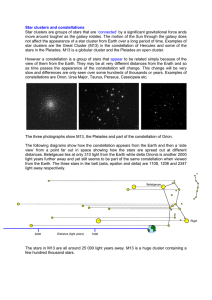
Scientists classify stars by
... would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from us makes their brightness different. ...
... would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from us makes their brightness different. ...
Sample exam 2
... stars. What does this suggest about the age of the cluster? What might you look for (and in what part of the EM spectrum) to support your age hypothesis? 13. Suppose you are looking at the emission spectrum of gaseous helium. You dutifully write down the wavelengths of emission. You notice a power d ...
... stars. What does this suggest about the age of the cluster? What might you look for (and in what part of the EM spectrum) to support your age hypothesis? 13. Suppose you are looking at the emission spectrum of gaseous helium. You dutifully write down the wavelengths of emission. You notice a power d ...
The Life Cycle of a star
... White dwarfs • Gravity causes the last of the star’s matter to collapse inward and compact, this is the white dwarf stage. • At this stage the star’s matter is extremely ...
... White dwarfs • Gravity causes the last of the star’s matter to collapse inward and compact, this is the white dwarf stage. • At this stage the star’s matter is extremely ...
The Brightness of Stars
... Stars that are cool, ~3500K, will be reddish; stars that are hot, ~10,000K, will be white White light is a combination of all colors, so a hot star will appear brighter than a red star, all other things being equal, because not all light from a star is visible to the human eye – This fact obscures a ...
... Stars that are cool, ~3500K, will be reddish; stars that are hot, ~10,000K, will be white White light is a combination of all colors, so a hot star will appear brighter than a red star, all other things being equal, because not all light from a star is visible to the human eye – This fact obscures a ...
Unit 11 Vocabulary
... 12. stellar nebula - a cloud of superheated gases and other elements formed by the explosive death of a massive star. This is where stars are made. ...
... 12. stellar nebula - a cloud of superheated gases and other elements formed by the explosive death of a massive star. This is where stars are made. ...
Document
... – We observe stars at various stages of evolution, and can piece together a description of the evolution of stars in general – Computer models provide a “fast-forward” look at the evolution of stars. ...
... – We observe stars at various stages of evolution, and can piece together a description of the evolution of stars in general – Computer models provide a “fast-forward” look at the evolution of stars. ...
File
... OBJECTIVE: Compare a stars color, temperature, brightness, and size to its spectral class. PURPOSE: Plot stars according to brightness and temperature to create an HR diagram. PROCEDURES: 1. Study the star data table on the back. 2. The sun, used as a standard brightness, is given a value of 1. The ...
... OBJECTIVE: Compare a stars color, temperature, brightness, and size to its spectral class. PURPOSE: Plot stars according to brightness and temperature to create an HR diagram. PROCEDURES: 1. Study the star data table on the back. 2. The sun, used as a standard brightness, is given a value of 1. The ...
Name: ____________ Period: ______ STAR BIOGRAPHY Name of
... Color and Temperature of Star Spectral class: The color of the star. Hot stars are bluer, cool stars are redder. In descending order from hottest (most blue) to coolest (most red), the spectral classes are: O B A F G K M. Each spectral class letter can be subdivided into ten smaller steps or gradat ...
... Color and Temperature of Star Spectral class: The color of the star. Hot stars are bluer, cool stars are redder. In descending order from hottest (most blue) to coolest (most red), the spectral classes are: O B A F G K M. Each spectral class letter can be subdivided into ten smaller steps or gradat ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. October 2005
... Delta () Cephei. +3.5 to +4.4, period 5.37 days. The prototype for the Cepheid class of variable stars. Their period-luminosity relationship has lead them to being used as “standard candles” in measuring distances to nearby galaxies. Maximum brightness occurs on 6th, 12th, 17th, 22nd and 28th. Mu ( ...
... Delta () Cephei. +3.5 to +4.4, period 5.37 days. The prototype for the Cepheid class of variable stars. Their period-luminosity relationship has lead them to being used as “standard candles” in measuring distances to nearby galaxies. Maximum brightness occurs on 6th, 12th, 17th, 22nd and 28th. Mu ( ...
Figures I through VII in Section 1 on the following sheet
... PART A: Figures I through VII on the following sheet are spectra of some Type V stars. List them in order of decreasing temperature (_1_). List them in order of decreasing strength of their Hydrogen lines (_2_). Which spectrum would most likely have been produced by star B from figure X (_3_)? Of st ...
... PART A: Figures I through VII on the following sheet are spectra of some Type V stars. List them in order of decreasing temperature (_1_). List them in order of decreasing strength of their Hydrogen lines (_2_). Which spectrum would most likely have been produced by star B from figure X (_3_)? Of st ...
Astronomy Lecture Notes: Stellar Nomenclature I Introduction
... i. Apparent magnitude is a code for brightness ii. Established visually by Hipparcos around 140 B.C.E. iii. Now measured using solid state photometers iv. A backward scale with the brightest star represented by the lowest number v. The brightest star in the entire sky is Sirius in Canis Major at m = ...
... i. Apparent magnitude is a code for brightness ii. Established visually by Hipparcos around 140 B.C.E. iii. Now measured using solid state photometers iv. A backward scale with the brightest star represented by the lowest number v. The brightest star in the entire sky is Sirius in Canis Major at m = ...
Test#3
... a) they rotate slowly, b) they are a few km in radius c) they have large magnetic fields, d) some of them are observed to be pulsars 28. Which of the following objects can rotate a thousand times per second without being torn apart? a) white dwarf, b) main sequence star, c) red giant, d) neutron sta ...
... a) they rotate slowly, b) they are a few km in radius c) they have large magnetic fields, d) some of them are observed to be pulsars 28. Which of the following objects can rotate a thousand times per second without being torn apart? a) white dwarf, b) main sequence star, c) red giant, d) neutron sta ...
Lecture 10 Advanced Variable Star Stuff March 18 2003 8:00 PM
... blows off all of its outer layers and leaves behind a hot dense core. There is no more fuel for nuclear fusion (the elements left are mainly things like carbon and iron, not easy to fuse). If we add too much fuel, what happens? If you put too much fuel onto the white dwarf, you can push it over the ...
... blows off all of its outer layers and leaves behind a hot dense core. There is no more fuel for nuclear fusion (the elements left are mainly things like carbon and iron, not easy to fuse). If we add too much fuel, what happens? If you put too much fuel onto the white dwarf, you can push it over the ...
Gemini South telescope makes the case for multiple Earth
... companions to the primary “host” star, to within a distance that is less than that of Mercury from our Sun. Faint “M-class” stars such as TRAPPIST-1 are of great interest to astronomers: their diminutive size allows easier detection of small, terrestrial planets. In the TRAPPIST-1 system, two of the ...
... companions to the primary “host” star, to within a distance that is less than that of Mercury from our Sun. Faint “M-class” stars such as TRAPPIST-1 are of great interest to astronomers: their diminutive size allows easier detection of small, terrestrial planets. In the TRAPPIST-1 system, two of the ...
homework assignment 1
... 3. Compare the size of an electron to the size of the universe. By what factor is the universe bigger? Approximately how many orders of magnitude is this? ...
... 3. Compare the size of an electron to the size of the universe. By what factor is the universe bigger? Approximately how many orders of magnitude is this? ...
Day-6
... Very low-mass stars (< 0.08 M) never start hydrogen fusion. These are called brown dwarfs. ...
... Very low-mass stars (< 0.08 M) never start hydrogen fusion. These are called brown dwarfs. ...
Stars - cmamath
... Describe the life cycle of stars and be able to diagram it. Make and use an H-R diagram. Define luminosity and magnitude. ...
... Describe the life cycle of stars and be able to diagram it. Make and use an H-R diagram. Define luminosity and magnitude. ...
Worksheet: Stars and the HR Diagram
... Background: The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the br ...
... Background: The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the br ...
Review3-2016
... How do we use the atomic emission and absorption spectra to find the composition of a star? How do we determine the rotation period of a star? How do we determine the distance to a star using Stellar Parallax? What is an H-R diagram and what information does it give us? One of the Ca spectral lines ...
... How do we use the atomic emission and absorption spectra to find the composition of a star? How do we determine the rotation period of a star? How do we determine the distance to a star using Stellar Parallax? What is an H-R diagram and what information does it give us? One of the Ca spectral lines ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 • In this class we will ...
... MBol (!) − MBol (!) = 2.5 log10 [L(!)/L(!)] ...
... MBol (!) − MBol (!) = 2.5 log10 [L(!)/L(!)] ...
Roy - WordPress.com
... years away. Their orbital period is over 500 years. In 2009, a giant planet was found orbiting one of these stars. ...
... years away. Their orbital period is over 500 years. In 2009, a giant planet was found orbiting one of these stars. ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.