N - PembyPhysics
... the iron. Eddy currents are circulatory currents induced in the metal by the changing magnetic field. These currents produce an undesirable by-product—heat in the iron. Energy loss in a transformer can be reduced by using thinner laminations, very “soft” (low-carbon) iron and wire with a larger cros ...
... the iron. Eddy currents are circulatory currents induced in the metal by the changing magnetic field. These currents produce an undesirable by-product—heat in the iron. Energy loss in a transformer can be reduced by using thinner laminations, very “soft” (low-carbon) iron and wire with a larger cros ...
Magnetostatics – Magnetic Flux Density
... The units of B are therefore (H)(A)/m2, but it is more instructive to write webers per meter squared, or Wb/m2, where Wb=(H)(A). But for brevity, and perhaps to honor a deserving scientist, a tesla , T, equivalent to a Wb/m2, is the standard unit adopted by the International System of Units. ...
... The units of B are therefore (H)(A)/m2, but it is more instructive to write webers per meter squared, or Wb/m2, where Wb=(H)(A). But for brevity, and perhaps to honor a deserving scientist, a tesla , T, equivalent to a Wb/m2, is the standard unit adopted by the International System of Units. ...
Word
... dotted line the fields will cancel and there will be no net field. b. If the wires were free to move they would both rotate and settle along the diagonal with parallel currents. Any small movement which moves the wires away from being completely perpendicular will result in the wires being either at ...
... dotted line the fields will cancel and there will be no net field. b. If the wires were free to move they would both rotate and settle along the diagonal with parallel currents. Any small movement which moves the wires away from being completely perpendicular will result in the wires being either at ...
CBSE Class-X - Mathematic.in
... Q. 23. State Right hand thumb rule for finding the direction of magnetic field, around a current carrying straight conductor. How will the magnetic field be affected : a. On increasing the current b. On changing the direction of flow of current. Q. 24. What type of energy transformations take place ...
... Q. 23. State Right hand thumb rule for finding the direction of magnetic field, around a current carrying straight conductor. How will the magnetic field be affected : a. On increasing the current b. On changing the direction of flow of current. Q. 24. What type of energy transformations take place ...
Chapter 17 Powerpoint
... Generators are not perfectly efficient Not all 100% of the mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy. The efficiency depends on 3 things. 1. I2*R or copper losses in the winding ...
... Generators are not perfectly efficient Not all 100% of the mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy. The efficiency depends on 3 things. 1. I2*R or copper losses in the winding ...
Document
... • It can be turned on by turning on or off the current. • The direction of the field can be changed by reversing the current. • Changing the strength: – Increasing the amount of current. – Increasing the amount of loops. ...
... • It can be turned on by turning on or off the current. • The direction of the field can be changed by reversing the current. • Changing the strength: – Increasing the amount of current. – Increasing the amount of loops. ...
Department of Physics
... elements and definition of Magnetic Field. Biot-Savart’s Law and its simple applications: straight wire and circular loop. Current Loop as a E.M# Magnetic Dipole and its Dipole Moment (Analogy with Electric Dipole). Ampere’s Circuital Law and its application to (1) Solenoid and (2) Toroid Properties ...
... elements and definition of Magnetic Field. Biot-Savart’s Law and its simple applications: straight wire and circular loop. Current Loop as a E.M# Magnetic Dipole and its Dipole Moment (Analogy with Electric Dipole). Ampere’s Circuital Law and its application to (1) Solenoid and (2) Toroid Properties ...
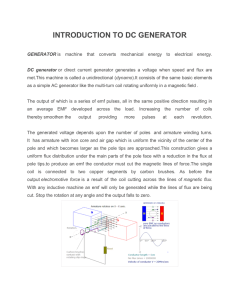
INTRODUCTION TO DC GENERATOR
... This is not the same as adding more turns to a single coil, which would increase the emf output.The main difference between the DC generator and the AC generator is in their connections to the armature coil,where a commutator is now used . A commutator is a combination of a rotating split-ring and s ...
... This is not the same as adding more turns to a single coil, which would increase the emf output.The main difference between the DC generator and the AC generator is in their connections to the armature coil,where a commutator is now used . A commutator is a combination of a rotating split-ring and s ...
`The Atoms Family` (A Great Electrical Resource Site) `Just for Kids
... Some motors run on direct current (DC). It is 'direct', because the electricity flows in only one direction. Alternating current (AC) flows back and forth 60 times per second ...
... Some motors run on direct current (DC). It is 'direct', because the electricity flows in only one direction. Alternating current (AC) flows back and forth 60 times per second ...
Name: Transformers, Car Coils and RC Circuits – Practice 1. Write
... Name: _______________________________ Transformers, Car Coils and RC Circuits – Practice 1. Write down Maxwell’s equations. ...
... Name: _______________________________ Transformers, Car Coils and RC Circuits – Practice 1. Write down Maxwell’s equations. ...
Document
... inductance of the two coils. The SI unit of mutual inductance is the henry (H). The mutual inductance of the two coils depends on its separation and orientation. The emf induced in coil 1 due to changes in I2 takes the form ...
... inductance of the two coils. The SI unit of mutual inductance is the henry (H). The mutual inductance of the two coils depends on its separation and orientation. The emf induced in coil 1 due to changes in I2 takes the form ...
Chapter 32
... were to circle the tokamak twice during the time the field was changing, how much ...
... were to circle the tokamak twice during the time the field was changing, how much ...