Unit 1
... • Photons have a difficult time moving through a star’s atmosphere • If the photon has the right energy, it will be absorbed by an atom and raise an electron to a higher energy level • Creates absorption spectra, a unique “fingerprint” for the star’s composition. The strength of this spectra is dete ...
... • Photons have a difficult time moving through a star’s atmosphere • If the photon has the right energy, it will be absorbed by an atom and raise an electron to a higher energy level • Creates absorption spectra, a unique “fingerprint” for the star’s composition. The strength of this spectra is dete ...
Chapter 21 notes - Clinton Public Schools
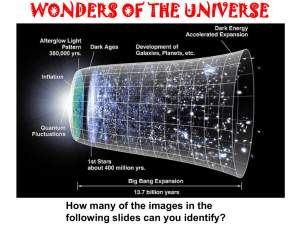
... Section 5: The Expanding Universe: How the universe was formed: Astronomers believe the universe was incredibly hot and dense, exploded in what astronomers called the Big Bang. According to the big bang theory, the universe formed in an instant, billion of years ago, in an enormous explosion. Since ...
... Section 5: The Expanding Universe: How the universe was formed: Astronomers believe the universe was incredibly hot and dense, exploded in what astronomers called the Big Bang. According to the big bang theory, the universe formed in an instant, billion of years ago, in an enormous explosion. Since ...
Down Under from North Florida
... However, astute Gainesville area residents can easily spot this bright star low over the southern winter horizon with careful planning. See Figure 1. Note: Atmospheric extinction may dim Canopus (mag. -0.62) by one or two magnitudes, which therefore unfortunately belies its actual brilliance. Still, ...
... However, astute Gainesville area residents can easily spot this bright star low over the southern winter horizon with careful planning. See Figure 1. Note: Atmospheric extinction may dim Canopus (mag. -0.62) by one or two magnitudes, which therefore unfortunately belies its actual brilliance. Still, ...
neutron star - The University of Chicago
... ➢ Core-collapse supernovae result from the iron core collapse of massive stars. ➢ The process of iron-core collapse is one of the most complicated problems in modern astrophysics and involves virtually all fields of modern physics. ➢ Multi-dimensional supercomputer simulations key to understanding c ...
... ➢ Core-collapse supernovae result from the iron core collapse of massive stars. ➢ The process of iron-core collapse is one of the most complicated problems in modern astrophysics and involves virtually all fields of modern physics. ➢ Multi-dimensional supercomputer simulations key to understanding c ...
What tool do astronomers use to understand the evolution of stars?
... t B M B L A 1 300 300 60 Sun's lifetime ~ 10 billion years = 1010 yr = 10 Gyr. Lifetime of 5 solar mass star is 1010 yr/60 ~ 1010/102 yr = 108 yr = 102106 yr = 100 million yr = 100 Myr This is the age of the star cluster. ...
... t B M B L A 1 300 300 60 Sun's lifetime ~ 10 billion years = 1010 yr = 10 Gyr. Lifetime of 5 solar mass star is 1010 yr/60 ~ 1010/102 yr = 108 yr = 102106 yr = 100 million yr = 100 Myr This is the age of the star cluster. ...
Precession of Earth
... wobbling around the precessional axis; 1/2° one way or the other; period of 18 years; due to the Moon; slightly effects seasons. ...
... wobbling around the precessional axis; 1/2° one way or the other; period of 18 years; due to the Moon; slightly effects seasons. ...
guide to orion 3-d flythrough
... The central area of the nebula is called the Trapezium cluster. It is dominated by four young, massive stars in a kite-like arrangement. The brightest of these stars, which has a luminosity 100,000 times that of the Sun, provides the energy that creates the nebula as we see it. It produces a flood o ...
... The central area of the nebula is called the Trapezium cluster. It is dominated by four young, massive stars in a kite-like arrangement. The brightest of these stars, which has a luminosity 100,000 times that of the Sun, provides the energy that creates the nebula as we see it. It produces a flood o ...
Document
... Orion. The nebula is located just to the south of the star Alnitak, which is farthest east on Orion's Belt, and is part of the much larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. ...
... Orion. The nebula is located just to the south of the star Alnitak, which is farthest east on Orion's Belt, and is part of the much larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. ...
ppt - Serbian Virtual Observatory - astronomical observatory belgrade
... For all eleven double stars there exist measurements (sufficient number) on the basis of which one can obtain the apparent orbit. Nevertheless, we prefer a combined approach using both apparent orbits and estimation. The first step in the estimation is in fact testing the hypothesis that both stars ...
... For all eleven double stars there exist measurements (sufficient number) on the basis of which one can obtain the apparent orbit. Nevertheless, we prefer a combined approach using both apparent orbits and estimation. The first step in the estimation is in fact testing the hypothesis that both stars ...
PHYS 390 Lecture 3
... If one can determine the luminosity of a star WITHOUT knowing d, then a measurement of the flux F on Earth can be inverted to find d. That is: (i) extract L from some observable characteristic of the star (ii) measure F on Earth (iii) use F = L / 4πd2 to solve for d. The problem with this approach i ...
... If one can determine the luminosity of a star WITHOUT knowing d, then a measurement of the flux F on Earth can be inverted to find d. That is: (i) extract L from some observable characteristic of the star (ii) measure F on Earth (iii) use F = L / 4πd2 to solve for d. The problem with this approach i ...
Ch 19 Directed Reading
... 17. A huge explosion in which a large star dies is called a _____________________________. 18. A star made up of neutrons is called a _____________________________. 19. A spinning neutron star that emits pulses of energy is called a _____________________________. 20. An object so massive and dense t ...
... 17. A huge explosion in which a large star dies is called a _____________________________. 18. A star made up of neutrons is called a _____________________________. 19. A spinning neutron star that emits pulses of energy is called a _____________________________. 20. An object so massive and dense t ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... “smeared out.” Giant stars, which have relatively low atmospheric pressures, are characterized by narrow spectral lines. ...
... “smeared out.” Giant stars, which have relatively low atmospheric pressures, are characterized by narrow spectral lines. ...
Name: Period : _____ Bulldog Review #9 1. The Milky Wa
... 17. In which stage is our sun currently found? A. Stage 1 B. Stage 2 C. Stage 3 D. Stage 4 18. Which unit of measurement do astronomers use when measuring the distance between two stars found in the Milky Way? A. meter B. light-year C. kilometer D. astronomical unit 19. ______________ is a force tha ...
... 17. In which stage is our sun currently found? A. Stage 1 B. Stage 2 C. Stage 3 D. Stage 4 18. Which unit of measurement do astronomers use when measuring the distance between two stars found in the Milky Way? A. meter B. light-year C. kilometer D. astronomical unit 19. ______________ is a force tha ...
Astronomy 103 – Midterm 2 – October 29, 2014
... 24. Once the luminosity of a star is known, what has to be measured in order to find the star’s radius? a) parallax angle to find distance b) color to find distance c) color to find surface temperature d) parallax angle to find surface temperature ...
... 24. Once the luminosity of a star is known, what has to be measured in order to find the star’s radius? a) parallax angle to find distance b) color to find distance c) color to find surface temperature d) parallax angle to find surface temperature ...
Physical Science Lecture Notes
... a. Core – Fusion takes place here, reaches temps of 15,000,000 degrees Centigrade. Most of the mass of the sun is found here. b. Radiation Zone – energy transferred from core out of the interior of the sun, reaches temperatures of 100,000 degrees Centigrade c. Convection Zone – Convection Currents b ...
... a. Core – Fusion takes place here, reaches temps of 15,000,000 degrees Centigrade. Most of the mass of the sun is found here. b. Radiation Zone – energy transferred from core out of the interior of the sun, reaches temperatures of 100,000 degrees Centigrade c. Convection Zone – Convection Currents b ...
Star Spectra - Renton School District
... “smeared out.” Giant stars, which have relatively low atmospheric pressures, are characterized by narrow spectral lines. ...
... “smeared out.” Giant stars, which have relatively low atmospheric pressures, are characterized by narrow spectral lines. ...
Chapter 10 Hertzsprung-Russel Diagrams and Distance to Stars
... began to look at stars that were found in clusters. In general, it’s safe to assume that all the stars in a cluster, except for a few random anomalies, are at roughly the same distance away. Even if this distance is unknown, scientists realized that it was still possible to directly compare the rela ...
... began to look at stars that were found in clusters. In general, it’s safe to assume that all the stars in a cluster, except for a few random anomalies, are at roughly the same distance away. Even if this distance is unknown, scientists realized that it was still possible to directly compare the rela ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... • Under collapse, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
... • Under collapse, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.