NIE10x301Sponsor Thank You (Page 1)
... star formation and is also called a starburst galaxy. It’s also sometimes called The Cigar Galaxy because it’s seen almost edge-on. They’re both about 12 million ly away, and easily glimpsed together in 10x50 binoculars. M51 lies under the end of the “handle” of the Big Dipper. To find it, imagine a ...
... star formation and is also called a starburst galaxy. It’s also sometimes called The Cigar Galaxy because it’s seen almost edge-on. They’re both about 12 million ly away, and easily glimpsed together in 10x50 binoculars. M51 lies under the end of the “handle” of the Big Dipper. To find it, imagine a ...
Slide 1
... Stellar spectra are much more informative than the blackbody curves. There are seven general categories of stellar spectra, corresponding to different ...
... Stellar spectra are much more informative than the blackbody curves. There are seven general categories of stellar spectra, corresponding to different ...
Introduction to the HR Diagram
... carbon. Most of these stars go through a Mira variable instability strip with a periodic light curve of ~80 - 1000 days. Stars that have evolved to the giant branch are commonly referred to as red giants. Eventually these red giants will shrug off a planetary nebula and leave a white dwarf core remn ...
... carbon. Most of these stars go through a Mira variable instability strip with a periodic light curve of ~80 - 1000 days. Stars that have evolved to the giant branch are commonly referred to as red giants. Eventually these red giants will shrug off a planetary nebula and leave a white dwarf core remn ...
Powerpoint - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... One important aspect of this project was creating a way to visualize the results of these simulations. Below are color contour plots of temperature, material density, speed, and a representation of the magnetic field, all of which are data that are included in the output files of the simulations. In ...
... One important aspect of this project was creating a way to visualize the results of these simulations. Below are color contour plots of temperature, material density, speed, and a representation of the magnetic field, all of which are data that are included in the output files of the simulations. In ...
Astronomy 114 Problem Set # 7 Due: 30 Apr 2007 SOLUTIONS 1
... Note that Hubble law is a function of distance, so the farther we observe, the better accuracy we can gain in the Hubble law. 7 Freedman & Kaufmann Chap. 26, Problem 29, pg. 605 The image shows very evident bright regions that may be sites of OB associations and HII regions (note the Hydrogen α colo ...
... Note that Hubble law is a function of distance, so the farther we observe, the better accuracy we can gain in the Hubble law. 7 Freedman & Kaufmann Chap. 26, Problem 29, pg. 605 The image shows very evident bright regions that may be sites of OB associations and HII regions (note the Hydrogen α colo ...
Lecture 5: Stars
... We only know the absolute luminosity if we know the distance, but we only know the parallax distances out to about 100 pc (further to some bright stars). The problem is that if we see a star with a surface temperature of 3000K – is it a nearby red dwarf, or a distant red giant? Without more informat ...
... We only know the absolute luminosity if we know the distance, but we only know the parallax distances out to about 100 pc (further to some bright stars). The problem is that if we see a star with a surface temperature of 3000K – is it a nearby red dwarf, or a distant red giant? Without more informat ...
Document
... - Estimated 1M years old - Most stars clouded from view by dust - Only 4-5 stars visible with small scope ...
... - Estimated 1M years old - Most stars clouded from view by dust - Only 4-5 stars visible with small scope ...
Document
... Neutrons (and protons) are made of quarks. Gravity could crush neutrons into free quarks. Called strange matter (a type of quark). Astronomers think they may have seen a quark star. ...
... Neutrons (and protons) are made of quarks. Gravity could crush neutrons into free quarks. Called strange matter (a type of quark). Astronomers think they may have seen a quark star. ...
star - TeacherWeb
... Light from stars that are moving toward the Earth is shifted slightly toward the blue end of the spectrum. When a source of light (like a star) is stationary, the wavelengths of light remain the same distance apart. When a source of light is moving toward you, the wavelengths of light get closer tog ...
... Light from stars that are moving toward the Earth is shifted slightly toward the blue end of the spectrum. When a source of light (like a star) is stationary, the wavelengths of light remain the same distance apart. When a source of light is moving toward you, the wavelengths of light get closer tog ...
Early Spring Observing – Millstone News Night Sky
... Color in Stars The Beehive contains a larger star population than most other nearby clusters. Under dark skies the Beehive Cluster looks like a nebulous object to the naked eye; thus it has been known since ancient times. We often find it, rather than the constellation it is found in (Cancer). From ...
... Color in Stars The Beehive contains a larger star population than most other nearby clusters. Under dark skies the Beehive Cluster looks like a nebulous object to the naked eye; thus it has been known since ancient times. We often find it, rather than the constellation it is found in (Cancer). From ...
Sirius Star1 - Emmi
... seen from Earth other than the sun. Brightness is different than luminosity. ...
... seen from Earth other than the sun. Brightness is different than luminosity. ...
Classification_of_Stars_By_Luminosity
... The systemisation of apparent magnitude In the nineteenth century systems were developed for measuring exactly how much light was arriving from a star. The intensity of the light (the energy arriving every second per metre 2 at Earth) was calculated. This is sometimes referred to as the apparent br ...
... The systemisation of apparent magnitude In the nineteenth century systems were developed for measuring exactly how much light was arriving from a star. The intensity of the light (the energy arriving every second per metre 2 at Earth) was calculated. This is sometimes referred to as the apparent br ...
Stages 12 to 14
... Stage 13 – White Dwarf Stage Isolated white dwarfs are hard to observe, and most are still in the planetary nebula phase. However, if they are part of a binary system, the expanding shells can be sucked into the companion star, leaving an isolate white dwarf in orbit around the companion star. If t ...
... Stage 13 – White Dwarf Stage Isolated white dwarfs are hard to observe, and most are still in the planetary nebula phase. However, if they are part of a binary system, the expanding shells can be sucked into the companion star, leaving an isolate white dwarf in orbit around the companion star. If t ...
Life cycle of low mass stars
... more massive. Created by the massive collapse of a red supergiant. Earth would be the size of a football field and weigh 100 million tons High temperature but not very bright. Gravity > internal pressure Option 2: 6b. Black hole Black hole = objects smaller and more dense than Neutron stars. Created ...
... more massive. Created by the massive collapse of a red supergiant. Earth would be the size of a football field and weigh 100 million tons High temperature but not very bright. Gravity > internal pressure Option 2: 6b. Black hole Black hole = objects smaller and more dense than Neutron stars. Created ...
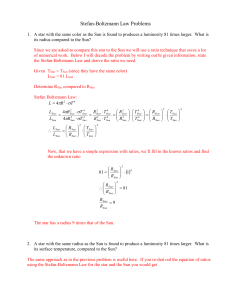
Stefan-Boltzmann Law Problems
... 1. A star with the same color as the Sun is found to produces a luminosity 81 times larger. What is its radius compared to the Sun? Since we are asked to compare this star to the Sun we will use a ratio technique that saves a lot of numerical work. Below I will decode the problem by writing out ht g ...
... 1. A star with the same color as the Sun is found to produces a luminosity 81 times larger. What is its radius compared to the Sun? Since we are asked to compare this star to the Sun we will use a ratio technique that saves a lot of numerical work. Below I will decode the problem by writing out ht g ...
Asymptotic Giant Branch
... The solid and dashed lines are from theoretical models calculated for a 1.5 solar mass star with varying mass of the 13C pocket. The solid line corresponds to ⅔ of the standard mass (which is 4×10−6 solar masses). The upper and lower dashed curve represent the envelope of a set of calculations where ...
... The solid and dashed lines are from theoretical models calculated for a 1.5 solar mass star with varying mass of the 13C pocket. The solid line corresponds to ⅔ of the standard mass (which is 4×10−6 solar masses). The upper and lower dashed curve represent the envelope of a set of calculations where ...
Our Universe
... • In Nuclear fusion, hydrogen atoms are converted into helium, releasing the ENORMOUS amount of energy that causes stars to become very hot! • The amount of energy released per gram of mass is equal to the amount of energy released by 22,000 tons of TNT. (The nuclear explosion at Hiroshima only rele ...
... • In Nuclear fusion, hydrogen atoms are converted into helium, releasing the ENORMOUS amount of energy that causes stars to become very hot! • The amount of energy released per gram of mass is equal to the amount of energy released by 22,000 tons of TNT. (The nuclear explosion at Hiroshima only rele ...
Star Basics
... The spectra of O-Type stars shows the presence of hydrogen and helium. At these temperatures most of the hydrogen is ionized, so the hydrogen lines are weak. Both HeI and HeII (singly ionized helium) are seen in the higher temperature examples. The radiation from O5 stars is so intense that it can i ...
... The spectra of O-Type stars shows the presence of hydrogen and helium. At these temperatures most of the hydrogen is ionized, so the hydrogen lines are weak. Both HeI and HeII (singly ionized helium) are seen in the higher temperature examples. The radiation from O5 stars is so intense that it can i ...
PSC100 Transparant Replacement for Chapter 8 Measurement of
... * Measure time for reflected signal to return to Earth. * Calculate distance as speed of light x time of travel. Stellar Parallax * Measure angle to star at two different times. * Use largest base line possible, the diameter of Earth’s orbit around the Sun * This means data readings must be taken 6 ...
... * Measure time for reflected signal to return to Earth. * Calculate distance as speed of light x time of travel. Stellar Parallax * Measure angle to star at two different times. * Use largest base line possible, the diameter of Earth’s orbit around the Sun * This means data readings must be taken 6 ...
Stars
... ______ 8. The colors that appear when a chemical element emits light are called a. continuous lines. b. absorption lines. c. color lines. d. emission lines. ______ 9. Each element in a hot gas can be identified by a. a unique set of bright emission lines. b. a unique set of bright absorption lines. ...
... ______ 8. The colors that appear when a chemical element emits light are called a. continuous lines. b. absorption lines. c. color lines. d. emission lines. ______ 9. Each element in a hot gas can be identified by a. a unique set of bright emission lines. b. a unique set of bright absorption lines. ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.