
LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-18
... CH3 –NH2 + HCl ---> CH3 –NH3 +ClThe reaction in the example above results in a hydrochloride salt of the amine and is a very important reaction in pharmacy. Many drugs contain an amine functional group, and if they contain many carbon atoms, they are not very soluble in water. The salts formed from ...
... CH3 –NH2 + HCl ---> CH3 –NH3 +ClThe reaction in the example above results in a hydrochloride salt of the amine and is a very important reaction in pharmacy. Many drugs contain an amine functional group, and if they contain many carbon atoms, they are not very soluble in water. The salts formed from ...
Final Exam Review Sheet Chemistry 110a/1998
... cation, and anion using a resonance and molecular orbital argument. How does the allylic radical compare in stability to 3°, 2°, and 1°? How about the allylic cation, in this regard? The pKa of an allylic hydrogen is 41: how can you use this value to say that the allylic anion is more stable than th ...
... cation, and anion using a resonance and molecular orbital argument. How does the allylic radical compare in stability to 3°, 2°, and 1°? How about the allylic cation, in this regard? The pKa of an allylic hydrogen is 41: how can you use this value to say that the allylic anion is more stable than th ...
5. Use your phone to take a picture of each completed model. Put it
... words to someone who has not seen it? The “octet” rule appears to be a very important rule governing the structures of molecules. In light of your work with models, provide a simple explanation for the importance of 8 electrons. As a test of what you have learned from this exercise, predict and draw ...
... words to someone who has not seen it? The “octet” rule appears to be a very important rule governing the structures of molecules. In light of your work with models, provide a simple explanation for the importance of 8 electrons. As a test of what you have learned from this exercise, predict and draw ...
Document
... Introduction to Bonding • Chemical bond: an interaction between atoms or ions that results in a reduction of the potential energy of the system, thereby becoming more stable • Three types of bonds: ionic, metallic, and covalent • The bond type depends on the atoms’ electronegativities ...
... Introduction to Bonding • Chemical bond: an interaction between atoms or ions that results in a reduction of the potential energy of the system, thereby becoming more stable • Three types of bonds: ionic, metallic, and covalent • The bond type depends on the atoms’ electronegativities ...
CSUS Department of Chemistry Molecular Shapes Chem. 1A Page
... Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) Section 8.6 in your text. One aspect of chemistry that often proves to be difficult for many students is the visualization of compounds, ions and molecules in three dimensional space. In lecture and homework you have seen how the octet rule is ...
... Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) Section 8.6 in your text. One aspect of chemistry that often proves to be difficult for many students is the visualization of compounds, ions and molecules in three dimensional space. In lecture and homework you have seen how the octet rule is ...
CHM 260 – Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
... Section 1 – At the end of this section, the student should be able to: 1. Understand why there are so many organic compounds. 2. List some common elements, besides carbon, found in many organic compounds. 3. Describe the types of orbitals found in each of the first four main energy levels. 4. Write ...
... Section 1 – At the end of this section, the student should be able to: 1. Understand why there are so many organic compounds. 2. List some common elements, besides carbon, found in many organic compounds. 3. Describe the types of orbitals found in each of the first four main energy levels. 4. Write ...
Sample Exam 1
... (9 pts) Draw one valid Lewis structure for each compound. Assign formal charges to atoms if necessary. a. nitromethane, CH3NO2 b. ozone, O3 c. hydrazine, N2H4 ...
... (9 pts) Draw one valid Lewis structure for each compound. Assign formal charges to atoms if necessary. a. nitromethane, CH3NO2 b. ozone, O3 c. hydrazine, N2H4 ...
SCH4C Organic Test
... 4. T The study of hydrocarbons is the study of a class of organic compounds that contain mostly carbon and hydrogen. _________________________ ...
... 4. T The study of hydrocarbons is the study of a class of organic compounds that contain mostly carbon and hydrogen. _________________________ ...
SC 119 PRACTICE Assessment:
... Explain why propane has a lower boiling point than water. Provide an analysis of the interparticle forces between two molecules of propane and interparticle forces between two molecules of water and use these analyses to support your answer. ...
... Explain why propane has a lower boiling point than water. Provide an analysis of the interparticle forces between two molecules of propane and interparticle forces between two molecules of water and use these analyses to support your answer. ...
Aromatic Compounds
... Alkyl groups have an electron-donating inductive effect Nitration of toluene occurs ortho and para to the alkyl group because a resonance form places the positive charge directly on the alkyl-substituted carbon where it can be stabilized by the electron-donating inductive effect of the alkyl group ...
... Alkyl groups have an electron-donating inductive effect Nitration of toluene occurs ortho and para to the alkyl group because a resonance form places the positive charge directly on the alkyl-substituted carbon where it can be stabilized by the electron-donating inductive effect of the alkyl group ...
8.2-Organic Nomenclature packet
... between the carbon atoms is shorter in the double bond. It is also more reactive than a single bond since the bond (the second pair of electrons) is farther from the nuclei. Naming is a little bit more complex for alkenes than alkanes. Since the double bond could appear at various sites in a typic ...
... between the carbon atoms is shorter in the double bond. It is also more reactive than a single bond since the bond (the second pair of electrons) is farther from the nuclei. Naming is a little bit more complex for alkenes than alkanes. Since the double bond could appear at various sites in a typic ...
Synthesis of a New Structure B2H4 from B2H6 Highly Selective
... B2D4 conform to the calculated structure shown in Fig. 2. On that basis they assigned this new species as diborane(4). Because the infrared absorption features appear with vacuum-ultraviolet photons of wavelength 180 nm, the photolysis threshold to synthesize diborane(4) is about 6.6 eV. Although th ...
... B2D4 conform to the calculated structure shown in Fig. 2. On that basis they assigned this new species as diborane(4). Because the infrared absorption features appear with vacuum-ultraviolet photons of wavelength 180 nm, the photolysis threshold to synthesize diborane(4) is about 6.6 eV. Although th ...
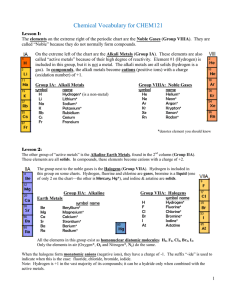
Vocabulary CHEM121
... Acids: anything giving H+ when dissolved in water Bases: anything giving OH- when dissolved in water Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecular/covalent compounds: Non-metals can combine with other non-metals to form molecules. Molecules are covalently bonded groups of atoms—they do not ...
... Acids: anything giving H+ when dissolved in water Bases: anything giving OH- when dissolved in water Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecular/covalent compounds: Non-metals can combine with other non-metals to form molecules. Molecules are covalently bonded groups of atoms—they do not ...
Untitled
... A HYDROXYL GROUP consists of a hydrogen atom bonded to an oxygen atom, which in turn is bonded to the carbon skeleton. In a CARBONYL GROUP a carbon atom is linked by a double bond to an oxygen atom. If this functional group is found at either end then it is called an ALDEHYDE, but if it is located i ...
... A HYDROXYL GROUP consists of a hydrogen atom bonded to an oxygen atom, which in turn is bonded to the carbon skeleton. In a CARBONYL GROUP a carbon atom is linked by a double bond to an oxygen atom. If this functional group is found at either end then it is called an ALDEHYDE, but if it is located i ...
Παρουσίαση του PowerPoint
... paper plan the work they are about to undertake. Possible routes are drawn out, criticized, modified again when the behavior of the compounds in the flask turns out to be different from what was expected, until finally success is achieved. The aim of this lecture is to show how this planning is done ...
... paper plan the work they are about to undertake. Possible routes are drawn out, criticized, modified again when the behavior of the compounds in the flask turns out to be different from what was expected, until finally success is achieved. The aim of this lecture is to show how this planning is done ...
Chem 216 H W13 Notes - Dr. Masato Koreeda Thin
... (1) UV lamp – The UV lamp in the lab emits UV light having the 254 nm wavelength. The silica gel TLC plates we use have an inorganic fluorescent agent (<0.5%) impregnated into the adsorbent layer. When illuminated with an ultraviolet (UV) lamp, the absorbent then glows the pale green or blue colored ...
... (1) UV lamp – The UV lamp in the lab emits UV light having the 254 nm wavelength. The silica gel TLC plates we use have an inorganic fluorescent agent (<0.5%) impregnated into the adsorbent layer. When illuminated with an ultraviolet (UV) lamp, the absorbent then glows the pale green or blue colored ...
Technical Data Sheet - Lučební závody Kolín
... effective for reduction of compounds containing carbonyl and carboxyl groups such as aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their esters, acid anhydrides, acyl halides, lactones, amides, imides, lactams and also for reduction of oximes, aromatic nitriles, chlorinated hydrocarbons, nitro compounds ...
... effective for reduction of compounds containing carbonyl and carboxyl groups such as aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their esters, acid anhydrides, acyl halides, lactones, amides, imides, lactams and also for reduction of oximes, aromatic nitriles, chlorinated hydrocarbons, nitro compounds ...
Newtechniques[1]
... The 13C NMR spectra can be used to uniquely identify each amino acid. Glycine and alanine will produce 13C NMR spectra with the following number of peaks. A. B. C. D. ...
... The 13C NMR spectra can be used to uniquely identify each amino acid. Glycine and alanine will produce 13C NMR spectra with the following number of peaks. A. B. C. D. ...
Test 1 Key - WEB . WHRSD . ORG
... Figure 2–1 46. Calculating Based on Figure 2–1, what is the mass number of carbon? 47. Applying Concepts Based on Figure 2–1, what is the atomic number of oxygen? 48. Applying Concepts Using Figure 2–1, how many electrons does an atom of aluminum contain? 49. Applying Concepts According to Figure 2– ...
... Figure 2–1 46. Calculating Based on Figure 2–1, what is the mass number of carbon? 47. Applying Concepts Based on Figure 2–1, what is the atomic number of oxygen? 48. Applying Concepts Using Figure 2–1, how many electrons does an atom of aluminum contain? 49. Applying Concepts According to Figure 2– ...
Electron Dot Diagrams for Four Simple Molecules ammonia, NH3
... 6. Complete the paragraph below using the words in the list. Some words may need to be used twice. Some will not be used at all. covalent Group 18 inner valence (or outer) two four eight hydrogen molecule non-metals metals A ________________ is a group of two or more atoms that are bonded together b ...
... 6. Complete the paragraph below using the words in the list. Some words may need to be used twice. Some will not be used at all. covalent Group 18 inner valence (or outer) two four eight hydrogen molecule non-metals metals A ________________ is a group of two or more atoms that are bonded together b ...
chapter 2
... 3. If a noble gas could form a +1 ion, which of the noble gases would form a +1 ion most easily? Rn because it is the largest so there is a lot of electron shielding on the outermost electrons, making it easier to lose one electron and gain a +1 charge. CHAPTER 12 1. With respect to electrons, how d ...
... 3. If a noble gas could form a +1 ion, which of the noble gases would form a +1 ion most easily? Rn because it is the largest so there is a lot of electron shielding on the outermost electrons, making it easier to lose one electron and gain a +1 charge. CHAPTER 12 1. With respect to electrons, how d ...
Chemistry of Carbon
... Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds C atoms are versatile building blocks bonding properties 4 stable covalent bonds ...
... Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds C atoms are versatile building blocks bonding properties 4 stable covalent bonds ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.

















![Newtechniques[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008290568_1-ce9574822ee68efb0424b4d58f36c344-300x300.png)




