Statistics 1 Revision Notes
... Suppose the die is weighted to increase the chance of a six. We might then find, after experimenting, that the probability of a six is and the probability of a one is , with the probability of other faces remaining at . In this case we have refined, or improved, the model to give a truer picture. Ex ...
... Suppose the die is weighted to increase the chance of a six. We might then find, after experimenting, that the probability of a six is and the probability of a one is , with the probability of other faces remaining at . In this case we have refined, or improved, the model to give a truer picture. Ex ...
The confidence level of an interval estimate of a parameter is the
... • The estimator should be an unbiased estimator. That is, the expected value or the mean of the estimates obtained from samples of a given size is equal to the parameter being estimated. • The estimator should be consistent. For a consistent estimator, as sample size increases, the value of the esti ...
... • The estimator should be an unbiased estimator. That is, the expected value or the mean of the estimates obtained from samples of a given size is equal to the parameter being estimated. • The estimator should be consistent. For a consistent estimator, as sample size increases, the value of the esti ...
Characterization - NYU Computer Science
... Not confined to categorical data nor particular measures. How it is done? Collect the task-relevant data( initial relation) using a relational database query Perform generalization by attribute removal or attribute generalization. Apply aggregation by merging identical, generalized tuples and a ...
... Not confined to categorical data nor particular measures. How it is done? Collect the task-relevant data( initial relation) using a relational database query Perform generalization by attribute removal or attribute generalization. Apply aggregation by merging identical, generalized tuples and a ...
Experiment 2 Random Error and Basic Statistics
... 4.1 Introduction In this experiment we ask you to perform a simple repetitive measurement in order to investigate random and systematic errors. The idea is that we will compare the time interval from the large digital “clock” at the front of the room, with a more precise instrument (the hand timers) ...
... 4.1 Introduction In this experiment we ask you to perform a simple repetitive measurement in order to investigate random and systematic errors. The idea is that we will compare the time interval from the large digital “clock” at the front of the room, with a more precise instrument (the hand timers) ...
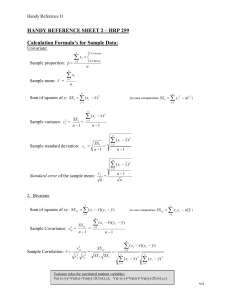
Formulas - UF-Stat
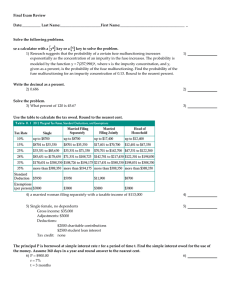
... 15. A waiter believes that his tips from various customers have a slightly right skewed distribution with a mean of 10 dollars and a standard deviation of 2.50 dollars. What is the probability that the average of 35 customers will be more than 13 dollars? a) almost 1 b) almost zero c) 0.1151 d) 0.88 ...
... 15. A waiter believes that his tips from various customers have a slightly right skewed distribution with a mean of 10 dollars and a standard deviation of 2.50 dollars. What is the probability that the average of 35 customers will be more than 13 dollars? a) almost 1 b) almost zero c) 0.1151 d) 0.88 ...
Using Stata for One Sample Tests
... The parameters are variable name = hypothesized probability of success. Likewise, to get the socalled exact (Clopper-Pearson) confidence interval, use the ci command with the binomial parameter: . ci black, binomial level(99) -- Binomial Exact -Variable | Obs Mean Std. Err. [99% Conf. Interval] ---- ...
... The parameters are variable name = hypothesized probability of success. Likewise, to get the socalled exact (Clopper-Pearson) confidence interval, use the ci command with the binomial parameter: . ci black, binomial level(99) -- Binomial Exact -Variable | Obs Mean Std. Err. [99% Conf. Interval] ---- ...
11.2
... Set up the hypotheses Select the level of significance α Compute the test statistic Compare the test statistic with the appropriate critical values Reach a do not reject or reject the null hypothesis conclusion ...
... Set up the hypotheses Select the level of significance α Compute the test statistic Compare the test statistic with the appropriate critical values Reach a do not reject or reject the null hypothesis conclusion ...
for Version 1.0, June 2011 TECHNICAL APPENDIX
... Statistical inference is the process whereby statistics computed from the sample data are used to infer population parameters. For example, ground truth travel time is generally defined as the average travel time of a link during some time interval. This is equivalent to stating that ground truth ...
... Statistical inference is the process whereby statistics computed from the sample data are used to infer population parameters. For example, ground truth travel time is generally defined as the average travel time of a link during some time interval. This is equivalent to stating that ground truth ...