1 Ay 124 Winter 2014 – HOMEWORK #2 Problem 1
... than 1M , whose lifetimes are shorter than the age of the galaxy. a) Find the slope x such that an observer in a homogeneous, isotropic region counts, at every apparent bolmetric magnitude, equal numbers of stars in each octave of luminosity. What type of star dominates the counts if x is flatter t ...
... than 1M , whose lifetimes are shorter than the age of the galaxy. a) Find the slope x such that an observer in a homogeneous, isotropic region counts, at every apparent bolmetric magnitude, equal numbers of stars in each octave of luminosity. What type of star dominates the counts if x is flatter t ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • Main sequence stars are “young” stars • If a star is leaving the main sequence, it is at the end of its lifespan of burning hydrogen into helium ...
... • Main sequence stars are “young” stars • If a star is leaving the main sequence, it is at the end of its lifespan of burning hydrogen into helium ...
chapter8
... Polaris has just about the same spectral type (and thus surface temperature) as our sun, but it is 10,000 times brighter than our sun. Thus, Polaris is 100 times larger than the sun. ...
... Polaris has just about the same spectral type (and thus surface temperature) as our sun, but it is 10,000 times brighter than our sun. Thus, Polaris is 100 times larger than the sun. ...
Small images
... • When a massive star becomes a red giant, it may spill its H-envelope onto its companion changing the evolution of both. E.g. Type Ib supernova ...
... • When a massive star becomes a red giant, it may spill its H-envelope onto its companion changing the evolution of both. E.g. Type Ib supernova ...
here - Lund Observatory
... The trigonometric parallax for Sirius has been determined to 0.375’’. Stars of the same spectral and luminosity class are supposed to have the same absolute magnitudes and intrinsic colour indices. The interstellar reddening of the two binary components is assumed to be the same. The two cluster sta ...
... The trigonometric parallax for Sirius has been determined to 0.375’’. Stars of the same spectral and luminosity class are supposed to have the same absolute magnitudes and intrinsic colour indices. The interstellar reddening of the two binary components is assumed to be the same. The two cluster sta ...
Parallels: Proto-Planetary Disks and rings
... • 51 Pegasi b: The first planet around a star like the Sun. Astronomers found it using the Observatoire de Haute-Provence in France, a ground-based facility. This planet is also known as a “hot Jupiter” because it appears to be a very warm gas-giant-type world. • Kepler 186-f: the first Earth-size p ...
... • 51 Pegasi b: The first planet around a star like the Sun. Astronomers found it using the Observatoire de Haute-Provence in France, a ground-based facility. This planet is also known as a “hot Jupiter” because it appears to be a very warm gas-giant-type world. • Kepler 186-f: the first Earth-size p ...
CONSTELLATION CASSIOPEIA named after the
... named after the queen of Aethiopia. Cassiopeia was the wife of Cepheus, King of Aethiopia and mother of Princess Andromeda. It is a constellation in the northern sky and one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations t ...
... named after the queen of Aethiopia. Cassiopeia was the wife of Cepheus, King of Aethiopia and mother of Princess Andromeda. It is a constellation in the northern sky and one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations t ...
The Transfer Equation
... • You want to detect the faint star of an unresolved binary system comprising a B5V star and an M0V companion. What wavelength regime would you choose to try to detect the M0V star? What is the ratio of the flux from the B star to the flux from the M star at that wavelength? • You want to detect the ...
... • You want to detect the faint star of an unresolved binary system comprising a B5V star and an M0V companion. What wavelength regime would you choose to try to detect the M0V star? What is the ratio of the flux from the B star to the flux from the M star at that wavelength? • You want to detect the ...
stars_2nd_edit
... Because of their small size these stars burn their fuel very slowly, which allows them to live a very long time. Some red dwarf stars will live trillions of years before they run out of fuel. ...
... Because of their small size these stars burn their fuel very slowly, which allows them to live a very long time. Some red dwarf stars will live trillions of years before they run out of fuel. ...
Characteristics of Stars
... diagram below). This is the same thing that happens when you look at a close object with first one eye and then the other. For example, hold your thumb at the tip of your nose. Look at your thumb with first your right eye and then your left. Your thumb appears to move because your eyes are not at ex ...
... diagram below). This is the same thing that happens when you look at a close object with first one eye and then the other. For example, hold your thumb at the tip of your nose. Look at your thumb with first your right eye and then your left. Your thumb appears to move because your eyes are not at ex ...
your star chart here - Australasian Science Magazine
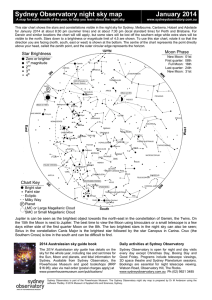
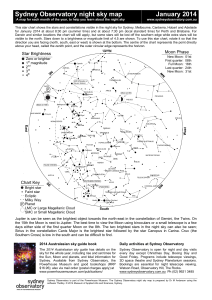
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still ap ...
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still ap ...
What`s Up - April 2016
... star in the sky, lighting the keel of the great ship Argo. If they were at the same distance, Canopus would appear far brighter than Sirius. Canopus is 15000 times as luminous as the sun, a rare yellow-white supergiant 313 light years away. If placed at the center of our solar system, its surface wo ...
... star in the sky, lighting the keel of the great ship Argo. If they were at the same distance, Canopus would appear far brighter than Sirius. Canopus is 15000 times as luminous as the sun, a rare yellow-white supergiant 313 light years away. If placed at the center of our solar system, its surface wo ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. April 2006. 1
... Gamma Virginis. This interesting binary is best placed for observation from late evening through the early hours star. Now past periastron it should be possible to split visually with the 16” under good seeing conditions and worth trying with smaller apertures to record when it can be resolved. Anot ...
... Gamma Virginis. This interesting binary is best placed for observation from late evening through the early hours star. Now past periastron it should be possible to split visually with the 16” under good seeing conditions and worth trying with smaller apertures to record when it can be resolved. Anot ...
Questions to answer - high school teachers at CERN
... a few hundred meters but in the case of a star is only a few cm. So the atmospheric turbulence may affect the image of the stars but not those of the planets. That is why the stars twinkle at night but the planets do not. ...
... a few hundred meters but in the case of a star is only a few cm. So the atmospheric turbulence may affect the image of the stars but not those of the planets. That is why the stars twinkle at night but the planets do not. ...
Stars: the Hertzsprung
... Take spectrum of star, find it is F2V, absolute magnitude is then M = +4.0. Observe star brightness, find apparent magnitude m = 9.5. Calculate distance: ...
... Take spectrum of star, find it is F2V, absolute magnitude is then M = +4.0. Observe star brightness, find apparent magnitude m = 9.5. Calculate distance: ...
Constellations
... A natural human tendency is to see patterns and relationships between objects even when no true connection exists. Long ago, people connected the brightest stars into configurations called constellations, which ancient astronomers named after mythological beings, heroes, and animals—whatever was imp ...
... A natural human tendency is to see patterns and relationships between objects even when no true connection exists. Long ago, people connected the brightest stars into configurations called constellations, which ancient astronomers named after mythological beings, heroes, and animals—whatever was imp ...
Final Exam Practice Part I
... 7. What is Nuclear Fusion? 8. How does nuclear fusion produce energy? 9. Nuclear fusion can only occur in the center of the solar system. Why is that? 10. What would happen to the orbit of a planet if it suddenly started orbiting faster? 11. As a new star is born, what type of atoms first begin to f ...
... 7. What is Nuclear Fusion? 8. How does nuclear fusion produce energy? 9. Nuclear fusion can only occur in the center of the solar system. Why is that? 10. What would happen to the orbit of a planet if it suddenly started orbiting faster? 11. As a new star is born, what type of atoms first begin to f ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.