The Stars
... Stars are like the sun, some being smaller and some larger, but so far away that they look like points of light. By the end of the 5th grade, students should know that The sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a disk-shaped galaxy of stars, part of which can be seen as a glowing ba ...
... Stars are like the sun, some being smaller and some larger, but so far away that they look like points of light. By the end of the 5th grade, students should know that The sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a disk-shaped galaxy of stars, part of which can be seen as a glowing ba ...
20081 Study Guide_77-120
... Answers to Analysis and Conclusions 1. The plate does not actually change position, although it does appear to move when it is viewed from different locations. 2. The apparent change in position of the plate is greater at short distances than it is farther away because the angle formed by the observ ...
... Answers to Analysis and Conclusions 1. The plate does not actually change position, although it does appear to move when it is viewed from different locations. 2. The apparent change in position of the plate is greater at short distances than it is farther away because the angle formed by the observ ...
Everything Under and Over The Stars
... happen to the solar system? There was a recent supernova called SN1993J in a star system, which is not mentioned. The powerful shockwave traveled at 44 million mph, but 5 years later it slowed down because of drag caused by particles. There has been a supernova in the Milky Way, around the 1700’s. A ...
... happen to the solar system? There was a recent supernova called SN1993J in a star system, which is not mentioned. The powerful shockwave traveled at 44 million mph, but 5 years later it slowed down because of drag caused by particles. There has been a supernova in the Milky Way, around the 1700’s. A ...
Scientists classify stars by
... would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from us makes their brightness different. ...
... would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from us makes their brightness different. ...
Sample exam 2
... 13. Suppose you are looking at the emission spectrum of gaseous helium. You dutifully write down the wavelengths of emission. You notice a power dial on the side of emission lamp and, just for fun, decide to turn up the power. The color of the helium lamp changes and you look through the spectroscop ...
... 13. Suppose you are looking at the emission spectrum of gaseous helium. You dutifully write down the wavelengths of emission. You notice a power dial on the side of emission lamp and, just for fun, decide to turn up the power. The color of the helium lamp changes and you look through the spectroscop ...
Stellar Metamorphosis: The Nearest Star
... September 21, 2013 Cocoa, FL 32922 Abstract: In stellar metamorphosis humanities’ closest star is the Earth itself. Explanation is provided. In the so-called “established sciences” the closest star to the Earth is the Sun, and the closest star to Earth besides the Sun is Proxima Centauri. This is no ...
... September 21, 2013 Cocoa, FL 32922 Abstract: In stellar metamorphosis humanities’ closest star is the Earth itself. Explanation is provided. In the so-called “established sciences” the closest star to the Earth is the Sun, and the closest star to Earth besides the Sun is Proxima Centauri. This is no ...
No Slide Title
... The neutron star may continue to gain mass from nearby stars. At a critical moment, it becomes so dense it collapses in on itself, becoming a single point of zero size! Its gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape from inside a certain boundary - the EVENT HORIZON. The star is now a BLACK ...
... The neutron star may continue to gain mass from nearby stars. At a critical moment, it becomes so dense it collapses in on itself, becoming a single point of zero size! Its gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape from inside a certain boundary - the EVENT HORIZON. The star is now a BLACK ...
The North Star
... The North Star is the brightest star in the constellation Ursa Minor. The star is about two times brighter then what it was when Ptolemy (a roman citizen of Greek) looked at it. ...
... The North Star is the brightest star in the constellation Ursa Minor. The star is about two times brighter then what it was when Ptolemy (a roman citizen of Greek) looked at it. ...
Unit 1
... – RR Lyrae and Cepheid variables are useful for finding distances to the stars, as the star’s period is proportional to its luminosity. ...
... – RR Lyrae and Cepheid variables are useful for finding distances to the stars, as the star’s period is proportional to its luminosity. ...
Astronomy Day 2006: A short presentation on eclipsing binary stars
... multiple systems are binary stars, two stars orbiting each other; binaries can be orbited by a third star, forming a ternary or triple star, and there are more complex cases like binaries orbiting other binaries or ternaries, etc. Some multiple star systems contain as many as eight stars. ...
... multiple systems are binary stars, two stars orbiting each other; binaries can be orbited by a third star, forming a ternary or triple star, and there are more complex cases like binaries orbiting other binaries or ternaries, etc. Some multiple star systems contain as many as eight stars. ...
Astro 18 – Section Week 2
... The deeper absorption line at 760nm is caused by our atmosphere's oxygen molecule. The two absorption lines at 720 and 890nm (from methane) appear on Saturn and Titan, but the rings do not have them ...
... The deeper absorption line at 760nm is caused by our atmosphere's oxygen molecule. The two absorption lines at 720 and 890nm (from methane) appear on Saturn and Titan, but the rings do not have them ...
Astro 18 – Section Week 2
... The deeper absorption line at 760nm is caused by our atmosphere's oxygen molecule. The two absorption lines at 720 and 890nm (from methane) appear on Saturn and Titan, but the rings do not have them ...
... The deeper absorption line at 760nm is caused by our atmosphere's oxygen molecule. The two absorption lines at 720 and 890nm (from methane) appear on Saturn and Titan, but the rings do not have them ...
Stellar Evolution
... We do not know that all stars, regardless of their size, eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity Low Mass Stars – consume fuel at a slow rate, may remain on main-sequence for up to 100 billion years, end up collapsing into white dwarfs Medium Mass Stars – go into red-giant stage, foll ...
... We do not know that all stars, regardless of their size, eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity Low Mass Stars – consume fuel at a slow rate, may remain on main-sequence for up to 100 billion years, end up collapsing into white dwarfs Medium Mass Stars – go into red-giant stage, foll ...
A star is a - Trimble County Schools
... Appear to be tiny specks of white light Most vary in color and are much larger than Earth Motion • Stars move through the night sky towards the west • Stars rotate around the North Star, Polaris – _____________________________ = stars that circle around Polaris • Because of the earth’s rotation, som ...
... Appear to be tiny specks of white light Most vary in color and are much larger than Earth Motion • Stars move through the night sky towards the west • Stars rotate around the North Star, Polaris – _____________________________ = stars that circle around Polaris • Because of the earth’s rotation, som ...
Lives of stars
... temperature will be higher, but it sill be very small (about size of the earth) so it will not emit as much light. Which letter represents this state of the sun? What do call this type of star? 10.Which letters are in its hydrostatic equilibrium or main sequence? 11.Which of the main sequence stars ...
... temperature will be higher, but it sill be very small (about size of the earth) so it will not emit as much light. Which letter represents this state of the sun? What do call this type of star? 10.Which letters are in its hydrostatic equilibrium or main sequence? 11.Which of the main sequence stars ...
24-2 Characteristics of Stars
... Color and Temperature of Stars • Coolest stars = red • Hot stars = white • Hottest stars = bluewhite ...
... Color and Temperature of Stars • Coolest stars = red • Hot stars = white • Hottest stars = bluewhite ...
Starry Night¨ Times - October 2008
... recognizable and beloved constellations. By far, the most popular celestial gem in the constellation of Orion is M42, The Great Orion Nebula. Although it is 1500 lightyears away, M42 is a great target to view in small telescopes. This is due not only to its brightness, but also to its wonderful clou ...
... recognizable and beloved constellations. By far, the most popular celestial gem in the constellation of Orion is M42, The Great Orion Nebula. Although it is 1500 lightyears away, M42 is a great target to view in small telescopes. This is due not only to its brightness, but also to its wonderful clou ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance Spectroscopy
... • Stars less than 0.5 solar mass can’t compress any more • Stars from 0.5-2 solar masses get so compressed that gravitational contraction and radiation from the fusion shell releases energy that is absorbed by some of the electrons • The core can then compress more • Helium fusion can occur ...
... • Stars less than 0.5 solar mass can’t compress any more • Stars from 0.5-2 solar masses get so compressed that gravitational contraction and radiation from the fusion shell releases energy that is absorbed by some of the electrons • The core can then compress more • Helium fusion can occur ...
May 2017 - Museums Wellington
... Saturn, along with some of our brightest stars. Jupiter will be one of the first objects to appear, visible in the north east shortly after the Sun has set. Just to the right of Jupiter is Spica, the brightest star in the constellation of Virgo, and below, just above the horizon is orange coloured A ...
... Saturn, along with some of our brightest stars. Jupiter will be one of the first objects to appear, visible in the north east shortly after the Sun has set. Just to the right of Jupiter is Spica, the brightest star in the constellation of Virgo, and below, just above the horizon is orange coloured A ...
Homework 5 (stellar properties)
... diagram.) Which equation relates these two quantities to the size (radius) of a star (after all, the luminosity class is simply a way to group stars by size…)? (Hint: Look at problem 3.) ...
... diagram.) Which equation relates these two quantities to the size (radius) of a star (after all, the luminosity class is simply a way to group stars by size…)? (Hint: Look at problem 3.) ...
a star is born reading
... years. It will take that long to cool off. As it cools, it will become a white dwarf. Once it stops glowing, it will become a black dwarf. There are no known black dwarfs in our universe. Blue giant stars are very bright and very hot. They burn fuel very quickly. It runs out in ten thousand to 100 t ...
... years. It will take that long to cool off. As it cools, it will become a white dwarf. Once it stops glowing, it will become a black dwarf. There are no known black dwarfs in our universe. Blue giant stars are very bright and very hot. They burn fuel very quickly. It runs out in ten thousand to 100 t ...
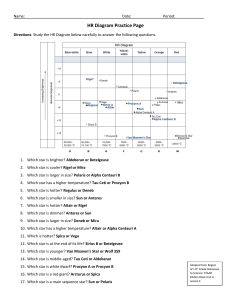
HR Diagram Practice Page
... 4. Which star has a higher temperature? Tau Ceti or Procyon B 5. Which star is hotter? Regulus or Deneb 6. Which star is smaller in size? Sun or Antares 7. Which star is hotter? Altair or Rigel 8. Which star is dimmer? Antares or Sun 9. Which star is larger in size? Deneb or Mira 10. Which star has ...
... 4. Which star has a higher temperature? Tau Ceti or Procyon B 5. Which star is hotter? Regulus or Deneb 6. Which star is smaller in size? Sun or Antares 7. Which star is hotter? Altair or Rigel 8. Which star is dimmer? Antares or Sun 9. Which star is larger in size? Deneb or Mira 10. Which star has ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.