Dec 2016 - Astronomical Society of Northern New England
... and collapses down to the size of the earth, it becomes 125,000 times denser than steel, so that each cupful of this exotic material would weigh more than a cement truck. However, it is not nearly as dense as a neutron star, where each baseball sized chunk would weigh 20 trillion kilograms, or 40 ti ...
... and collapses down to the size of the earth, it becomes 125,000 times denser than steel, so that each cupful of this exotic material would weigh more than a cement truck. However, it is not nearly as dense as a neutron star, where each baseball sized chunk would weigh 20 trillion kilograms, or 40 ti ...
Section 1
... (as well as rotation, magnetic field, mass loss, maculation, and other properties). The line spectra are used to classify stars, according to their temperature and photospheric pressure. With this criterion, we can assign a spectral type to a star. Originally, such classifications used photographic ...
... (as well as rotation, magnetic field, mass loss, maculation, and other properties). The line spectra are used to classify stars, according to their temperature and photospheric pressure. With this criterion, we can assign a spectral type to a star. Originally, such classifications used photographic ...
McDonald Observatory Planet Search - tls
... • Long period variations are most likely due to giant planets around stars with Mstar > 1 Mסּ • Short period variations are due to radial pulsations in the fundamental and overtone modes • Pulsations can be used to get funamental parameters of ...
... • Long period variations are most likely due to giant planets around stars with Mstar > 1 Mסּ • Short period variations are due to radial pulsations in the fundamental and overtone modes • Pulsations can be used to get funamental parameters of ...
COMING EVENTS The Pluto Files Volume 37 Number 03 March
... Copies of the Celestial Mechanic can also be found on the web at http://www.ku.edu/~aal/celestialmechanic ...
... Copies of the Celestial Mechanic can also be found on the web at http://www.ku.edu/~aal/celestialmechanic ...
Collapse of an unstable Neutron Star to a Black Hole
... star merger process a new supramassive or hypermassive neutron star is formed, which could be stable for longer times or collapse almost immediately to a black hole. During this process a short gamma ray burst is emitted, releasing in less than one second the energy emitted by our Galaxy over one ye ...
... star merger process a new supramassive or hypermassive neutron star is formed, which could be stable for longer times or collapse almost immediately to a black hole. During this process a short gamma ray burst is emitted, releasing in less than one second the energy emitted by our Galaxy over one ye ...
Chasing the Pole — Howard L. Cohen
... Page 2 of 6 Polaris the Star—Some Basics Since Polaris is so widely known, the literature is filled with an abundance of information about this north pointing star, especially about its interesting physical characteristics. In fact, this star goes by at least three dozen monikers including Alpha Ur ...
... Page 2 of 6 Polaris the Star—Some Basics Since Polaris is so widely known, the literature is filled with an abundance of information about this north pointing star, especially about its interesting physical characteristics. In fact, this star goes by at least three dozen monikers including Alpha Ur ...
Analemma - Stony Brook University
... King Acrisius of Argos Danae Zeus Perseus Dictys King Polydectes Medusa Hermes Athena the Graeae The Gorgons ...
... King Acrisius of Argos Danae Zeus Perseus Dictys King Polydectes Medusa Hermes Athena the Graeae The Gorgons ...
X-ray binaries
... The latest large catalogue (Li et al. arXiv: 0707.0544) includes 187 galactic and Magellanic Clouds LMXBs with NSs and BHs as accreting components. Donors can be WDs, or normal low-mass stars (main sequence or sub-giants). Many sources are found in globular clusters. Also there are more and more LMX ...
... The latest large catalogue (Li et al. arXiv: 0707.0544) includes 187 galactic and Magellanic Clouds LMXBs with NSs and BHs as accreting components. Donors can be WDs, or normal low-mass stars (main sequence or sub-giants). Many sources are found in globular clusters. Also there are more and more LMX ...
death_high_mass
... The planetary nebula phase is short lived. • The radius of a typical planetary nebula is about 1 light year. • The gas is glowing, so we see an emission nebula. • Typical elements in at planetary nebula are hydrogen, helium, carbon, oxygen and nitrogen. Also some neon present. ...
... The planetary nebula phase is short lived. • The radius of a typical planetary nebula is about 1 light year. • The gas is glowing, so we see an emission nebula. • Typical elements in at planetary nebula are hydrogen, helium, carbon, oxygen and nitrogen. Also some neon present. ...
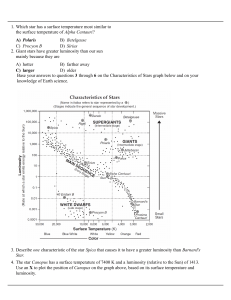
A) Polaris B) Betelgeuse C) Procyon B D) Sirius 1. Which star has a
... the same luminosity as the star Aldebaran approximately the same temperature as the Rigel. Algol is best classified as a A) main sequence star B) red giant star C) white dwarf star D) red dwarf star 60. Two stars of the same color are plotted on an H-R diagram. Star A is more luminous than star B. W ...
... the same luminosity as the star Aldebaran approximately the same temperature as the Rigel. Algol is best classified as a A) main sequence star B) red giant star C) white dwarf star D) red dwarf star 60. Two stars of the same color are plotted on an H-R diagram. Star A is more luminous than star B. W ...
Evolved Stellar Populations
... of the Local Group and in particular the Magellanic Clouds (nearby, known distance, low extinction, …interacting irregular galaxies). Distinguish between cluster and field stars. A global picture of any LGG is lacking. ...
... of the Local Group and in particular the Magellanic Clouds (nearby, known distance, low extinction, …interacting irregular galaxies). Distinguish between cluster and field stars. A global picture of any LGG is lacking. ...
Chapter 13: Interstellar Matter and Star Formation
... 4. M-class stars may remain protostars for hundreds of millions of year. G stars (like the Sun) spend about 30 million years in the protostar phase. Massive O- and B-type stars remain protostars for only tens of thousands of years before joining the main sequence. 5. O and B stars may undergo a peri ...
... 4. M-class stars may remain protostars for hundreds of millions of year. G stars (like the Sun) spend about 30 million years in the protostar phase. Massive O- and B-type stars remain protostars for only tens of thousands of years before joining the main sequence. 5. O and B stars may undergo a peri ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagrams
... converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. These stars are in the most stable part of their existence; this stage generally lasts for about 5 billion years. As stars begin to die, they become giants and supergiants (above the main sequence). These stars have ...
... converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. These stars are in the most stable part of their existence; this stage generally lasts for about 5 billion years. As stars begin to die, they become giants and supergiants (above the main sequence). These stars have ...
(BDA) Contribution To Space Weather Investigations
... for application to space weather forecasting. BDA will be very useful for galactic and extra-galactic investigations of the southern sky not accessible to VLA. ILWS - International Living With Star ...
... for application to space weather forecasting. BDA will be very useful for galactic and extra-galactic investigations of the southern sky not accessible to VLA. ILWS - International Living With Star ...
γ The potential for intensity interferometry with -ray telescope arrays
... mv of a CTA concept is illustrated in the right panel of Fig. 1. Targets are limited to a mv ≈ 8.5m for a S/N = 5, and a 5 hours integration in case of 50% visibility (see Le Bohec et al., these proceedings). These specifications allow important interferometric studies regarding binary stars, stella ...
... mv of a CTA concept is illustrated in the right panel of Fig. 1. Targets are limited to a mv ≈ 8.5m for a S/N = 5, and a 5 hours integration in case of 50% visibility (see Le Bohec et al., these proceedings). These specifications allow important interferometric studies regarding binary stars, stella ...
Review: How does a star`s mass determine its life story?
... same place cannot be in the same state • Adding mass to a white dwarf increases its gravity, forcing electrons into a smaller space • In order to avoid being in the same state some of the electrons need to move faster ...
... same place cannot be in the same state • Adding mass to a white dwarf increases its gravity, forcing electrons into a smaller space • In order to avoid being in the same state some of the electrons need to move faster ...
The Constellations
... • There are a total of 88 constellations—defined by IAU (International Astronomical Union) in 1928. ...
... • There are a total of 88 constellations—defined by IAU (International Astronomical Union) in 1928. ...
Pulsating variable stars and the Hertzsprung
... stars in different stages of their evolution. It is a plot showing a relationship between luminosity (or absolute magnitude) and stars' surface temperature (or spectral type). The bottom scale is ranging from high-temperature blue-white stars (left side of the diagram) to low-temperature red stars ( ...
... stars in different stages of their evolution. It is a plot showing a relationship between luminosity (or absolute magnitude) and stars' surface temperature (or spectral type). The bottom scale is ranging from high-temperature blue-white stars (left side of the diagram) to low-temperature red stars ( ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.