J S U N I L T U... 2011 “Chase Excellence- Success Will Follow” ll Follow”
... (d) INSAT is an artificial satellite. ( ) (e) There are nine planets in the solar system. ( ) (f) Constellation Orion can be seen only with a telescope. ( ) Answer: (a) False: Stars are not a member of the solar system. The sun and the celestial bodies revolving around it form the solar system. (b) ...
... (d) INSAT is an artificial satellite. ( ) (e) There are nine planets in the solar system. ( ) (f) Constellation Orion can be seen only with a telescope. ( ) Answer: (a) False: Stars are not a member of the solar system. The sun and the celestial bodies revolving around it form the solar system. (b) ...
Astronomy news
... seven nearby, INSs discovered with ROSAT and often dubbed XDINS. RX J1856.5-3754 received particular interest since it is the brightest XDIN, its X-ray flux doesn’t show any apparent contamination from non thermal magnetospheric emission, and a parallactic distance (117 12 pc) has been reported. It ...
... seven nearby, INSs discovered with ROSAT and often dubbed XDINS. RX J1856.5-3754 received particular interest since it is the brightest XDIN, its X-ray flux doesn’t show any apparent contamination from non thermal magnetospheric emission, and a parallactic distance (117 12 pc) has been reported. It ...
Chapter11
... Sources of Shock Waves Triggering Star Formation (1) Previous star formation can trigger further star formation through: a) Shocks from ...
... Sources of Shock Waves Triggering Star Formation (1) Previous star formation can trigger further star formation through: a) Shocks from ...
Constellation Part II readingConstellation Part II reading(es)
... The stars are distant objects. Their distances vary, but they are all very far away. Excluding our Sun, the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is more than 4 light years away. As Earth spins on its axis, we, as Earth-bound observers, spin past this background of distant stars. As Earth spins, the stars ...
... The stars are distant objects. Their distances vary, but they are all very far away. Excluding our Sun, the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is more than 4 light years away. As Earth spins on its axis, we, as Earth-bound observers, spin past this background of distant stars. As Earth spins, the stars ...
Measuring Stars
... Hydrogen Spectrum Star B is A) Made of two kinds of hydrogen B) Moving away from us AND moving towards us C) Actually two stars moving at different speeds ...
... Hydrogen Spectrum Star B is A) Made of two kinds of hydrogen B) Moving away from us AND moving towards us C) Actually two stars moving at different speeds ...
1 Ay 124 Winter 2014 – HOMEWORK #1
... Assume for the time being that the Galaxy has no dust, and that we are observing along a line of sight at b = 0 deg and l = 180 deg. We are interested in observing the most distant solar-type stars (MV ' +5.1) possible, but our apparent magnitude limit for the observations is mV = 24.0. The central ...
... Assume for the time being that the Galaxy has no dust, and that we are observing along a line of sight at b = 0 deg and l = 180 deg. We are interested in observing the most distant solar-type stars (MV ' +5.1) possible, but our apparent magnitude limit for the observations is mV = 24.0. The central ...
Level 2 Earth and Space Science (91192) 2015
... Pleiades is known to us as Matariki, and is an open star cluster of over 1400 stars. Its appearance in the early morning sky marks the dawn of the Māori New Year. In this cluster there is a star named HD 23514, which has been observed with dust particles around it that are thought to be the beginnin ...
... Pleiades is known to us as Matariki, and is an open star cluster of over 1400 stars. Its appearance in the early morning sky marks the dawn of the Māori New Year. In this cluster there is a star named HD 23514, which has been observed with dust particles around it that are thought to be the beginnin ...
White Dwarfs - Indiana University
... – All WDs have a common origin (PNN) with some hydrogen, upper limit of 10-4 solar masses to 10-15 solar masses of hydrogen (recall that 10-4 is the limit where H burning stops) – Only about 10-15 is needed to produce an optically thick H layer at the ...
... – All WDs have a common origin (PNN) with some hydrogen, upper limit of 10-4 solar masses to 10-15 solar masses of hydrogen (recall that 10-4 is the limit where H burning stops) – Only about 10-15 is needed to produce an optically thick H layer at the ...
Document
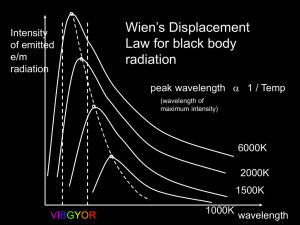
... Estimate the intensity of the radiation emitted per unit area from a star if it’s effective surface Temp is 6000K Estimate the energy emitted from a star if its peak wavelength is 600nm. Total power radiated Power output = E x surface area of star Surface area of a star = 4 R 2 Where R is the rad ...
... Estimate the intensity of the radiation emitted per unit area from a star if it’s effective surface Temp is 6000K Estimate the energy emitted from a star if its peak wavelength is 600nm. Total power radiated Power output = E x surface area of star Surface area of a star = 4 R 2 Where R is the rad ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... you’d be shining and how you’d be visible from halfway across the galaxy. But you mo-rons must not have bothered to read the fine print that said that you’d explode in seven million years! And if you did read it then you’re even stupider than you look. Seven million is not a long time!” – Eric Schul ...
... you’d be shining and how you’d be visible from halfway across the galaxy. But you mo-rons must not have bothered to read the fine print that said that you’d explode in seven million years! And if you did read it then you’re even stupider than you look. Seven million is not a long time!” – Eric Schul ...
Spectral Variations of Several RV Tauri Type Stars Patrick Durant
... minima. See Nesmith & Cash (adjacent poster, this conference) for examples of the light curves. Typical periods between successive deep minima are 30 to 150 days. ...
... minima. See Nesmith & Cash (adjacent poster, this conference) for examples of the light curves. Typical periods between successive deep minima are 30 to 150 days. ...
Slide 1
... but much WHAT IS AMAZING: Stars of different masses fall along a brighter than narrow path in L/T diagram MS stars → Must be much larger ...
... but much WHAT IS AMAZING: Stars of different masses fall along a brighter than narrow path in L/T diagram MS stars → Must be much larger ...
Document
... Even if the multiple images are too close together to be resolved separately, they will still make the background source appear (temporarily) brighter. We call this case gravitational microlensing. We can plot a light curve showing how the brightness of the background source changes with time. If t ...
... Even if the multiple images are too close together to be resolved separately, they will still make the background source appear (temporarily) brighter. We call this case gravitational microlensing. We can plot a light curve showing how the brightness of the background source changes with time. If t ...
The Temperatures of Stars
... The Harvard Computers At the same time, the Observatory received funding from a wealthy donor to complete a large survey of stellar spectral types: the Henry Draper Survey. The work of collecting measurements, cataloging the results, and analyzing them fell to the female computers. Since they could ...
... The Harvard Computers At the same time, the Observatory received funding from a wealthy donor to complete a large survey of stellar spectral types: the Henry Draper Survey. The work of collecting measurements, cataloging the results, and analyzing them fell to the female computers. Since they could ...
Chapter21
... 22. As matter accumulates rapidly on a white dwarf, the star becomes smaller and its core becomes hotter. When the core temperature reaches 10 billion K, carbon fusion begins. The energy released by carbon fusion triggers a series of nuclear reactions that blow the star apart. 23. X-ray bursts occur ...
... 22. As matter accumulates rapidly on a white dwarf, the star becomes smaller and its core becomes hotter. When the core temperature reaches 10 billion K, carbon fusion begins. The energy released by carbon fusion triggers a series of nuclear reactions that blow the star apart. 23. X-ray bursts occur ...
Stellar Evolution Review
... a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shifted into the infrared ...
... a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shifted into the infrared ...
`earthlike` and second the probability that they have suitable climate
... which are ‘earthlike’ and second the probability that they have suitable climate. ...
... which are ‘earthlike’ and second the probability that they have suitable climate. ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... – A fundamental limit to the number of electrons that can be squeezed into a given volume – When this limit is reached, there appears a “pressure” that keeps any more electrons from entering the volume – This “electron pressure” supports the white dwarf against its own gravity ...
... – A fundamental limit to the number of electrons that can be squeezed into a given volume – When this limit is reached, there appears a “pressure” that keeps any more electrons from entering the volume – This “electron pressure” supports the white dwarf against its own gravity ...
Milky Way galaxy - Uplift North Hills Prep
... Before October 6, 1923, astronomers thought the Andromeda Nebula and similar objects were bright pockets of matter inside the Milky Way. On that day astronomer Edwin Hubble noticed, looking at the photograps, a particular type of star inside the Andromeda Nebula. Hubble realized that the star (Ceph ...
... Before October 6, 1923, astronomers thought the Andromeda Nebula and similar objects were bright pockets of matter inside the Milky Way. On that day astronomer Edwin Hubble noticed, looking at the photograps, a particular type of star inside the Andromeda Nebula. Hubble realized that the star (Ceph ...
key - Scioly.org
... a) Sirius A releases 26 times as much energy as our Sun. b) The existence of Sirius B was predicted by Bessel in 1844. It was first observed in 1862 by Alvan Clark (4 points: 1 point for each answer) c) Oxygen and carbon (2 points) 33) HM Cancri or RX J0806.3+152 (7 points) a) 321.5 seconds (5.4 m ...
... a) Sirius A releases 26 times as much energy as our Sun. b) The existence of Sirius B was predicted by Bessel in 1844. It was first observed in 1862 by Alvan Clark (4 points: 1 point for each answer) c) Oxygen and carbon (2 points) 33) HM Cancri or RX J0806.3+152 (7 points) a) 321.5 seconds (5.4 m ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.