ASTRONOMY 1102 1
... in chapters 27, 28, 29 anmd 30 of Astronomy: from the Earth to the Universe. The test will consist as usual of two parts: multiple choice questions and problems. I give below an example of what the test will look like and a couple of examples of questions and problems. Review class notes: do not mem ...
... in chapters 27, 28, 29 anmd 30 of Astronomy: from the Earth to the Universe. The test will consist as usual of two parts: multiple choice questions and problems. I give below an example of what the test will look like and a couple of examples of questions and problems. Review class notes: do not mem ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... descriptions given in question text • Q7: Luminosity, temperature and area of a star are related by the Stefan-BoltzmannLaw: L = b A T4, so use scaling arguments to figure out L from R,T and R from L,T ...
... descriptions given in question text • Q7: Luminosity, temperature and area of a star are related by the Stefan-BoltzmannLaw: L = b A T4, so use scaling arguments to figure out L from R,T and R from L,T ...
Stars, Galaxies & Universe
... A. Satellite telescopes are much closer to the stars. B. Satellite telescopes are able to see through solid objects. C. Satellite telescopes can detect wavelengths that are blocked by the atmosphere. D. Satellite telescopes have the ability to see the future. ...
... A. Satellite telescopes are much closer to the stars. B. Satellite telescopes are able to see through solid objects. C. Satellite telescopes can detect wavelengths that are blocked by the atmosphere. D. Satellite telescopes have the ability to see the future. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... Nebula and other nebulae (stars in formation) on this page. Continue by reading up on Main Sequence Stars and find out how our sun compares in mass to other stars like Sirius, and Proxima Centauri. Based on its mass, will our sun be around for a while? Approximately how long before our sun consumes ...
... Nebula and other nebulae (stars in formation) on this page. Continue by reading up on Main Sequence Stars and find out how our sun compares in mass to other stars like Sirius, and Proxima Centauri. Based on its mass, will our sun be around for a while? Approximately how long before our sun consumes ...
Lecture 13: The stars are suns
... • Apparent brightness is not a measure of the luminosity (in watts) of a star. Star of given brightness could be: dim but close, or luminous and distant. • Inverse Square Law for light tell us that the flux is inversely proportional to the distance squared: f= ...
... • Apparent brightness is not a measure of the luminosity (in watts) of a star. Star of given brightness could be: dim but close, or luminous and distant. • Inverse Square Law for light tell us that the flux is inversely proportional to the distance squared: f= ...
Spectropolarimetric view of the lower atmosphere of
... II - Sciences et techniques, IN2P3 – Université de Montpellier II Place Eugène Bataillon - CC 72 34095 Montpellier Cédex 05, France ...
... II - Sciences et techniques, IN2P3 – Université de Montpellier II Place Eugène Bataillon - CC 72 34095 Montpellier Cédex 05, France ...
Name _________ Date _____________ Period ______ Skills
... _____ 18. Stars are now classified by a. their elements. b. their temperature. c. their age. d. their size. _____ 19. Class O stars, the hottest stars, are a. yellow. b. orange. c. red. d. blue. 20. Early astronomers called the brightest stars in the sky ______________________ stars. 21. What type o ...
... _____ 18. Stars are now classified by a. their elements. b. their temperature. c. their age. d. their size. _____ 19. Class O stars, the hottest stars, are a. yellow. b. orange. c. red. d. blue. 20. Early astronomers called the brightest stars in the sky ______________________ stars. 21. What type o ...
1 How luminous are stars?
... stars. Bright, hot, blue main-sequence stars (high-mass) are very rare. Giants and supergiants are extremely rare. ...
... stars. Bright, hot, blue main-sequence stars (high-mass) are very rare. Giants and supergiants are extremely rare. ...
File - Adopt A Constellation
... • Constellations - A pattern or group of stars in the sky that humans observe in a pattern and give a name. • People of ancient time saw the constellations as character or animals in the sky. They made up stories to explain how the object, animal, or character came into the night sky • Earth rotate ...
... • Constellations - A pattern or group of stars in the sky that humans observe in a pattern and give a name. • People of ancient time saw the constellations as character or animals in the sky. They made up stories to explain how the object, animal, or character came into the night sky • Earth rotate ...
Earth in space
... expanding so that objects (galaxies) move away from one another The galaxies aren’t expanding…just the spaces between them ...
... expanding so that objects (galaxies) move away from one another The galaxies aren’t expanding…just the spaces between them ...
15compact2s
... The radius of the event horizon is called the Schwarzschild radius: Compressing a mass to a size smaller than its Schwarzschild radius creates a black hole ...
... The radius of the event horizon is called the Schwarzschild radius: Compressing a mass to a size smaller than its Schwarzschild radius creates a black hole ...
Star Cycle2013
... _____________ that marks the end of a very massive star’s life. When it occurs, the exploding star can outshine all of the other stars in the galaxy in total for several days and may leave behind only a crushed core. ...
... _____________ that marks the end of a very massive star’s life. When it occurs, the exploding star can outshine all of the other stars in the galaxy in total for several days and may leave behind only a crushed core. ...
chapter9
... absorbed by interstellar clouds Red light can more easily penetrate the cloud, but is still absorbed to some extent ...
... absorbed by interstellar clouds Red light can more easily penetrate the cloud, but is still absorbed to some extent ...
Images from the Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope
... The name ‘Cancer’ means ‘the crab’ in Latin. It is the faintest of the 12 zodiac constellations and contains some famous DSOs: the open cluster Praesepe, aka the Beehive Cluster (M44), and the open cluster M67. Cancer does not have any stars brighter than 4th mag. Stars α, δ, and γ Cancri lie close ...
... The name ‘Cancer’ means ‘the crab’ in Latin. It is the faintest of the 12 zodiac constellations and contains some famous DSOs: the open cluster Praesepe, aka the Beehive Cluster (M44), and the open cluster M67. Cancer does not have any stars brighter than 4th mag. Stars α, δ, and γ Cancri lie close ...
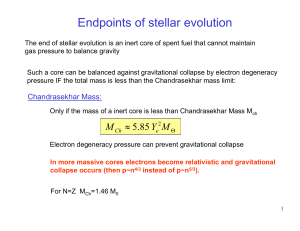
Endpoints of stellar evolution
... Little Ghost Nebula distance 2-5 kLy blue: OIII green: HII red: NII ...
... Little Ghost Nebula distance 2-5 kLy blue: OIII green: HII red: NII ...
Prep/Review Questions - Faculty Web Sites at the University
... Why does even a small telescope reveal many more stars than are visible to the naked eye? You have three eyepieces with focal lengths of 200, 100, and 20 mm to use with your telescope, which has a focal length of 1800 mm. Which eyepiece will give you an image with 90 power magnification? Which eyepi ...
... Why does even a small telescope reveal many more stars than are visible to the naked eye? You have three eyepieces with focal lengths of 200, 100, and 20 mm to use with your telescope, which has a focal length of 1800 mm. Which eyepiece will give you an image with 90 power magnification? Which eyepi ...
AY1 Homework for Quiz 2: Spring 2017
... ___ A. It will have become slightly more massive than the Sun is now because lightweight hydrogen has been converted into heavier Helium ___ B. It will be enriched in helium compared to the Sun ___ ...
... ___ A. It will have become slightly more massive than the Sun is now because lightweight hydrogen has been converted into heavier Helium ___ B. It will be enriched in helium compared to the Sun ___ ...
Mirrored Image Sep06.pub - High Desert Astronomical Society
... in the direction in time for most to see it. It most likely hit the ground somewhere north of Barstow! There were so many objects to look at, one hardly knew where to start. Neptune through Dave Meyer's Celestron 14” scope was a beautiful turquoise dot, very pretty. There were four 10” dobs, Dave Fl ...
... in the direction in time for most to see it. It most likely hit the ground somewhere north of Barstow! There were so many objects to look at, one hardly knew where to start. Neptune through Dave Meyer's Celestron 14” scope was a beautiful turquoise dot, very pretty. There were four 10” dobs, Dave Fl ...
AST 105: Introduction to the Solar System HOMEWORK # 3
... Human ears are not sensitive to radio waves. The waves have to be converted electronically to audible frequencies which is not a unique process. Audible frequencies could be encoded into radio waves, but how would we know what the algorithm was? On Earth we use two main encoding systems, frequency m ...
... Human ears are not sensitive to radio waves. The waves have to be converted electronically to audible frequencies which is not a unique process. Audible frequencies could be encoded into radio waves, but how would we know what the algorithm was? On Earth we use two main encoding systems, frequency m ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.