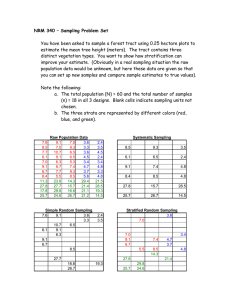
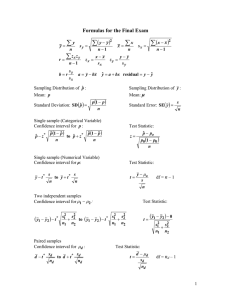
Statistics: Error (Chpt. 5)
... 2. Method errors (from non-ideal behavior of reagents used in analysis) - slow reactivity between analyte and titrant, side reactions, end point vs. equiv. point - often most difficult to detect - fixed by doing analysis of standard samples (standard reference material) and/or by ...
... 2. Method errors (from non-ideal behavior of reagents used in analysis) - slow reactivity between analyte and titrant, side reactions, end point vs. equiv. point - often most difficult to detect - fixed by doing analysis of standard samples (standard reference material) and/or by ...
Action Research
... variable (such as a test score). Mean scores for two groups are compared to see if differences are 'statistically' significant. If difference is 'SS' then there is a 'true' difference btw groups. ...
... variable (such as a test score). Mean scores for two groups are compared to see if differences are 'statistically' significant. If difference is 'SS' then there is a 'true' difference btw groups. ...
statistics
... Measures of central tendency presented without measures of variability can be _______________! ...
... Measures of central tendency presented without measures of variability can be _______________! ...
Review Sheet for Midterm Exam
... (c) Find P (B). (d) Find P (A ∩ B). (e) Find P (A ∪ B). Example : It is known that 75 percent of the population has mad cow disease. An experiment consists of selecting two members of the population and noting whether or not they have mad cow. (a) Find the probability exactly one selected member has ...
... (c) Find P (B). (d) Find P (A ∩ B). (e) Find P (A ∪ B). Example : It is known that 75 percent of the population has mad cow disease. An experiment consists of selecting two members of the population and noting whether or not they have mad cow. (a) Find the probability exactly one selected member has ...
Exam 1
... 10a) H0: Working out regularly does not affect intelligence. = 100 HA: Working out regularly does affect intelligence. 100 (although I’m personally inclined to think < 100 ☺) 10b) Horatio should reject the null hypothesis. The confidence interval does not contain 100 – indicating we’re prett ...
... 10a) H0: Working out regularly does not affect intelligence. = 100 HA: Working out regularly does affect intelligence. 100 (although I’m personally inclined to think < 100 ☺) 10b) Horatio should reject the null hypothesis. The confidence interval does not contain 100 – indicating we’re prett ...
Statistic
... We use samples to learn about populations We seldom observe the populations we want to know about Because we have to use samples, we engage in inference from samples to populations However, because of sampling variability, samples are not little mirror images of the population of interest. Given tha ...
... We use samples to learn about populations We seldom observe the populations we want to know about Because we have to use samples, we engage in inference from samples to populations However, because of sampling variability, samples are not little mirror images of the population of interest. Given tha ...
Displaying data and interpreting results
... Measure of precision in your data Method for testing subgroup differences The more precise your results, the more confidence you can have in them All sample-based surveys lack some amount of precision due to nonsampling error and sampling error A measure of sampling error is called standard error fo ...
... Measure of precision in your data Method for testing subgroup differences The more precise your results, the more confidence you can have in them All sample-based surveys lack some amount of precision due to nonsampling error and sampling error A measure of sampling error is called standard error fo ...