Course Schedule, Syllabus and Grading Policy
... boundary value problems, a conducting sphere ( either grounded or nongrounded ) will be a good problem to solve, in this regard the method of images will also be introduced to students. Also the electrostatics in dielectric media which will include the solution of Laplace equation in dielectric medi ...
... boundary value problems, a conducting sphere ( either grounded or nongrounded ) will be a good problem to solve, in this regard the method of images will also be introduced to students. Also the electrostatics in dielectric media which will include the solution of Laplace equation in dielectric medi ...
induced magnetic field
... A step-up transformer, with N2 >> N1, can boost the voltage of a generator up to several hundred thousand volts. Delivering power with smaller currents at higher voltages reduces losses due to the resistance of the wires. High-voltage transmission lines carry electric power to urban areas, where ...
... A step-up transformer, with N2 >> N1, can boost the voltage of a generator up to several hundred thousand volts. Delivering power with smaller currents at higher voltages reduces losses due to the resistance of the wires. High-voltage transmission lines carry electric power to urban areas, where ...
اﻟﻔﯾزﯾﺎء ( ﺑﺎﻟﻟﻐﺔ اﻻﻧﺟﻟﯾزﯾﺔ
... 2) If the capacitance of a capacitor in an AC circuit is increased to its double. (with respect to its capacitive reactance). 3) If the intensity of incident light on a metal surface (whose frequency is greater than the critical frequency) in an evacuated tube is increased to double. (with respect t ...
... 2) If the capacitance of a capacitor in an AC circuit is increased to its double. (with respect to its capacitive reactance). 3) If the intensity of incident light on a metal surface (whose frequency is greater than the critical frequency) in an evacuated tube is increased to double. (with respect t ...
Generating Electricity
... • The losses in the line are proportional to the resistance and the current squared or RI2 and the power in the line is proportional to VI (voltage times current) • The solution to these losses is to transmit the power at much higher voltages than the users need, and step the voltage down along the ...
... • The losses in the line are proportional to the resistance and the current squared or RI2 and the power in the line is proportional to VI (voltage times current) • The solution to these losses is to transmit the power at much higher voltages than the users need, and step the voltage down along the ...
File
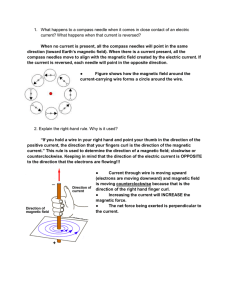
... 13. Explain why auroras are seen mostly near the North Pole and South Pole. Auroras are usually seen near Earth’s magnetic poles. Earth’s magnetic poles are located near Earth’s geographic North and South Poles. 14. Explain why some pieces of iron are more magnetic than others. Some pieces of iron a ...
... 13. Explain why auroras are seen mostly near the North Pole and South Pole. Auroras are usually seen near Earth’s magnetic poles. Earth’s magnetic poles are located near Earth’s geographic North and South Poles. 14. Explain why some pieces of iron are more magnetic than others. Some pieces of iron a ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... 15. Maxwell’s equations, production of electromagnetic waves 16. Energy of EM waves, the Poynting vector, radiation pressure Laboratory experiments 1. Plane capacitor and dielectric constant of different materials 2. Ohm’s law in DC circuits 3. Capacitor and inductivity in DC circuit 4. Electromagne ...
... 15. Maxwell’s equations, production of electromagnetic waves 16. Energy of EM waves, the Poynting vector, radiation pressure Laboratory experiments 1. Plane capacitor and dielectric constant of different materials 2. Ohm’s law in DC circuits 3. Capacitor and inductivity in DC circuit 4. Electromagne ...
File
... Directions: Play around with the website so that you can answer the questions about the solenoid. 1. What happens to the compass as the current is increased? 2. What happens when the “current direction” box is checked? 3. What happens when the “magnetic field vector” box is checked? 4. What happens ...
... Directions: Play around with the website so that you can answer the questions about the solenoid. 1. What happens to the compass as the current is increased? 2. What happens when the “current direction” box is checked? 3. What happens when the “magnetic field vector” box is checked? 4. What happens ...
Lecture 17 - Purdue Physics
... Two current loops are perpendicular to the z axis and are centered on the this axis. • Current I1 is clockwise. • I2 is the induced current in the bottom loop. If I2 is clockwise, which statement is true? ...
... Two current loops are perpendicular to the z axis and are centered on the this axis. • Current I1 is clockwise. • I2 is the induced current in the bottom loop. If I2 is clockwise, which statement is true? ...
Physics 202 Midterm Exam 2 Practice Exam
... 2. Answer all multiple questions in this test book by indicating the best answer among choices. You must do this both on your test book and on your Scantron sheet. Follow instructions on the Scantron sheet on how to mark valid answers. 3. When you finish, you need to turn in both this test book and ...
... 2. Answer all multiple questions in this test book by indicating the best answer among choices. You must do this both on your test book and on your Scantron sheet. Follow instructions on the Scantron sheet on how to mark valid answers. 3. When you finish, you need to turn in both this test book and ...