hydrogen and towards the more electronegative atom. ...
Spontaneous Emission Rates in Forbidden Lines
... to minutes). This makes the laboratory determination of transition rates extremely difficult if not impossible. In order to make use of these emission line diagnostics, we must therefore have highly reliable theoretical values for the involved transition rates that can only be achieved through compu ...
... to minutes). This makes the laboratory determination of transition rates extremely difficult if not impossible. In order to make use of these emission line diagnostics, we must therefore have highly reliable theoretical values for the involved transition rates that can only be achieved through compu ...
IO-IY
... 19. A diffraction grating is used in the first order to separate the wavelengths in the Balmer series of atomic hydrogen. (Section 27.7 discusses diffraction gratings.) The grating and an observation screen (see Figure 27.32) are separated by a distance of 81.0 cm. You may assume that () is small, s ...
... 19. A diffraction grating is used in the first order to separate the wavelengths in the Balmer series of atomic hydrogen. (Section 27.7 discusses diffraction gratings.) The grating and an observation screen (see Figure 27.32) are separated by a distance of 81.0 cm. You may assume that () is small, s ...
Document
... SOLUTION: (a) ClO4- is perchlorate; Fe must have a 2+ charge since there are 2 ClO4- ions. This is iron(II) perchlorate. (b) The anion sulfite is SO32-; therefore you need 2 Na+ for each sulfite. The formula is Na2SO3. (c) The ionic compound is barium hydroxide. When water is included in the formula ...
... SOLUTION: (a) ClO4- is perchlorate; Fe must have a 2+ charge since there are 2 ClO4- ions. This is iron(II) perchlorate. (b) The anion sulfite is SO32-; therefore you need 2 Na+ for each sulfite. The formula is Na2SO3. (c) The ionic compound is barium hydroxide. When water is included in the formula ...
prereq reading
... Bohr’s hypothesis was a combination of Rutherford’s atomic model, Planck’s quantum theory, Einstein’s photon theory of light, which proposed that the single electron revolves around the nucleus in a circular orbit. The energy being defined by the singly charged electron and nucleus (proton) and the ...
... Bohr’s hypothesis was a combination of Rutherford’s atomic model, Planck’s quantum theory, Einstein’s photon theory of light, which proposed that the single electron revolves around the nucleus in a circular orbit. The energy being defined by the singly charged electron and nucleus (proton) and the ...
Theory of Chemical Bonds
... the wave function of the atomic orbitals. During the calculation of the eigenvalues of the Schrödinger equation with equ. 4.15, we get integrals which contain the square of the wave function of an atomic orbital (∫ψ1*H ψ1dτ). These integral represent the Coulomb interaction energy between the electr ...
... the wave function of the atomic orbitals. During the calculation of the eigenvalues of the Schrödinger equation with equ. 4.15, we get integrals which contain the square of the wave function of an atomic orbital (∫ψ1*H ψ1dτ). These integral represent the Coulomb interaction energy between the electr ...
Unit 1: Basic Chemistry for Biology QUIZ STUDY GUIDE Things to
... -You will see 12 of them on the quiz tomorrow. ...
... -You will see 12 of them on the quiz tomorrow. ...
The Spectrum of Helium and Calcium
... Figure 1. Some energy levels of He, with an allowed and a forbidden transition to the ground state. 3c. Fine splitting. The 3 P levels in Fig. 1 are actually each split into three levels because S = 1 can add to L = 1 to give total angular momentum J = 0, 1, 2. Similarly, the 3 D levels are split in ...
... Figure 1. Some energy levels of He, with an allowed and a forbidden transition to the ground state. 3c. Fine splitting. The 3 P levels in Fig. 1 are actually each split into three levels because S = 1 can add to L = 1 to give total angular momentum J = 0, 1, 2. Similarly, the 3 D levels are split in ...
Attachment: Click to download
... Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams Use atomic mass units. an atomic mass unit (amu) is one twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom This gives us a basis for comparison The decimal numbers on the table are atomic masses in amu ...
... Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams Use atomic mass units. an atomic mass unit (amu) is one twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom This gives us a basis for comparison The decimal numbers on the table are atomic masses in amu ...
Chap8_theatom
... In water waves, the quantity that varies periodically is the height of the water surface; in sound waves, it is air pressure; in light waves, it is electric and magnetic fields. What varies in the case of matter waves?? The quantity whose variations make up matter waves is called the wave function, ...
... In water waves, the quantity that varies periodically is the height of the water surface; in sound waves, it is air pressure; in light waves, it is electric and magnetic fields. What varies in the case of matter waves?? The quantity whose variations make up matter waves is called the wave function, ...























