Document
... • Many methods in this class • Know absolute luminosity somehow – Apparent magnitude gives distance by inverse square law ...
... • Many methods in this class • Know absolute luminosity somehow – Apparent magnitude gives distance by inverse square law ...
life cycles of stars
... Determining the age of a star cluster • Imagine we have a cluster of stars that were all formed at the same time, but have a variety of different masses • Using what we know about stellar evolution is there a way to determine the age of the star cluster? ...
... Determining the age of a star cluster • Imagine we have a cluster of stars that were all formed at the same time, but have a variety of different masses • Using what we know about stellar evolution is there a way to determine the age of the star cluster? ...
Diapositiva 1
... The spectra of two nebulous objects near NGC 1999 (ApJ 113, 697). On a series of direct photographs taken with the Crosslyer reflector in 1946 and 1947 and centered on the diffuse nebula NGC 1999, there appear several peculiar nebulous objects. The brightest of these (referred to hereafter as "No. 1 ...
... The spectra of two nebulous objects near NGC 1999 (ApJ 113, 697). On a series of direct photographs taken with the Crosslyer reflector in 1946 and 1947 and centered on the diffuse nebula NGC 1999, there appear several peculiar nebulous objects. The brightest of these (referred to hereafter as "No. 1 ...
Constellation Catalog
... Constellation was first cataloged by Ptolemy in 2nd century B.C. The constellation is named after Andromeda who, in Greek Mythology, was the daughter of Cassiopeia and Cepheus. Cassiopeia bragged that her daughter was prettier than the sea nymphs. The Sea Nymphs heard this and were angered so they t ...
... Constellation was first cataloged by Ptolemy in 2nd century B.C. The constellation is named after Andromeda who, in Greek Mythology, was the daughter of Cassiopeia and Cepheus. Cassiopeia bragged that her daughter was prettier than the sea nymphs. The Sea Nymphs heard this and were angered so they t ...
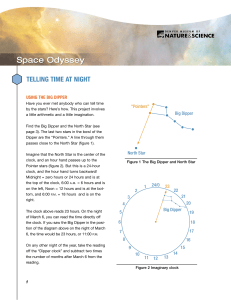
telling time at night
... Once you have determined the north direction, look up about one-third* of the way from horizon to zenith, the top of the sky. The North Star is fairly bright (second magnitude) and visible from the city, but not as bright as the brightest stars (first magnitude). The Big Dipper rotates around the No ...
... Once you have determined the north direction, look up about one-third* of the way from horizon to zenith, the top of the sky. The North Star is fairly bright (second magnitude) and visible from the city, but not as bright as the brightest stars (first magnitude). The Big Dipper rotates around the No ...
intergalactic move
... Andromeda Galaxy. It was named after a Greek princess (read more about her on the following pages!). The Andromeda Galaxy is a spiral galaxy. Unfortunately it’s swirling arms are only visible with a telescope, through binoculars Andromeda just looks like a blurry blotch. ...
... Andromeda Galaxy. It was named after a Greek princess (read more about her on the following pages!). The Andromeda Galaxy is a spiral galaxy. Unfortunately it’s swirling arms are only visible with a telescope, through binoculars Andromeda just looks like a blurry blotch. ...
plagiarism - things to know - Science Department
... which wavelength of light will be most the star, rock or person determines which strongly radiated depends on the wavelength of light will be most strongly temperature of the star, rock or person. For radiated. In the constellation Orion, the example, the star Betelgeuse in the upper left star is Be ...
... which wavelength of light will be most the star, rock or person determines which strongly radiated depends on the wavelength of light will be most strongly temperature of the star, rock or person. For radiated. In the constellation Orion, the example, the star Betelgeuse in the upper left star is Be ...
B LOG - Science Centre
... The Dipper is part of a much larger star pattern, the constellation Ursa Major (Greater Bear) although it had a variety of meanings in many cultures. Most common is that of a bear or a ladle/dipper used for scooping water. Other representations include a plough, an ox or horse pulling a plough and t ...
... The Dipper is part of a much larger star pattern, the constellation Ursa Major (Greater Bear) although it had a variety of meanings in many cultures. Most common is that of a bear or a ladle/dipper used for scooping water. Other representations include a plough, an ox or horse pulling a plough and t ...
The star Epsilon UMa, or more commonly known as Alioth
... way to remember these classes in order is by remembering that “Only Bored Astronomers Find Gratification Knowing Mnemonics”. Alioth’s spectral type is A in which for these stars the color of the light emitted ranges from a very light blue to white and the approximate surface temperature ranges from ...
... way to remember these classes in order is by remembering that “Only Bored Astronomers Find Gratification Knowing Mnemonics”. Alioth’s spectral type is A in which for these stars the color of the light emitted ranges from a very light blue to white and the approximate surface temperature ranges from ...
ppt
... down to a solar mass, rises more slowly down to its max at 0.1-0.2 M⊙ and declines to the substellar regime ...
... down to a solar mass, rises more slowly down to its max at 0.1-0.2 M⊙ and declines to the substellar regime ...
Observations of binary systems with pulsating components
... Obtaining stellar masses from visual orbits requires quite a lot of work: • observations may take years, • relative orbit has to be freed from the effect of inclination, • one needs to know the distance (parallax) of the system. Because of these limitations, this method has been used to obtain relia ...
... Obtaining stellar masses from visual orbits requires quite a lot of work: • observations may take years, • relative orbit has to be freed from the effect of inclination, • one needs to know the distance (parallax) of the system. Because of these limitations, this method has been used to obtain relia ...
Heavy Metal from Ancient Superstars
... fuel, they become white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes. In the process, much of the stellar material is returned to interstellar space ...
... fuel, they become white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes. In the process, much of the stellar material is returned to interstellar space ...
Constellations Overview
... The most famous of all the constellations are the 12 that make up the Zodiac. All planets can be observed only in these 12 constellations as they pass across the sky during the course of their year. This is because the orbits of all the planets lie within ± 8º of the ecliptic. The Sun also moves t ...
... The most famous of all the constellations are the 12 that make up the Zodiac. All planets can be observed only in these 12 constellations as they pass across the sky during the course of their year. This is because the orbits of all the planets lie within ± 8º of the ecliptic. The Sun also moves t ...
The hawaiian star compass and the unit circle
... spanning 11.25 degrees, i.e., 360 degrees divided by 32 (Thompson, 2005).The following seven houses repeat within each quadrant (Thompson, 2005): ◊ On either side of Hikina (east) and Komohana (west) is Lā (“Sun”), since the sun stays in this house for most of the year as it moves back and forth be ...
... spanning 11.25 degrees, i.e., 360 degrees divided by 32 (Thompson, 2005).The following seven houses repeat within each quadrant (Thompson, 2005): ◊ On either side of Hikina (east) and Komohana (west) is Lā (“Sun”), since the sun stays in this house for most of the year as it moves back and forth be ...
Doppler Effect
... star are moving toward or away from each other, and whether the Earth and the star have large or small relative speeds. What did Vera Rubin and her colleagues measure with the Doppler Effect? What did they discover about a galaxy’s rotation? About a galaxy’s mass? ...
... star are moving toward or away from each other, and whether the Earth and the star have large or small relative speeds. What did Vera Rubin and her colleagues measure with the Doppler Effect? What did they discover about a galaxy’s rotation? About a galaxy’s mass? ...
CloudsToSolarSystems_EXES
... Molecular gas (as mapped by CO emission) extends over even more of the space mapped out in previous image. ...
... Molecular gas (as mapped by CO emission) extends over even more of the space mapped out in previous image. ...
Camelopardalis-Better-Know-A-Constellation
... • Although Camelopardalis is the 18th largest constellation, (757 sq. deg. ) it is not a particularly bright constellation, as the brightest stars are only of fourth magnitude. • β Camelopardalis is the brightest star, at apparent magnitude 4.03. This star is a double star, with components of magnit ...
... • Although Camelopardalis is the 18th largest constellation, (757 sq. deg. ) it is not a particularly bright constellation, as the brightest stars are only of fourth magnitude. • β Camelopardalis is the brightest star, at apparent magnitude 4.03. This star is a double star, with components of magnit ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 18 Notes: Neutron Stars
... we can take the observed magnetic fields of white dwarfs as a rough guess, since the massive star core is basically an iron white dwarf before it collapses. These cover a very wide range, but typical values are ∼ 105 gauss, which means that we expect neutron stars to have magnetic fields of order 10 ...
... we can take the observed magnetic fields of white dwarfs as a rough guess, since the massive star core is basically an iron white dwarf before it collapses. These cover a very wide range, but typical values are ∼ 105 gauss, which means that we expect neutron stars to have magnetic fields of order 10 ...
astro2_lec1 - Astronomy & Astrophysics Group
... For many years the prevailing belief was that ellipticals evolve into spirals, from left to right in the tuning fork (although Hubble did not argue for the tuning fork diagram as an evolutionary sequence). ...
... For many years the prevailing belief was that ellipticals evolve into spirals, from left to right in the tuning fork (although Hubble did not argue for the tuning fork diagram as an evolutionary sequence). ...
The Night Sky This Month - Usk Astronomical Society
... above the horizon at sunset so observe Saturn as soon as you can this month, in the south-west. Uranus is at opposition on the 15th and is visible throughout the night this month. At a magnitude of 5.70 it may well be seen with binoculars. A small telescope might show a blue hue, but since Uranus us ...
... above the horizon at sunset so observe Saturn as soon as you can this month, in the south-west. Uranus is at opposition on the 15th and is visible throughout the night this month. At a magnitude of 5.70 it may well be seen with binoculars. A small telescope might show a blue hue, but since Uranus us ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.