SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 6
... Figure SI3 a)-b) Inductor configuration for rotating magnetic field generation. Each phase consists of a sinusoidal signal, 90 degrees out-of-phase with each other. c) Physical inductor configuration, used to generate rotating magnetic field. The inner dimensions of the configuration are 105 mm by 1 ...
... Figure SI3 a)-b) Inductor configuration for rotating magnetic field generation. Each phase consists of a sinusoidal signal, 90 degrees out-of-phase with each other. c) Physical inductor configuration, used to generate rotating magnetic field. The inner dimensions of the configuration are 105 mm by 1 ...
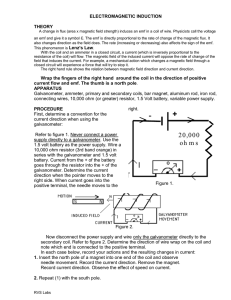
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION THEORY
... Now disconnect the power supply and wire only the galvanometer directly to the secondary coil. Refer to figure 2. Determine the direction of wire wrap on the coil and note which end is connected to the positive terminal. In each case below, record your actions and the resulting changes in current: 1 ...
... Now disconnect the power supply and wire only the galvanometer directly to the secondary coil. Refer to figure 2. Determine the direction of wire wrap on the coil and note which end is connected to the positive terminal. In each case below, record your actions and the resulting changes in current: 1 ...
Electromagnet Review Slides
... 1. You can increase the current in the solenoid. 2. You can add more loops of wire to the solenoid. 3. You can wind the coils of the solenoid closer together. 4. You can use a stronger ferromagnetic material for the core. ...
... 1. You can increase the current in the solenoid. 2. You can add more loops of wire to the solenoid. 3. You can wind the coils of the solenoid closer together. 4. You can use a stronger ferromagnetic material for the core. ...
circuits - worksheet..
... 10. What is the magnetic field 2.50 cm from a straight wire carrying a current of 0.858 A? If the current is from left to right, what is the direction of the magnetic field? B = ì0 I/2ðr = (4ðx10 -7 TAm/A A 0.858 A) / (2ð A 0.0250 m) = 6.864x10 -6 T = 6.86x10 -6 T or 6.86 ìT directionality: By right ...
... 10. What is the magnetic field 2.50 cm from a straight wire carrying a current of 0.858 A? If the current is from left to right, what is the direction of the magnetic field? B = ì0 I/2ðr = (4ðx10 -7 TAm/A A 0.858 A) / (2ð A 0.0250 m) = 6.864x10 -6 T = 6.86x10 -6 T or 6.86 ìT directionality: By right ...
key - circuits 10
... 4. A proton is released from rest in a uniform electric field, E = 7.25 x 105 V/m. It’s displacement is 0.420 m in the direction of the field. (a) What is the change in electrical potential? (b) What is the change in electrical potential energy? (c) What is its velocity after it traveled the 0.420 ...
... 4. A proton is released from rest in a uniform electric field, E = 7.25 x 105 V/m. It’s displacement is 0.420 m in the direction of the field. (a) What is the change in electrical potential? (b) What is the change in electrical potential energy? (c) What is its velocity after it traveled the 0.420 ...
Exercise 1: As the bar in Figure below moves to the right, an electric
... in the coil if the displacement occurs in 0.25s Exercise 7: A flat loop of wire consisting of a single turn of crosssectional area 8.00 cm2 is perpendicular to a magnetic field that increases uniformly in magnitude from 0.500 T to 2.50 T in 1.00 s. What is the resulting induced current if the loop h ...
... in the coil if the displacement occurs in 0.25s Exercise 7: A flat loop of wire consisting of a single turn of crosssectional area 8.00 cm2 is perpendicular to a magnetic field that increases uniformly in magnitude from 0.500 T to 2.50 T in 1.00 s. What is the resulting induced current if the loop h ...
PHYS1120ExamIIIRevie.. - University of Colorado Boulder
... Ch. 29 Faraday's Law Faraday's Law: An emf (= battery voltage) is caused by a changing magnetic flux: dF E( N loops) = - N ( where is the flux through 1 loop) dt magnetic flux F = ...
... Ch. 29 Faraday's Law Faraday's Law: An emf (= battery voltage) is caused by a changing magnetic flux: dF E( N loops) = - N ( where is the flux through 1 loop) dt magnetic flux F = ...
Electricity and Magnetism Summary Notes
... When electricity flows through a wire the wire can get hot. This can be dangerous as it can create an electrical fire. It is also used in electric fires, irons, stoves and light bulbs. As electricity can be dangerous we need a method to ensure that we stay safe even if something goes wrong. Also som ...
... When electricity flows through a wire the wire can get hot. This can be dangerous as it can create an electrical fire. It is also used in electric fires, irons, stoves and light bulbs. As electricity can be dangerous we need a method to ensure that we stay safe even if something goes wrong. Also som ...
Electromagnetic Induction©98
... electrical currents are accompanied by a magnetic field, the strength of which depends, among other things, upon the current.) The electric field is generated by the changing magnetic field can be detected by the electric force that charged bodies in the region experience. If there is a conductor th ...
... electrical currents are accompanied by a magnetic field, the strength of which depends, among other things, upon the current.) The electric field is generated by the changing magnetic field can be detected by the electric force that charged bodies in the region experience. If there is a conductor th ...
Unit 10C Magnetism
... Curve your fingers Place your thumb (which is presumably pretty straight) in direction of current. Curved fingers represent curve of magnetic field. Field vector at any point is tangent to field line. ...
... Curve your fingers Place your thumb (which is presumably pretty straight) in direction of current. Curved fingers represent curve of magnetic field. Field vector at any point is tangent to field line. ...
- Mitra.ac.in
... Aim: To impart basic knowledge of electric circuits, magnetic circuits, D.C. machines and transformers, A.C. machines and control systems. Objectives: To expose the students to the analysis of electric and magnetic circuits, performance characteristics of D.C. machines, A.C. machines and transformer ...
... Aim: To impart basic knowledge of electric circuits, magnetic circuits, D.C. machines and transformers, A.C. machines and control systems. Objectives: To expose the students to the analysis of electric and magnetic circuits, performance characteristics of D.C. machines, A.C. machines and transformer ...
VCE Physics exam PDF
... What type of output does a generator give? A generator works in the opposite way to a motor. As a generator spins, current is induced in the coil. This current flow will change direction every half-turn, so it is AC. Slip rings are used to harness the AC. If a DC output is required, the reversal mu ...
... What type of output does a generator give? A generator works in the opposite way to a motor. As a generator spins, current is induced in the coil. This current flow will change direction every half-turn, so it is AC. Slip rings are used to harness the AC. If a DC output is required, the reversal mu ...
Name: Study Guide for Investigation 4 Test Label all of the letters on
... In an electromagnet, if two rivet heads come together and they are set up the exact same way, what will happen? Do you think they will repel, attract, or cancel out the magnetism in each other? The two electromagnets will repel. Know how to read a line graph! The x and y axis will be labeled and the ...
... In an electromagnet, if two rivet heads come together and they are set up the exact same way, what will happen? Do you think they will repel, attract, or cancel out the magnetism in each other? The two electromagnets will repel. Know how to read a line graph! The x and y axis will be labeled and the ...