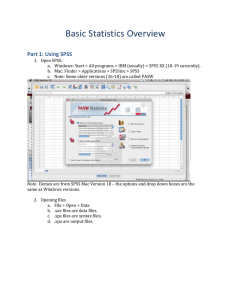
Lab 1 - Professor Mo Geraghty
... 11. Write a paragraph summarizing your results. Do you see any problems or bias with this study? ...
... 11. Write a paragraph summarizing your results. Do you see any problems or bias with this study? ...
Lecture 8 Quantitative Procedures (2)
... Simple t-test: This test is typically used with score data from two independent samples of subjects (e.g. trained and non-trained). The nullhypothesis is that there is NO difference in the two population means. In other words , the observed difference between the sample means is due only to chance. ...
... Simple t-test: This test is typically used with score data from two independent samples of subjects (e.g. trained and non-trained). The nullhypothesis is that there is NO difference in the two population means. In other words , the observed difference between the sample means is due only to chance. ...
Lecture 8
... Simple t-test: This test is typically used with score data from two independent samples of subjects (e.g. trained and non-trained). The nullhypothesis is that there is NO difference in the two population means. In other words , the observed difference between the sample means is due only to chance. ...
... Simple t-test: This test is typically used with score data from two independent samples of subjects (e.g. trained and non-trained). The nullhypothesis is that there is NO difference in the two population means. In other words , the observed difference between the sample means is due only to chance. ...
Document
... ◦ if the population size N is large in relation to the sample size n, then the distribution of X is approximately a binomial distribution with parameters n and p. For the remainder of this text we will suppose that the underlying population is large in relation to the sample size, and we will take t ...
... ◦ if the population size N is large in relation to the sample size n, then the distribution of X is approximately a binomial distribution with parameters n and p. For the remainder of this text we will suppose that the underlying population is large in relation to the sample size, and we will take t ...
Sample Exam Questions
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 23) A marketing research company is estimating which of two soft drinks college students prefer. A random sample of 329 college students produced the following 95% confidence interval for the prop ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 23) A marketing research company is estimating which of two soft drinks college students prefer. A random sample of 329 college students produced the following 95% confidence interval for the prop ...