Review for Exam 2.
... • → thumb points in direction of current • B-field for long straight wire: B = • B-field at center of circular arc: B ...
... • → thumb points in direction of current • B-field for long straight wire: B = • B-field at center of circular arc: B ...
The Transformer Explained Using Faraday`s Law File
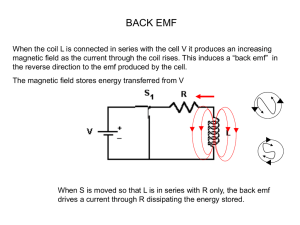
... When the coil L is connected in series with the cell V it produces an increasing magnetic field as the current through the coil rises. This induces a “back emf” in the reverse direction to the emf produced by the cell. The magnetic field stores energy transferred from V ...
... When the coil L is connected in series with the cell V it produces an increasing magnetic field as the current through the coil rises. This induces a “back emf” in the reverse direction to the emf produced by the cell. The magnetic field stores energy transferred from V ...
Science 9 Unit 4: Electricity Name
... Some motors run on direct current (DC). It is 'direct', because the electricity flows in only one direction. Alternating current (AC) flows back and forth 60 times per second. ...
... Some motors run on direct current (DC). It is 'direct', because the electricity flows in only one direction. Alternating current (AC) flows back and forth 60 times per second. ...
Author - Princeton ISD
... P. 5G Investigate and describe the relationship between electric and magnetic fields in applications such as generators, motors and transformers See Instructional Focus Document (IFD) for TEK Specificity ...
... P. 5G Investigate and describe the relationship between electric and magnetic fields in applications such as generators, motors and transformers See Instructional Focus Document (IFD) for TEK Specificity ...
Reading Guide CH 28KEYJWW
... the material is warm enough that atoms move around too much to ever align magnetically. ...
... the material is warm enough that atoms move around too much to ever align magnetically. ...
document
... • Stay still charge distribution generates divergence driven, swirl free electric field (which can be sensed by any charged object, hence we have the name “electric”). • Charge in static motion generates not only the above mentioned electric field, but also swirl driven, divergence free magnetic fie ...
... • Stay still charge distribution generates divergence driven, swirl free electric field (which can be sensed by any charged object, hence we have the name “electric”). • Charge in static motion generates not only the above mentioned electric field, but also swirl driven, divergence free magnetic fie ...
Vocabulary for 4.3
... 2. magnetic field- space around a magnet where the force of the magnet acts 3. compass- instrument that points to magnetic north by using the magnetic field of the earth 4. permanent magnet- magnet that holds its magnetic properties for a long time 5. electromagnet- temporary magnet made when electr ...
... 2. magnetic field- space around a magnet where the force of the magnet acts 3. compass- instrument that points to magnetic north by using the magnetic field of the earth 4. permanent magnet- magnet that holds its magnetic properties for a long time 5. electromagnet- temporary magnet made when electr ...
HW13
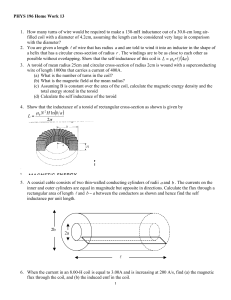
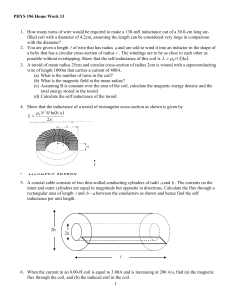
... 1. How many turns of wire would be required to make a 130-mH inductance out of a 30.0-cm long airfilled coil with a diameter of 4.2cm, assuming the length can be considered very large in comparison with the diameter? 2. You are given a length of wire that has radius a and are told to wind it into ...
... 1. How many turns of wire would be required to make a 130-mH inductance out of a 30.0-cm long airfilled coil with a diameter of 4.2cm, assuming the length can be considered very large in comparison with the diameter? 2. You are given a length of wire that has radius a and are told to wind it into ...
Appendix II
... current in order to minimize line losses, the magnetic forces associated with power lines are not large. However, electrical devices such as motors, generators, transformers, relays, doorbells, etc., that need to convert electrical power into a force must utilize the magnetic force produced by the c ...
... current in order to minimize line losses, the magnetic forces associated with power lines are not large. However, electrical devices such as motors, generators, transformers, relays, doorbells, etc., that need to convert electrical power into a force must utilize the magnetic force produced by the c ...
Chp. 22 Outline Induction - Redlands High School
... a transformer not change? Distinguish between a step-up and step-down transformer in terms of the number of turns on the primary and secondary and whether voltage or current are stepped up or down. How is Ohm’s law used for a transformer? 8) Why was AC picked over DC to transfer electrical energy? W ...
... a transformer not change? Distinguish between a step-up and step-down transformer in terms of the number of turns on the primary and secondary and whether voltage or current are stepped up or down. How is Ohm’s law used for a transformer? 8) Why was AC picked over DC to transfer electrical energy? W ...
Practice Packet: Magnetism and Electromagnetic Induction Name
... 13) Which way would the North Pole of a compass needle point if you were at the magnetic South Pole? ...
... 13) Which way would the North Pole of a compass needle point if you were at the magnetic South Pole? ...
Lecture 20
... In situations where there is a variation in the current magnitude it is rather inadequate to define just the total current flow in the system. One can then use the current density as the primary parameter which is defined as the current flow per unit area. ...
... In situations where there is a variation in the current magnitude it is rather inadequate to define just the total current flow in the system. One can then use the current density as the primary parameter which is defined as the current flow per unit area. ...