
Math4all.info - Way 2 Freshers
... peak value b) rms value c) any value d) average value 9.The Q-factor of a resonant circuit is equal to a) 1CWR b) 1WL c) CWR d) fCW 10.In a step-down transformer, the number of turns in a) Primary are less b) Primary are more c) Primary and secondary equal d) secondary are infinite 11.In AC circuits ...
... peak value b) rms value c) any value d) average value 9.The Q-factor of a resonant circuit is equal to a) 1CWR b) 1WL c) CWR d) fCW 10.In a step-down transformer, the number of turns in a) Primary are less b) Primary are more c) Primary and secondary equal d) secondary are infinite 11.In AC circuits ...
Practice Exam 2 - UIC Department of Physics
... C) A is brightest, C is dimmest, and B is in between. D) A is the brightest, and B and C have equal brightness but less than A. E) All three bulbs have the same brightness. Answer: D 2) An RC circuit is connected across an ideal DC voltage source through an open switch. The switch is closed at time ...
... C) A is brightest, C is dimmest, and B is in between. D) A is the brightest, and B and C have equal brightness but less than A. E) All three bulbs have the same brightness. Answer: D 2) An RC circuit is connected across an ideal DC voltage source through an open switch. The switch is closed at time ...
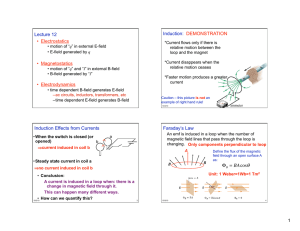
12: Electromagnetic Induction - SJHS-IB
... the value of direct current that would dissipate power at the same rate through a resistor. ...
... the value of direct current that would dissipate power at the same rate through a resistor. ...
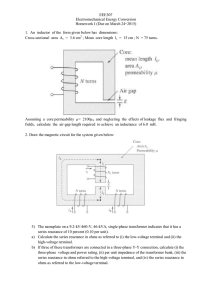
EEE307 Electromechanical Energy Conversion Homework I (Due
... 3) The nameplate on a 9.2-kV:460-V, 46-kVA, single-phase transformer indicates that it has a series reactance of 10 percent (0.10 per unit). a) Calculate the series reactance in ohms as referred to (i) the low-voltage terminal and (ii) the high-voltage terminal. b) If three of these transformers are ...
... 3) The nameplate on a 9.2-kV:460-V, 46-kVA, single-phase transformer indicates that it has a series reactance of 10 percent (0.10 per unit). a) Calculate the series reactance in ohms as referred to (i) the low-voltage terminal and (ii) the high-voltage terminal. b) If three of these transformers are ...
Final Poster 1052 kb Friday, December 12, 2008
... • Current circuit design is very economical. Commercially developed probes can be quite expensive, but will provide the needed accuracy to measure the fields created. ...
... • Current circuit design is very economical. Commercially developed probes can be quite expensive, but will provide the needed accuracy to measure the fields created. ...
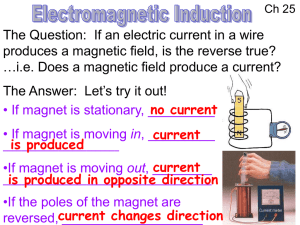
2016 Farada review sheet[1][1]
... What are three ways to change magnetic flux? <6a> Be able to use Faraday’s law and Lenz’s law to recognize situations in which changing flux through a loop will cause an induced emf or current in the loop. (is it a complete loop? Is the flux changing with time? Resistance?) <5,13,14-16> Be abl ...
... What are three ways to change magnetic flux? <6a> Be able to use Faraday’s law and Lenz’s law to recognize situations in which changing flux through a loop will cause an induced emf or current in the loop. (is it a complete loop? Is the flux changing with time? Resistance?) <5,13,14-16> Be abl ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... North and South Poles of a Magnet Magnets have a north and south pole. • If a magnet is broken into smaller pieces, each piece will still have a north and south pole. • Opposite poles attract, like poles repel. ...
... North and South Poles of a Magnet Magnets have a north and south pole. • If a magnet is broken into smaller pieces, each piece will still have a north and south pole. • Opposite poles attract, like poles repel. ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... Video: Bill Nye: Magnetism - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8PyqL9y7VZo Teacher demo: (can have students do this as an activity) Electromagnets (An electromagnet is a temporary magnet made by wrapping a wire coil carrying a current around an iron core.) Materials: Large nail Battery (D-cell and ...
... Video: Bill Nye: Magnetism - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8PyqL9y7VZo Teacher demo: (can have students do this as an activity) Electromagnets (An electromagnet is a temporary magnet made by wrapping a wire coil carrying a current around an iron core.) Materials: Large nail Battery (D-cell and ...














![2016 Farada review sheet[1][1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001271395_1-fc9c1a7e3076b57ba2cfadfbf9c2de3d-300x300.png)





