Lecture 13 Main Sequence and Low Mass Evolution
... • The higher the mass, the shorter its life. • Examples: Sun: ~ 10 Billion Years 30 Msun O‐star: ~ 2 Million years 0.1 Msun M‐star: ~ 3 Trillion years ...
... • The higher the mass, the shorter its life. • Examples: Sun: ~ 10 Billion Years 30 Msun O‐star: ~ 2 Million years 0.1 Msun M‐star: ~ 3 Trillion years ...
Astrowheel activity for Wednesday Feb 16
... For the rising time, mark the position of the desired object on the PSW (if it is not already marked) and rotate the PSW until that spot just touches the Eastern edge of the oval (as objects rise in the East and set in the West). In general, the object will NOT hit the edge exactly at the 'E' mark - ...
... For the rising time, mark the position of the desired object on the PSW (if it is not already marked) and rotate the PSW until that spot just touches the Eastern edge of the oval (as objects rise in the East and set in the West). In general, the object will NOT hit the edge exactly at the 'E' mark - ...
Light of Distant Stars - Glasgow Science Centre
... searching for extrasolar planets, and, despite it having revealed a number of planets, it’s actually the worst way of doing it. Ask the group to discuss why they think this is a particularly poor way of searching for planets. Hopefully someone will hit along the idea that the probability of a planet ...
... searching for extrasolar planets, and, despite it having revealed a number of planets, it’s actually the worst way of doing it. Ask the group to discuss why they think this is a particularly poor way of searching for planets. Hopefully someone will hit along the idea that the probability of a planet ...
PowerPoint
... • Quantum mechanics– electrons can be wave-like – Electrons around nucleus have certain orbits– defines emission and absorption of each atom – When excited, atoms emit certain lines (like in class)– fingerprint or barcode of atom ...
... • Quantum mechanics– electrons can be wave-like – Electrons around nucleus have certain orbits– defines emission and absorption of each atom – When excited, atoms emit certain lines (like in class)– fingerprint or barcode of atom ...
Lecture 6-1: Schematic Evolution of Stars as seen from the core
... collapse to make the density infinite). ...
... collapse to make the density infinite). ...
Galaxies, Cosmology and the Accelera`ng Universe
... thin disk but were sca?ered • (some recent observa6ons suggest that there is not such a big difference between the thick and thin disks: there is one disk that just has fewer and fewer stars ...
... thin disk but were sca?ered • (some recent observa6ons suggest that there is not such a big difference between the thick and thin disks: there is one disk that just has fewer and fewer stars ...
Unit 1
... hydrogen into helium is called its main sequence lifetime – Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence – Lifetime depends on the star’s mass and luminosity • More luminous stars burn their energy more rapidly than less luminous stars. • High-mass stars are more luminous than low-mass stars ...
... hydrogen into helium is called its main sequence lifetime – Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence – Lifetime depends on the star’s mass and luminosity • More luminous stars burn their energy more rapidly than less luminous stars. • High-mass stars are more luminous than low-mass stars ...
James`s 5-Page Final Exam Review
... ii. When is this equation applicable? b. Intermediate Kepler’s Third Law: i. What units do you use for P and a? ii. When is this equation applicable? c. Newton’s Version of Kepler’s Third Law: i. What units do you use for P and a? ii. When is this equation applicable? 34) Examples with Kepler’s Thir ...
... ii. When is this equation applicable? b. Intermediate Kepler’s Third Law: i. What units do you use for P and a? ii. When is this equation applicable? c. Newton’s Version of Kepler’s Third Law: i. What units do you use for P and a? ii. When is this equation applicable? 34) Examples with Kepler’s Thir ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 11 Notes: Stellar
... contrast, instability occurs when any small deviation from an equilibrium solution tends to drive the system further and further away from it. The classic example of an unstable system is a pencil standing on its point. If one could get the pencil to balance completely perfectly, it would be in equi ...
... contrast, instability occurs when any small deviation from an equilibrium solution tends to drive the system further and further away from it. The classic example of an unstable system is a pencil standing on its point. If one could get the pencil to balance completely perfectly, it would be in equi ...
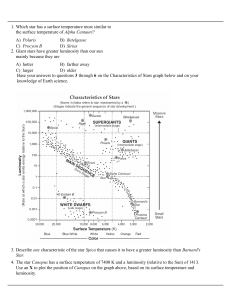
2-star-life-cycle-and-star-classification
... the same luminosity as the star Aldebaran approximately the same temperature as the Rigel. Algol is best classified as a A) main sequence star B) red giant star C) white dwarf star D) red dwarf star 60. Two stars of the same color are plotted on an H-R diagram. Star A is more luminous than star B. W ...
... the same luminosity as the star Aldebaran approximately the same temperature as the Rigel. Algol is best classified as a A) main sequence star B) red giant star C) white dwarf star D) red dwarf star 60. Two stars of the same color are plotted on an H-R diagram. Star A is more luminous than star B. W ...
Stars A globular cluster is a tightly grouped swarm of stars held
... The distance from the sun to Proxima Centauri is more than 25 trillion miles (40 trillion kilometers). This distance is so great that light takes 4.2 years to travel between the two stars. Scientists say that Proxima Centauri is 4.2 light-years from the sun. One light-year, the distance that light t ...
... The distance from the sun to Proxima Centauri is more than 25 trillion miles (40 trillion kilometers). This distance is so great that light takes 4.2 years to travel between the two stars. Scientists say that Proxima Centauri is 4.2 light-years from the sun. One light-year, the distance that light t ...
Acceleration of Coronal Mass Ejection In Long Rising Solar
... released by the Sun over its whole main sequence life. The catastrophic consequence is a supernova explosion. • The product at the core is a neutral star, or even a black hole (if the degenerate pressure of neutrons can not withhold the gravitational pressure) • Heavy elements generated in the core ...
... released by the Sun over its whole main sequence life. The catastrophic consequence is a supernova explosion. • The product at the core is a neutral star, or even a black hole (if the degenerate pressure of neutrons can not withhold the gravitational pressure) • Heavy elements generated in the core ...
February 13
... From Earth we can only measure a star’s parallax to about 100 pc. The distance to the center of the galaxy is 8 kpc or 80 times this distance. Why are parallax measurements so limited? What could you do to get parallax measurements for more distant stars? ...
... From Earth we can only measure a star’s parallax to about 100 pc. The distance to the center of the galaxy is 8 kpc or 80 times this distance. Why are parallax measurements so limited? What could you do to get parallax measurements for more distant stars? ...
GRAVITATIONAL RADIATION FROM ACCRETING NEUTRON STARS
... One can hope, therefore, that some variant on one of these methods might allow one to search a few targets at nearly optimum sensitivity. 4. Conclusion. We have seen that it would be interesting to search for signals from accreting neutron stars, but these must allow for the modulation of the signal ...
... One can hope, therefore, that some variant on one of these methods might allow one to search a few targets at nearly optimum sensitivity. 4. Conclusion. We have seen that it would be interesting to search for signals from accreting neutron stars, but these must allow for the modulation of the signal ...
FREE Sample Here
... What causes the seasons? The rotation of the Earth on its axis produces the cycle of day and night, and the revolution of the Earth around the sun produces the cycle of the year. Because Earth orbits the sun, the sun appears to move eastward along the ecliptic through the constellations, completing ...
... What causes the seasons? The rotation of the Earth on its axis produces the cycle of day and night, and the revolution of the Earth around the sun produces the cycle of the year. Because Earth orbits the sun, the sun appears to move eastward along the ecliptic through the constellations, completing ...
observing cards - NC Science Festival
... small & round and possibly planet-like through primitive telescopes. It was very quickly recognized that these were not planets, but the name stuck. The planetary nebula phase of a star’s life represents a short but important time in the life of stars up to 8 times the mass of our Sun. If we compare ...
... small & round and possibly planet-like through primitive telescopes. It was very quickly recognized that these were not planets, but the name stuck. The planetary nebula phase of a star’s life represents a short but important time in the life of stars up to 8 times the mass of our Sun. If we compare ...
Stellar Winds and Mass Loss
... These can explain hot bubble around hot stars, ring nebulae around WR stars, and ultra compact HII regions, as well as PNe ...
... These can explain hot bubble around hot stars, ring nebulae around WR stars, and ultra compact HII regions, as well as PNe ...
Chemical Universe. - University of Texas Astronomy
... The fact that the oldest stars contain more europium (an r-process element made in supernovae) than barium (an s-process element), for example, means that the early formation of elements in our galaxy was influenced by supernova explosions more than anything else. Sneden also is trying to figure out ...
... The fact that the oldest stars contain more europium (an r-process element made in supernovae) than barium (an s-process element), for example, means that the early formation of elements in our galaxy was influenced by supernova explosions more than anything else. Sneden also is trying to figure out ...
Document
... Brightness • For two stars of the same luminosity with one star double the distance of the other from the Earth the closer star will look four times brighter. D ...
... Brightness • For two stars of the same luminosity with one star double the distance of the other from the Earth the closer star will look four times brighter. D ...
INTERSTELLAR MedLab
... b. Radiation can be polarized by the presence of dust grains aligned in a magnetic field. From this image, state whether or not the Crab Nebula contains a magnetic field. Explain your reasoning. ...
... b. Radiation can be polarized by the presence of dust grains aligned in a magnetic field. From this image, state whether or not the Crab Nebula contains a magnetic field. Explain your reasoning. ...
Stars PowerPoint
... – Circumpolar constellations can be seen all year long as they appear to move around the north or south pole. Ex-Big Dipper – Summer, fall, winter, and spring constellations can be seen only at certain times of the year because of Earth’s changing position in its orbit around the Sun. ...
... – Circumpolar constellations can be seen all year long as they appear to move around the north or south pole. Ex-Big Dipper – Summer, fall, winter, and spring constellations can be seen only at certain times of the year because of Earth’s changing position in its orbit around the Sun. ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.