STAR FORMATION (Ch. 19)
... slight dependence on other things, like its total metal abundance). Note: the “main sequence” is the location in the H-R diagram of all stars of different ...
... slight dependence on other things, like its total metal abundance). Note: the “main sequence” is the location in the H-R diagram of all stars of different ...
29_worlds_unnumbered..
... – It burns its fuel quickly and will only last millions instead of billions of years. – There may not be enough time for complex life to evolve. ...
... – It burns its fuel quickly and will only last millions instead of billions of years. – There may not be enough time for complex life to evolve. ...
- Amazing Space, STScI
... stars. There are two groups of stars in this picture. This first group of stars is called the Trumpler 16 star cluster. Continued … ...
... stars. There are two groups of stars in this picture. This first group of stars is called the Trumpler 16 star cluster. Continued … ...
Dec 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... well liked for its blue & gold colors. Ptolemaeus magnitude +11. The second closest star visible to Alphonsus the naked eye is Sirius at 8.6 ly followed by Epsilon Moon (e) Eridani at 10.5 ly and Procyon at 11.4 ly. There Tycho Starting from New Moon, the Moon cycles through are several stars closer ...
... well liked for its blue & gold colors. Ptolemaeus magnitude +11. The second closest star visible to Alphonsus the naked eye is Sirius at 8.6 ly followed by Epsilon Moon (e) Eridani at 10.5 ly and Procyon at 11.4 ly. There Tycho Starting from New Moon, the Moon cycles through are several stars closer ...
Lecture 17 Review
... The question is, what if the mass is greater than about 50 solar masses? If the forming star is too large, the gas cloud condenses quite fast, is unstable, gets very hot, and either explodes or fragments into smaller clouds which form individual stars. A second question is, can the mass of the gas ...
... The question is, what if the mass is greater than about 50 solar masses? If the forming star is too large, the gas cloud condenses quite fast, is unstable, gets very hot, and either explodes or fragments into smaller clouds which form individual stars. A second question is, can the mass of the gas ...
EF Eri: Its White Dwarf Primary and L Dwarf Secondary
... The Optical Spectrum during the LOW STATE: H emission faded quickly after 1997. Five years into the low state, EF Eri’s optical spectrum shows Zeeman split Balmer absorption lines caused by the WD B field and NO emission lines. No secondary star features are detected. Note non-BB WD shape. ...
... The Optical Spectrum during the LOW STATE: H emission faded quickly after 1997. Five years into the low state, EF Eri’s optical spectrum shows Zeeman split Balmer absorption lines caused by the WD B field and NO emission lines. No secondary star features are detected. Note non-BB WD shape. ...
After Dark M S
... both are supernovas, the natures of these two exploding stars are very different. The supernova in M51 may mark the death of a massive star. The supernova in M101 may mark the death of a white dwarf star in a binary star system. The discovery and origins of these two exploding stars, more than 20 mi ...
... both are supernovas, the natures of these two exploding stars are very different. The supernova in M51 may mark the death of a massive star. The supernova in M101 may mark the death of a white dwarf star in a binary star system. The discovery and origins of these two exploding stars, more than 20 mi ...
March 2010 - Pomona Valley Amateur Astronomers
... Our main speaker for the evening was Bob Branch. Long term Club members recalled Bob’s years with our Club and were glad to see him again and of course to learn more about his topic – E.E (Edward Emerson) Barnard. My own knowledge of this man was rudimentary and I was only familiar with an object ca ...
... Our main speaker for the evening was Bob Branch. Long term Club members recalled Bob’s years with our Club and were glad to see him again and of course to learn more about his topic – E.E (Edward Emerson) Barnard. My own knowledge of this man was rudimentary and I was only familiar with an object ca ...
OVERVIEW: Stars and space
... and (b) heavier elements were formed. Copy and answer questions (a) and (b) on pages 270 and 271. Outline the ways of trying to discover the presence of extra-terrestial life. Copy and answer question (c) on page 271. Copy the ‘Key points’ table on page 271. Answer the summary questions on page 271. ...
... and (b) heavier elements were formed. Copy and answer questions (a) and (b) on pages 270 and 271. Outline the ways of trying to discover the presence of extra-terrestial life. Copy and answer question (c) on page 271. Copy the ‘Key points’ table on page 271. Answer the summary questions on page 271. ...
The Reflector - Peterborough Astronomical Association
... But these discoveries were made by inferred evidence. One such method is to measure the orbit of the star to detect any wobble that may be caused by the gravitational tug of a nearby planet. Another technique measures the magnitude of the star searching for small repeated dips in its brightness that ...
... But these discoveries were made by inferred evidence. One such method is to measure the orbit of the star to detect any wobble that may be caused by the gravitational tug of a nearby planet. Another technique measures the magnitude of the star searching for small repeated dips in its brightness that ...
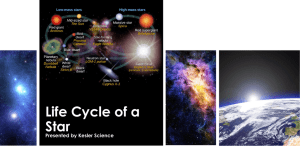
Life Cycle of a Star Vocabulary
... • The core collapses and results in a giant explosion. © KeslerScience.com ...
... • The core collapses and results in a giant explosion. © KeslerScience.com ...
Summer - Dark Sky Discovery
... This star is Polaris. If you are looking at this star, you are facing north. On the other side of Polaris is a W of stars (or an M depending on which way up it happens to be; the stars appear to rotate anti-clockwise round Polaris once every 24 hours). This is the constellation of Cassiopeia. These ...
... This star is Polaris. If you are looking at this star, you are facing north. On the other side of Polaris is a W of stars (or an M depending on which way up it happens to be; the stars appear to rotate anti-clockwise round Polaris once every 24 hours). This is the constellation of Cassiopeia. These ...
Types of Planets and Stars
... Main Sequence Stars -- make up the majority of stars in the universe. Earth’s sun is a main sequence star. These stars vary in size, mass, and brightness, but they all convert hydrogen into helium, also known as nuclear fusion. While our sun will spend 10 billion on its main sequence, a star ten t ...
... Main Sequence Stars -- make up the majority of stars in the universe. Earth’s sun is a main sequence star. These stars vary in size, mass, and brightness, but they all convert hydrogen into helium, also known as nuclear fusion. While our sun will spend 10 billion on its main sequence, a star ten t ...
Trainer`s Notes
... The planets in our solar system, starting from the Sun, are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Pluto was also considered a planet from 1930 until 2006 when the International Astronomer's Union (IAU) was prompted by the discovery Eris, a body larger than Pluto, to come ...
... The planets in our solar system, starting from the Sun, are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Pluto was also considered a planet from 1930 until 2006 when the International Astronomer's Union (IAU) was prompted by the discovery Eris, a body larger than Pluto, to come ...
Stars - Academic Computer Center
... • Binary stars provide a means of determining the masses of stars. • Other properties can also sometimes be determined from binary stars. ...
... • Binary stars provide a means of determining the masses of stars. • Other properties can also sometimes be determined from binary stars. ...
Stars and Constellations Power Point
... •A black hole is a region of spacetime from which nothing, not even light, can escape. •Black holes of stellar mass are expected to form when very massive stars collapse at the end of their life cycle. •After a black hole has formed it can continue to grow by absorbing mass from its surroundings. •T ...
... •A black hole is a region of spacetime from which nothing, not even light, can escape. •Black holes of stellar mass are expected to form when very massive stars collapse at the end of their life cycle. •After a black hole has formed it can continue to grow by absorbing mass from its surroundings. •T ...
Polaris
... satellite. Concerning the detailed physics, α UMi A is an F7 bright giant (II) or supergiant (Ib). The two smaller companions are: α UMi B an F3V main sequence star, orbiting in 2400 AU distance, and C a very close dwarf on a 18.5 AU orbit. Recent observations show that Polaris may be part of a loos ...
... satellite. Concerning the detailed physics, α UMi A is an F7 bright giant (II) or supergiant (Ib). The two smaller companions are: α UMi B an F3V main sequence star, orbiting in 2400 AU distance, and C a very close dwarf on a 18.5 AU orbit. Recent observations show that Polaris may be part of a loos ...
Transits
... • Our first spectrum of a habitable world may come from a planet orbiting an M star! ...
... • Our first spectrum of a habitable world may come from a planet orbiting an M star! ...
The Death of High Mass Stars
... searchlight is like a lighthouse, which we see as a pulsar if we happen to lie in the searchlight beam. ...
... searchlight is like a lighthouse, which we see as a pulsar if we happen to lie in the searchlight beam. ...
Photometry
... The number of photons observed can be converted into an apparent magnitude (m), which is simply a measure of how bright the stars look from Earth. The smaller the number, the brighter the star. Each color has a different apparent magnitude. (This simply means that some stars appear brighter in, say, ...
... The number of photons observed can be converted into an apparent magnitude (m), which is simply a measure of how bright the stars look from Earth. The smaller the number, the brighter the star. Each color has a different apparent magnitude. (This simply means that some stars appear brighter in, say, ...
Stellar Spectral Classes
... For which two spectral classes are these lines the prominent feature? ...
... For which two spectral classes are these lines the prominent feature? ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.